Module fusus.clean
Wipe marks from images.
Cleaning marks from images is based on OpenCV's template matching
This is fuzzy matching, so we have to employ considerable sophistication to get the true results and to discard the fake results.
One particular way to discard fake results is to mind the connectedness of the ink of a candidate mark with the surrounding ink. If there is such a connection, it is a strong indication that the candidate is not a mark to be removed, but part of a glyph.
See 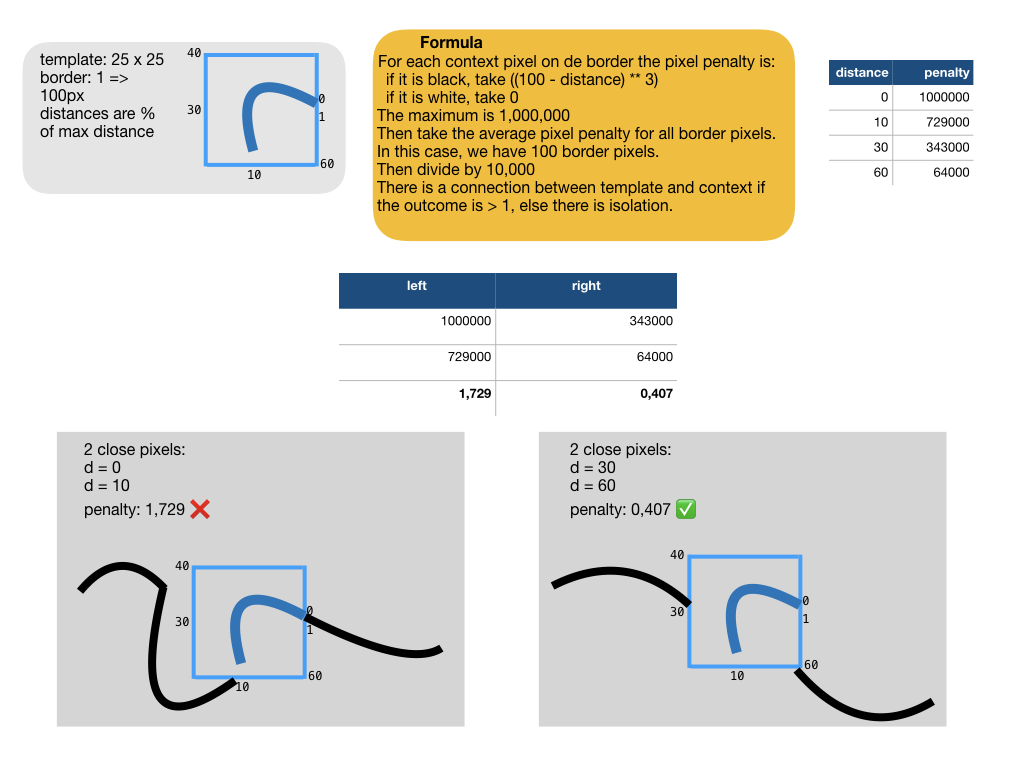
Expand source code Browse git
"""Wipe marks from images.
Cleaning marks from images is based on
[OpenCV's template matching](https://opencv-python-tutroals.readthedocs.io/en/latest/py_tutorials/py_imgproc/py_template_matching/py_template_matching.html#template-matching)
This is fuzzy matching, so we have to employ considerable sophistication to
get the true results and to discard the fake results.
One particular way to discard fake results is to mind the connectedness of the ink
of a candidate mark with the surrounding ink.
If there is such a connection, it is a strong indication that the candidate is not
a mark to be removed, but part of a glyph.
See 
"""
import numpy as np
import cv2
from .lib import FONT
def cluster(points, match):
"""Cluster points that are in a source.
When searching images for image templates,
we get a match image: for each point in the image a measure of how good the
match is at that point.
Typically, if a point has a high match value, surrounding points also have good
match values. We want to cluster such points, so that we can identify a match
with exactly one cluster.
Parameters
----------
points: iterable
Points where the image template matches the source image good enough
match: image as np array
The match image
Returns
-------
list
The list of clusters, where each cluster is represented as a pair of
point and the strength of the match in that point.
