Module fusus.lakhnawi
Lakhnawi pdf reverse engineering.
This is an effort to make the Lakhnawi PDF readable. It is a text-based PDF, no images are used to represent text.
Yet the text is not easily extracted, due to:
- the use of private-use unicode characters that refer to heavily customised fonts;
- some fonts have some glyphs with dual unicode points;
- the drawing order of characters does not reflect the reading order;
- horizontal whitespace is hard to detect due to oversized bounding boxes of many private-use characters.
We used the top-notch Python PDF library PyMUPDF, also know as fitz.
pip3 install PyMuPDF
But even this library could not solve the above issues. Here is how we solved the issues
Private use characters
We used font analysis software from PdfLib: FontReporter to generate a report of character and font usage in the Lakhnawi PDF.
Based on visual inspection of this font report and the occurrences of the private use tables we compiled a translation table mapping dirty strings (with private use characters) to clean strings (without private use characters).
Dual code points
In case of dual code points, we ignore the highest code points. Often the two code points refer to a normal Arabic code point and to a ligature or special form of the character. The unicode algorithm is very good nowadays to generate the special forms from the ordinary forms based on immediate context.
Reading order
We ordered the characters ourselves, based on the coordinates.
This required considerable subtlety, because we had to deal
with diacritics above and below the lines.
See clusterVert.
Horizontal whitespace
This is the most tricky point, because the information we retain from the PDF is, strictly speaking, insufficient to determine word boundaries. Word boundaries are partly in the eyes of the beholder, if the beholder knows Arabic. The objective part is in the amount of whitespace between characters and the form of the characters (initial, final, isolated). But the rules of Arabic orthography allow initial characters inside words, and there are the enclitic words.
So we only reached an approximate solution for this problem.
Footnotes
We have strippped footnotes and footnote references from the text.
Output format
The most important output are tab separated files with text and positions of
individual words.
See Lakhnawi.tsvPages().
This data is used to feed the conversion to Text-Fabric. See also:
Expand source code Browse git
"""Lakhnawi pdf reverse engineering.
This is an effort to make the Lakhnawi PDF readable.
It is a text-based PDF, no images are used to represent text.
Yet the text is not easily extracted, due to:
* the use of private-use unicode characters that refer to heavily customised fonts;
* some fonts have some glyphs with dual unicode points;
* the drawing order of characters does not reflect the reading order;
* horizontal whitespace is hard to detect due to oversized bounding boxes of many
private-use characters.
We used the top-notch Python PDF library
[PyMUPDF](https://pymupdf.readthedocs.io/en/latest/index.html), also know as *fitz*.
```
pip3 install PyMuPDF
```
But even this library could not solve the above issues.
Here is how we solved the issues
# Private use characters
We used font analysis software from PdfLib:
[FontReporter](https://www.pdflib.com/download/free-software/fontreporter/)
to generate a
[report of character and font usage in the Lakhnawi PDF](https://github.com/among/fusus/blob/master/ur/Lakhnawi/FontReport-Lakhnawi.pdf).
Based on visual inspection of this font report and the occurrences
of the private use tables we compiled a translation table mapping dirty strings
(with private use characters) to clean strings (without private use characters).
# Dual code points
In case of dual code points, we ignore the highest code points.
Often the two code points refer to a normal Arabic code point and to a ligature or
special form of the character.
The unicode algorithm is very good nowadays to generate the special forms
from the ordinary forms based on immediate context.
# Reading order
We ordered the characters ourselves, based on the coordinates.
This required considerable subtlety, because we had to deal
with diacritics above and below the lines.
See `clusterVert`.
# Horizontal whitespace
This is the most tricky point, because the information we retain from the PDF is,
strictly speaking, insufficient to determine word boundaries.
Word boundaries are partly in the eyes of the beholder, if the beholder knows Arabic.
The objective part is in the amount of whitespace between characters
and the form of the characters (initial, final, isolated).
But the rules of Arabic orthography allow initial characters inside words,
and there are the enclitic words.
So we only reached an approximate solution for this problem.
!!! caution "Footnotes"
We have strippped footnotes and footnote references from the text.
# Output format
The most important output are tab separated files with text and positions of
individual words.
See `Lakhnawi.tsvPages`.
This data is used to feed the conversion to Text-Fabric.
See also:
* `fusus.tfFromTsv`.
* [Text-Fabric](https://annotation.github.io/text-fabric/tf/index.html)
"""
import sys
import os
import collections
import re
from itertools import chain
from IPython.display import display, HTML, Image
import fitz
from tf.core.helpers import setFromSpec, unexpanduser
from .parameters import SOURCE_DIR, UR_DIR, ALL_PAGES, LINE_CLUSTER_FACTOR
from .lib import DEFAULT_EXTENSION, pprint, parseNums
from .char import (
UChar,
EMSPACE,
getSetFromDef,
isAlefFinal,
isArDigit,
isEuDigit,
isMeemOrYeh,
isWaw,
normalizeC,
normalizeD,
uName,
)
NAME = "Lakhnawi"
SOURCE = f"{SOURCE_DIR}/{NAME}/{NAME.lower()}.pdf"
FONT = f"{UR_DIR}/{NAME}/FontReport-{NAME}.pdf"
DEST = f"{SOURCE_DIR}/{NAME}/{NAME.lower()}.txt"
CSS = """
<style>
*,
*:before,
*:after {
box-sizing: border-box;
}
@page {
size: A4;
margin: 2cm;
}
div.window {
display: flex;
flex-flow: row nowrap;
justify-content: flex-start;
align-items: flex-start;
min-width: 1000pt;
height: 99vh;
}
div.sidebar {
flex: 1 1 300pt;
display: flex;
flex-flow: row nowrap;
border-right: 1pt solid var(--fog-rim);
padding-left: 8px;
padding-right: 12px;
height: 99vh;
overflow: auto;
-webkit-overflow-scrolling: touch;
}
div.toc {
flex: 1 1 50pt;
}
div.pages {
flex: 0 0 700pt;
}
div.pages.bypage {
height: 99vh;
overflow: auto;
-webkit-overflow-scrolling: touch;
}
div.page {
margin-right: 1cm;
padding-left: 0.5cm;
max-width: 600pt;
min-width: 600pt;
width: 600pt;
}
div.pagec {
margin-right: 1cm;
padding-right: 10%;
width: 90%;
text-align: center;
}
div.phead {
color: #777777;
font-size: small;
text-align: right;
width: 1cm;
margin-right: -1cm;
float: right;
}
.box {
border: 1pt solid #888888;
border-radius: 2pt;
}
.r {
font-family: normal, sans-serif;
font-size: 22pt;
direction: rtl;
unicode-bidi: isolate-override;
}
.rc, .lc {
font-family: normal, sans-serif;
font-size: 22pt;
background-color: white;
border: 2pt solid #ffcccc;
}
.rc {
direction: rtl;
unicode-bidi: isolate-override;
}
.lc {
direction: ltr;
unicode-bidi: isolate-override;
}
p {
text-align: left;
direction: ltr;
unicode-bidi: isolate-override;
}
p.r {
text-align: right;
direction: rtl;
unicode-bidi: isolate-override;
}
.l {
font-family: normal, sans-serif;
font-size: x-large;
direction: ltr;
unicode-bidi: isolate-override;
}
.c {
font-family: monospace;
font-size: x-small;
direction: ltr;
unicode-bidi: isolate-override;
}
.p {
font-family: monospace;
font-size: medium;
font-weight: bold;
background-color: yellow;
direction: ltr;
unicode-bidi: isolate-override;
}
.lrg {
font-size: 22pt;
font-weight: bold;