This point is the point in the cluster with the highest match value.
"""
def d(p1, p2):
if p1 == p2:
return 0
(x1, y1) = p1
(x2, y2) = p2
return abs(x1 - x2) + abs(y1 - y2)
clusters = []
for (i, p) in enumerate(points):
stored = False
rp = match[p]
for c in clusters:
(q, rq) = c
if d(p, q) <= 8:
if rp > rq:
c[0] = p
c[1] = rp
stored = True
break
if not stored:
clusters.append([p, rp])
return clusters
def measure(borderInside, borderOutside, threshold):
"""Measure the amount of ink that crosses the border of a certain region.
It is used to reject certain matches of image templates, where templates
contain strokes of ink. If a match is such that the stroke of ink connects
with the ink in the environment, the match is not a true example of the stroke
and will be rejected.
!!! note "Where to look for ink"
We look for ink in the image itself,
the ink in the search template is not relevant.
Parameters
----------
borderInside: image as np array
The part of the image bordering inside an area where the search template matches
borderOutside: image as np array
The part of the image bordering outside an area where the search template matches
Returns
-------
float
The ratio between the size of the ink connections across the border and the
total size of the border.
"""
connections = borderInside * borderOutside
return np.where(connections > threshold)[0].size / borderOutside.size
def connected(markH, markW, bw, threshold, img, hitPoint, sides=None):
"""Determine how much ink borders on a given rectangle.
Parameters
----------
markH: integer
height of the rectangle
markW: integer
width of the rectangle
bw: integer
width of the border around the rectangle that will be used to detect connections
threshold:
the value above which a connection is detected
img: np array
the source image
hitPoint: (int, int)
Y and X coordinate of top left corner of the rectangle in the image
sides: string, optional `None`
If `None`, computes connections on all sides.
Otherwise it should be a string consisting of at most these characters:
`l` (left), `r` (right), `t` (top), `b` (bottom).
Only these sides will be computed.
"""
(textH, textW) = img.shape
(hitY, hitX) = hitPoint
connDegree = 0
nparts = 0
realBw = min((bw, markW, markH))
# left boundary
fo = max((0, hitX - realBw)) if hitX > 0 else None
if fo is not None and (sides is None or "l" in sides):
to = hitX
texto = np.array(
(255 - img[hitY : hitY + markH, fo:to]).max(axis=1), dtype=np.uint16
)
fi = hitX
ti = hitX + realBw
texti = np.array(
(255 - img[hitY : hitY + markH, fi:ti]).max(axis=1), dtype=np.uint16
)
val = measure(texto, texti, threshold)
connDegree += val
nparts += 1
# right boundary
to = (
min((textW, hitX + markW + realBw + 1))
if hitX + markW + realBw < textW
else None
)
if to is not None and (sides is None or "r" in sides):
fo = hitX + markW
texto = np.array(
(255 - img[hitY : hitY + markH, fo:to]).max(axis=1), dtype=np.uint16
)
fi = hitX + markW - realBw
ti = hitX + markW
texti = np.array(
(255 - img[hitY : hitY + markH, fi:ti]).max(axis=1), dtype=np.uint16
)
val = measure(texto, texti, threshold)
connDegree += val
nparts += 1
# top boundary
f = max((0, hitY - realBw)) if hitY > 0 else None
if f is not None and (sides is None or "t" in sides):
t = hitY
texto = np.array(
(255 - img[f:t, hitX : hitX + markW]).max(axis=0), dtype=np.uint16
)
fi = hitY
ti = hitY + realBw + 1
texti = np.array(
(255 - img[fi:ti, hitX : hitX + markW]).max(axis=0), dtype=np.uint16
)
val = measure(texto, texti, threshold)
connDegree += val
nparts += 1
# bottom boundary
t = (
min((textH - 1, hitY + markH + realBw + 1))
if hitY + markH + realBw < textH
else None
)
if t is not None and (sides is None or "b" in sides):
f = hitY + markH
texto = np.array(
(255 - img[f:t, hitX : hitX + markW]).max(axis=0), dtype=np.uint16
)
ti = hitY + markH
fi = hitY + markH - realBw
texti = np.array(
(255 - img[fi:ti, hitX : hitX + markW]).max(axis=0), dtype=np.uint16
)
val = measure(texto, texti, threshold)
connDegree += val
nparts += 1
return connDegree
def reborder(gray, bw, color, crop=False):
"""Add a border around a grayscale image, optionally remove white margins first.