}
span.sp {
background-color: rgba(0, 255, 0, 0.5);
}
td.al {
text-align: left ! important;
}
div.cn {
text-align: center
}
div.ch.p {
background-color: #ffeedd;
text-align: center
}
span.cni {
background-color: #eeeeee;
padding-top: 4pt;
padding-bottom: 4pt;
padding-left: 8pt;
padding-right: 8pt;
border: 2pt solid #66aaaa;
display: inline-block;
}
div.ch,div.cht,div.chs {
border: 2pt solid #cccccc;
display: inline-flex;
flex-flow: column nowrap;
max-width: 10em;
}
div.ch {
background-color: #ddffff;
}
div.chs {
background-color: #ccffcc;
}
div.chm {
background-color: #44ff44;
}
div.sr {
display: flex;
flex-flow: row wrap;
direction: rtl;
unicode-bidi: isolate-override;
}
table.linecols {
max-width: 100%;
min-width: 100%;
width: 100%;
direction: rtl;
unicode-bidi: isolate-override;
}
td.cols {
padding-left: 0.5em;
padding-right: 0.5em;
text-align: right;
}
td.cols2 {
max-width: 50%;
min-width: 50%;
width: 500%;
}
td.cols3 {
max-width: 33%;
min-width: 33%;
width: 33%;
}
td.cols4 {
max-width: 25%;
min-width: 25%;
width: 25%;
}
td.cols4 {
max-width: 20%;
min-width: 20%;
width: 20%;
}
:root {
--fog-rim: hsla( 0, 0%, 60%, 0.5 );
}
</style>
"""
"""Styles to render extracted text.
The styles are chosen such that the extracted text looks as similar as possible to
the PDF display.
"""
POST_HTML = """
</body>
</html>
"""
"""HTML code postfixed to the HTML representation of a page.
"""
def preHtml(pageNum):
"""Generate HTML code to be prefixed to the HTML representation of a page.
Parameters
----------
pageNum: string
The page number of the page for which HTML is generated.
"""
return f"""\
<html>
<head>
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"/>
<meta charset="utf-8"/>
<title>Lakhnawi {pageNum}</title>
{CSS}
</head>
<body>
"""
def getToc(pageNums):
"""Generate a Table Of Contents for multiple HTML pages.
Parameter
---------
pageNums: iterable if int
The page numbers of the pages in the HTML file.
"""
limit = 60
html = []
html.append("""<div class="toc">""")
j = 0
for (i, pageNum) in enumerate(pageNums):
if j == limit:
j = 0
html.append("""</div>\n<div class="toc">""")
html.append(f"""<a href="#p{pageNum:>03}">p {pageNum}</a><br>""")
j += 1
html.append("""</div>""")
return "\n".join(html)
PRIVATE_SPACE = "\uea75"
PRIVATE_LETTERS_DEF = """
e800
e806
e807
e808
e809
e80a
e80e
e898
e8d4
e915
e917
ea79
"""
PRIVATE_DIAS_DEF = """
e812
e814
e815
e816
e817
e818
e81d
e823
e824
e825
e826
e827
e828
e829
e82b
e82e
e82f
e830
e831
e832
e833
e834
e835
e837
e838
e839
e83a
e83f
e840
e845
e846
e849
e84d
e85b
e85c
e863
e864
e86d
e87f
e880
e887
e888
e8de
e8df
e8e6
e8e7
e8e8
e8e9
e8ea
e8eb
e8ee
e8f4
e8f5
e8f6
e8f8
e8fb
e8fe
"""
PRIVATE_TATWEEL = "\ue821"
PRIVATE_FINAL_SPACE_CODES = """
e898
e915
e917
""".strip().split()
REPLACE_DEF = """
# see https://www.unicode.org/versions/Unicode13.0.0/ch09.pdf
# see https://www.compart.com/en/unicode/U+FE8E
# see https://r12a.github.io/scripts/arabic/block
e821 => : (ignore short tatweel)
e825 => 064e : FATHA
e849 => 064e : FATHA
e86d => 064e : FATHA
e87f => 064e : FATHA
e8e8 => 064e : FATHA
e823 => 064b : FATHATAN
e8e6 => 064b : FATHATAN
e826 => 064f : DAMMA
e8e9 => 064f : DAMMA
e824 => 064c : DAMMATAN
e8e7 => 064c : DAMMATAN
e840 => 0650 : KASRA
e864 => 0650 : KASRA
e888 => 0650 : KASRA
e8df => 0650 : KASRA
e83f => 064d : KASRATAN
e863 => 064d : KASRATAN
e887 => 064d : KASRATAN
e8de => 064d : KASRATAN
e827 => 0651 : SHADDA
e8ea => 0651 : SHADDA
e828 => 0652 : SUKUN
e8eb => 0652 : SUKUN
e829 => 0653 : MADDA
e84d => 0653 : MADDA
e82b => 0670 : ALEF(super)
e8ee => 0670 : ALEF(super)
e830 => 064e+0651 : SHADDA+FATHA
e8f4 => 064e+0651 : SHADDA+FATHA
e8f6 => 064e+0651 : SHADDA+FATHA
e831 => 064f+0651 : SHADDA+DAMMA
e8f5 => 064f+0651 : SHADDA+DAMMA
e82e => 064c+0651 : SHADDA+DAMMATAN
e832 => 0650+0651 : SHADDA+KASRA
e82f => 064d+0651 : SHADDA+KASRATAN [2]
e834 => 064d+0651 : SHADDA+KASRATAN [2]
e812 => 064d+0651 : SHADDA+KASRATAN [2]
e8f8 => 064d+0651 : SHADDA+KASRATAN [2]
e818 => 0653+0670 : MADDA+ALEF(super) [4]
e83a => 0653+0670 : MADDA+ALEF(super) [4]
e8fe => 0653+0670 : MADDA+ALEF(super) [4]
e81d => 0640+0650+0651 : TATWEEL+KASRA+SHADDA
# e898 => 0647 : HEH
e898 => feea : HEH final
e806 => 0627 : ALEF
e807 => 0627 : ALEF
e808 => 0671 : ALEF(wasla)
e809 => 0671 : ALEF(wasla)
e800 => 0622 : ALEF/MADDA
0627+e815 => 0623+064e : ALEF/HAMZA+FATHA
# 0627+e85b => 0623+064e : ALEF/HAMZA+FATHA
fe8e+e815 => 0623+064e : ALEF/HAMZA+FATHA
fe8e+e821+e815 => 0623+064e : ALEF/HAMZA+FATHA
e806+e85b => 0623+064e : ALEF/HAMZA+FATHA
# 0627+e85c => 0623+064f : ALEF/HAMZA+DAMMA
0627+e816 => 0623+064f : ALEF/HAMZA+DAMMA
e806+e85c => 0623+064f : ALEF/HAMZA+DAMMA
fe8e+e816 => 0623+064f : ALEF/HAMZA+DAMMA
fe8e+e821+e816 => 0623+064f : ALEF/HAMZA+DAMMA
# 0627+e814 => 0623+064c : ALEF/HAMZA+DAMMATAN
0627+e846 => 0625+064d : ALEF/HAMZA(low)+KASHRATAN
fe8e+e821+e846 => 0625+064d : ALEF/HAMZA(low)+KASRATAN
fe8e+e817 => 0623+0652 : ALEF/HAMZA+SUKUN [7]
e835 => 0654+064b : HAMZA+FATHATAN [3]
e837 => 0654+064e : HAMZA+FATHA [3]
e8fb => 0654+064e : HAMZA+FATHA [3]
e838 => 0654+064f : HAMZA+DAMMA [3]
e880 => 0654+064f : HAMZA+DAMMA [3]
e839 => 0654+0652 : HAMZA+SUKUN [3]
e845 => 0655+0650 : HAMZA(low)+KASRA
0648+e838 => 0624+064f : WAW/HAMZA+DAMMA
e80a => 0644 : LAM
e80e => 0644 : LAM
# e821+e8d4+e821+e830 => 0644 : LAM [10]
# e821+e8d4+e82b+e821 => 0644 : LAM [10]
# e8d4+e830 => 0644 : LAM [10]
e8d4+e833 => 0644 : LAM [10]
# e8d4+e821 => 0644 : LAM [10]
e8d4+e821+e827 => 0644 : LAM [10]
e8d4+e821+e833 => 0644 : LAM [10]
e8d4+e821+e821+e833 => 0644 : LAM [10]
e8d4+fc63 => 0644 : LAM [10]
e8d4+e827 => 0644 : LAM [10]
# e8d4 => 0644 : LAM [10]
# e8d4+064e+e82b => 0644 : LAM [11]
fefb+e85b => 0644+623+064e : LAM+ALEF/HAMZA+FATHA
fefb+e85c => 0644+0623+064f : LAM/ALEF/HAMZA+DAMMA
fefc+e87f => 0644+0623+064e : LAM/ALEF/HAMZA+FATHA