The border will add to the size of the image.
Parameters
----------
gray: np array
A grayscale image.
bw: int
Width of the new border.
color: int
Color of the new border (grayscale).
crop: boolean, optional `False`
If `True`, the image will be cropped first such as to remove all surrounding
white margins.
"""
if crop:
inv = 255 * (gray < 128).astype(np.uint8)
coords = cv2.findNonZero(inv)
x, y, w, h = cv2.boundingRect(coords)
cropped = gray[y : y + h, x : x + w]
else:
cropped = gray
bordered = cv2.copyMakeBorder(
cropped, bw, bw, bw, bw, cv2.BORDER_CONSTANT, value=color
)
return bordered
def addBox(C, img, left, top, right, bottom, kept, band, seq, connDegree):
"""Add a box around a mark that is to be cleaned.
When we display the marks that will be wiped from the image, we do so by
putting colored boxes around them.
This function adds one such box.
Parameters
C: object
The configuration object of the book engine.
img: image as np array
the image to operate on
left, top, right, bottom: int
specification of the rectangle of the box
kept: boolean
Whether the mark is to be kept. Kept marks and wiped marks will get
different colors.
band: string
The name of the band in which the mark is searched for. It will be displayed
near the box.
seq: integer
The number of the mark.
connDegree: integer
The degree of ink connection for this mark occurrence. It will be displayed
near the box.
Returns
-------
None
The source image receives a modification.
"""
fill = C.boxRemainRGB if kept else C.boxDeleteRGB
fillN = C.boxRemainNRGB if kept else C.boxDeleteNRGB
border = C.boxBorder
size = 0.5
weight = 1
colorDeg = (100, 100, 255)
ptSeq = (left, top - border - 2)
ptDeg = (left, bottom + border + 8)
cv2.rectangle(img, (left, top), (right, bottom), fill, border)
cv2.putText(
img,
f"{'' if band == 'main' else band[0]}{seq}",
ptSeq,
FONT,
size,
fillN,
weight,
cv2.LINE_AA,
)
connectionDegree = int(round(connDegree * 100))
if connectionDegree:
cv2.putText(
img,
str(connectionDegree),
ptDeg,
FONT,
size,
colorDeg,
weight,
cv2.LINE_AA,
)Functions
def addBox(C, img, left, top, right, bottom, kept, band, seq, connDegree)-
Add a box around a mark that is to be cleaned.
When we display the marks that will be wiped from the image, we do so by putting colored boxes around them. This function adds one such box.
Parameters
C: object The configuration object of the book engine. img: image as np array the image to operate on left, top, right, bottom: int specification of the rectangle of the box kept: boolean Whether the mark is to be kept. Kept marks and wiped marks will get different colors. band: string The name of the band in which the mark is searched for. It will be displayed near the box. seq: integer The number of the mark. connDegree: integer The degree of ink connection for this mark occurrence. It will be displayed near the box.
Returns
None- The source image receives a modification.