# fef4+e917 => 064a+0649+0670 : YEH+ALEF(super)
fef4+e917 => 064a+fef0+0670 : YEH+ALEF(super)
ea75+e828+ea79 => 062d+0652+0645 : HAH+SUKUN+MEEM
# fe92+0650+e915 => 0628+0650+064a : BEH+KASRA+YEH
fe92+0650+e915 => 0628+0650+fef2 : BEH+KASRA+YEH
fec3+0652+e821+e80e+064e+e807 => 0637+0652+e821+e80e+064e+e807 : [9]
fffd => : replacement character
# [1] it should be a LAM/ALEF ligature with wasla, but there is no such unicode char
# See https://savannah.gnu.org/bugs/?52454
# [2] it looks like shadda+fathatan, but there is no shadda+fathatan.
# Instead, it is shadda+kashratan, where the kashratan is placed high.
# [3] not a perfect solution. After fbe9 (alef maksura) the high hamza is not
# a recommended combination.
# [4] the result combination of madda and alef superscript does not render nicely
# [5] the hamza ends up on the left part of the ligature and combines
# there with the fatha/damma, the d should be positioned on the rightmost part
# of the ligature, but this does not happen
# [6] The shadda/kasra should render low, but it does render high.
# On page 185 line 4 is a yeh that has both this one and the shadda/fatha,
# where in the original the one is rendered below, and the other above the letter.
# In Unicode they end up both in a high position.
# [7] In the original, the sukun tops the alef and the hamza tops the sukun.
# In Unicode, it's the otherway round: the hamza tops the alif and the sukun is
# at the top.
# [9] Singular case on page 45 line 9 char 90 : a final tah inside a word
# [10] as in Allah. The shadda and alef superscript are filled in by the unicode
# algorithm.
# [11] as in Allah, but with fatha instead of shadda. Probaly a typo in a note,
# page 12 second last line.
"""
"""Character replace rules
There are two parts: (1) character replace rules (2) notes.
Each rule consists of a left hand side, then `=>`, then a right hand side,
then `:` and then a short description.
The short description may contain references to notes in the notes section,
which is a list of commented lines at the end of the whole string.
The left and right hand sides consist of one or more hexadecimal character codes,
joined by the `+` sign.
The meaning is that when the left hand side matches a portion of the input text,
the output text, which is otherwise a copy of the input text, will have that portion
replaced by the right hand side.
The exact application of rules has some subtleties which will be dealt with
in `Laknawi.trimLine`.
"""
def ptRepD(p):
"""Represent a float as an integer with enhanced precision.
Parameters
----------
p: float
We multiply it by 10, then round it to the nearest integer.
A none value is converted to `?`.
"""
return "?" if p is None else int(round(p * 10))
def ptRep(p):
"""Represent a float as an integer.
Parameters
----------
p: float
We round it to the nearest integer.
A none value is converted to `?`.