Expand source code Browse git
def addBox(C, img, left, top, right, bottom, kept, band, seq, connDegree): """Add a box around a mark that is to be cleaned. When we display the marks that will be wiped from the image, we do so by putting colored boxes around them. This function adds one such box. Parameters C: object The configuration object of the book engine. img: image as np array the image to operate on left, top, right, bottom: int specification of the rectangle of the box kept: boolean Whether the mark is to be kept. Kept marks and wiped marks will get different colors. band: string The name of the band in which the mark is searched for. It will be displayed near the box. seq: integer The number of the mark. connDegree: integer The degree of ink connection for this mark occurrence. It will be displayed near the box. Returns ------- None The source image receives a modification. """ fill = C.boxRemainRGB if kept else C.boxDeleteRGB fillN = C.boxRemainNRGB if kept else C.boxDeleteNRGB border = C.boxBorder size = 0.5 weight = 1 colorDeg = (100, 100, 255) ptSeq = (left, top - border - 2) ptDeg = (left, bottom + border + 8) cv2.rectangle(img, (left, top), (right, bottom), fill, border) cv2.putText( img, f"{'' if band == 'main' else band[0]}{seq}", ptSeq, FONT, size, fillN, weight, cv2.LINE_AA, ) connectionDegree = int(round(connDegree * 100)) if connectionDegree: cv2.putText( img, str(connectionDegree), ptDeg, FONT, size, colorDeg, weight, cv2.LINE_AA, ) def cluster(points, match)-
Cluster points that are in a source.
When searching images for image templates, we get a match image: for each point in the image a measure of how good the match is at that point.
Typically, if a point has a high match value, surrounding points also have good match values. We want to cluster such points, so that we can identify a match with exactly one cluster.
Parameters
points:iterable- Points where the image template matches the source image good enough
match:image as np array- The match image
Returns
list- The list of clusters, where each cluster is represented as a pair of point and the strength of the match in that point. This point is the point in the cluster with the highest match value.
Expand source code Browse git
def cluster(points, match): """Cluster points that are in a source. When searching images for image templates, we get a match image: for each point in the image a measure of how good the match is at that point. Typically, if a point has a high match value, surrounding points also have good match values. We want to cluster such points, so that we can identify a match with exactly one cluster. Parameters ---------- points: iterable Points where the image template matches the source image good enough match: image as np array The match image Returns ------- list The list of clusters, where each cluster is represented as a pair of point and the strength of the match in that point. This point is the point in the cluster with the highest match value. """ def d(p1, p2): if p1 == p2: return 0 (x1, y1) = p1 (x2, y2) = p2 return abs(x1 - x2) + abs(y1 - y2) clusters = [] for (i, p) in enumerate(points): stored = False rp = match[p] for c in clusters: (q, rq) = c if d(p, q) <= 8: if rp > rq: c[0] = p c[1] = rp stored = True break if not stored: clusters.append([p, rp]) return clusters def connected(markH, markW, bw, threshold, img, hitPoint, sides=None)-
Determine how much ink borders on a given rectangle.
Parameters
markH:integer- height of the rectangle
markW:integer- width of the rectangle
bw:integer- width of the border around the rectangle that will be used to detect connections
- threshold:
- the value above which a connection is detected
img:np array- the source image
hitPoint:(int, int)- Y and X coordinate of top left corner of the rectangle in the image
sides:string, optionalNone- If
None, computes connections on all sides. Otherwise it should be a string consisting of at most these characters:l(left),r(right),t(top),b(bottom). Only these sides will be computed.
Expand source code Browse git
def connected(markH, markW, bw, threshold, img, hitPoint, sides=None): """Determine how much ink borders on a given rectangle. Parameters ---------- markH: integer height of the rectangle markW: integer width of the rectangle bw: integer width of the border around the rectangle that will be used to detect connections threshold: the value above which a connection is detected img: np array the source image hitPoint: (int, int) Y and X coordinate of top left corner of the rectangle in the image sides: string, optional `None` If `None`, computes connections on all sides. Otherwise it should be a string consisting of at most these characters: `l` (left), `r` (right), `t` (top), `b` (bottom). Only these sides will be computed. """ (textH, textW) = img.shape (hitY, hitX) = hitPoint connDegree = 0 nparts = 0 realBw = min((bw, markW, markH)) # left boundary fo = max((0, hitX - realBw)) if hitX > 0 else None if fo is not None and (sides is None or "l" in sides): to = hitX texto = np.array( (255 - img[hitY : hitY + markH, fo:to]).max(axis=1), dtype=np.uint16 ) fi = hitX ti = hitX + realBw texti = np.array( (255 - img[hitY : hitY + markH, fi:ti]).max(axis=1), dtype=np.uint16 ) val = measure(texto, texti, threshold) connDegree += val nparts += 1 # right boundary to = ( min((textW, hitX + markW + realBw + 1)) if hitX + markW + realBw < textW else None ) if to is not None and (sides is None or "r" in sides): fo = hitX + markW texto = np.array( (255 - img[hitY : hitY + markH, fo:to]).max(axis=1), dtype=np.uint16 ) fi = hitX + markW - realBw ti = hitX + markW texti = np.array( (255 - img[hitY : hitY + markH, fi:ti]).max(axis=1), dtype=np.uint16 ) val = measure(texto, texti, threshold) connDegree += val nparts += 1 # top boundary f = max((0, hitY - realBw)) if hitY > 0 else None if f is not None and (sides is None or "t" in sides): t = hitY texto = np.array( (255 - img[f:t, hitX : hitX + markW]).max(axis=0), dtype=np.uint16 ) fi = hitY ti = hitY + realBw + 1 texti = np.array( (255 - img[fi:ti, hitX : hitX + markW]).max(axis=0), dtype=np.uint16 ) val = measure(texto, texti, threshold) connDegree += val nparts += 1 # bottom boundary t = ( min((textH - 1, hitY + markH + realBw + 1)) if hitY + markH + realBw < textH else None ) if t is not None and (sides is None or "b" in sides): f = hitY + markH texto = np.array( (255 - img[f:t, hitX : hitX + markW]).max(axis=0), dtype=np.uint16 ) ti = hitY + markH fi = hitY + markH - realBw texti = np.array( (255 - img[fi:ti, hitX : hitX + markW]).max(axis=0), dtype=np.uint16 ) val = measure(texto, texti, threshold) connDegree += val nparts += 1 return connDegree def measure(borderInside, borderOutside, threshold)-
Measure the amount of ink that crosses the border of a certain region.
It is used to reject certain matches of image templates, where templates contain strokes of ink. If a match is such that the stroke of ink connects with the ink in the environment, the match is not a true example of the stroke and will be rejected.
Where to look for ink
We look for ink in the image itself, the ink in the search template is not relevant.
Parameters
borderInside:image as np array- The part of the image bordering inside an area where the search template matches
borderOutside:image as np array- The part of the image bordering outside an area where the search template matches
Returns
float- The ratio between the size of the ink connections across the border and the total size of the border.
Expand source code Browse git
def measure(borderInside, borderOutside, threshold): """Measure the amount of ink that crosses the border of a certain region. It is used to reject certain matches of image templates, where templates contain strokes of ink. If a match is such that the stroke of ink connects with the ink in the environment, the match is not a true example of the stroke and will be rejected. !!! note "Where to look for ink" We look for ink in the image itself, the ink in the search template is not relevant. Parameters ---------- borderInside: image as np array The part of the image bordering inside an area where the search template matches borderOutside: image as np array The part of the image bordering outside an area where the search template matches Returns ------- float The ratio between the size of the ink connections across the border and the total size of the border. """ connections = borderInside * borderOutside return np.where(connections > threshold)[0].size / borderOutside.size def reborder(gray, bw, color, crop=False)-
Add a border around a grayscale image, optionally remove white margins first.
The border will add to the size of the image.
Parameters
gray:np array- A grayscale image.
bw:int- Width of the new border.
color:int- Color of the new border (grayscale).
crop:boolean, optionalFalse- If
True, the image will be cropped first such as to remove all surrounding white margins.
Expand source code Browse git
def reborder(gray, bw, color, crop=False): """Add a border around a grayscale image, optionally remove white margins first. The border will add to the size of the image. Parameters ---------- gray: np array A grayscale image. bw: int Width of the new border. color: int Color of the new border (grayscale). crop: boolean, optional `False` If `True`, the image will be cropped first such as to remove all surrounding white margins. """ if crop: inv = 255 * (gray < 128).astype(np.uint8) coords = cv2.findNonZero(inv) x, y, w, h = cv2.boundingRect(coords) cropped = gray[y : y + h, x : x + w] else: cropped = gray bordered = cv2.copyMakeBorder( cropped, bw, bw, bw, bw, cv2.BORDER_CONSTANT, value=color ) return bordered