"""
return "?" if p is None else int(round(p))
REPLACE_RE = re.compile(r"""^([0-9a-z+]+)\s*=>\s*([0-9a-z+]*)\s*:\s*(.*)$""", re.I)
LETTER_CODE_DEF = dict(
d=(1, "diacritic"),
)
"""Defines place holder `d` in rule definitions.
"""
LETTER_CODE = {cd: info[0] for (cd, info) in LETTER_CODE_DEF.items()}
CODE_LETTER = {info[0]: cd for (cd, info) in LETTER_CODE_DEF.items()}
LETTER_KIND = {info[0]: info[1] for info in LETTER_CODE_DEF.values()}
def getDictFromDef(defs):
"""Interpret a string as a dictionary.
Parameters
----------
defs: string
A string containing definitions of character replace rules.
!!! note "Only for rules"
We only use this functions for the rules in `REPLACE_DEF`.
"""
rules = []
rn = 0
good = True
for (i, line) in enumerate(defs.strip().split("\n")):
parts = line.split("#", maxsplit=1)
if len(parts) > 1:
line = parts[0]
line = line.strip()
if not line:
continue
match = REPLACE_RE.match(line)
if not match:
print(f"MALFORMED REPLACE DEF @{i}: {line}")
good = False
continue
rn += 1
(valStr, replStr, comment) = match.group(1, 2, 3)
vals = []
d = None
for (i, val) in enumerate(valStr.split("+")):
if val in {"d"}:
if d is not None:
print(f"MULTIPLE d in RULE @{i}: rule {rn}: {line}")
good = False
d = i
vals.append(LETTER_CODE[val])
else:
vals.append(chr(int(val, base=16)))
repls = []
e = None
if replStr:
for (i, repl) in enumerate(replStr.split("+")):
if repl in {"d"}:
if e is not None:
print(f"MULTIPLE d in RULE @{i}: rule {rn}: {line}")
good = False
e = i
repls.append(LETTER_CODE[repl])
else:
repls.append(chr(int(repl, base=16)))
if d is None and e is not None:
print(f"d in REPLACEMENT but not in MATCH @[i]: rule {rn}: {line}")
good = False
rules.append((rn, tuple(vals), d, tuple(repls), e))
if not good:
return None
result = {}
ruleIndex = {}
for (rn, vals, d, repls, e) in sorted(rules, key=lambda x: (-len(x[1]), str(x[1]))):
result.setdefault(vals[0], []).append((rn, vals, d, repls, e))
ruleIndex[rn] = (vals, d, repls, e)
return (result, ruleIndex)
U_LINE_RE = re.compile(r"""^U\+([0-9a-f]{4})([0-9a-f ]*)$""", re.I)
HEX_RE = re.compile(r"""^[0-9a-f]{4}$""", re.I)
PUA_RE = re.compile(r"""⌊([^⌋]*)⌋""")
RECT = "rect"
COLOR = "color"
FNRULE_WIDTH = 60
"""Width of the rule that separates body text from footnote text.
"""
# SPACE_THRESHOLD = 25
SPACE_THRESHOLD = 10
"""Amount of separation between words.
Character boxes this far apart imply that there is a white space between them.
The unit is 0.1 pixel.
"""
class Lakhnawi(UChar):
def __init__(self):
"""Text extraction from the Lakhnawi PDF.
This class makes use of the `fusus.char.UChar` class which
defines several categories of characters.
By extending that class, the Lakhnawi class makes use of those categories.
It also adds specific characters to some of those categories, especially
the private use characters that occur in the Lakhnawi PDF.
We use *fitz* (`pip3 install PyMuPDF`) for PDF reading.
"""
super().__init__()
self.heights = {}
"""Heights of characters, indexed by page number."""
self.clusteredHeights = {}
"""Clustered heights of characters, indexed by page number.
The clustered heights correspond to the lines on a page.
"""
self.lines = {}
"""Lines as tuples of original character objects, indexed by page number"""
self.text = {}
"""Lines as tuples of converted character objects, indexed by page number"""
self.fnRules = {}
"""Vertical positions of footnote lines, indexed by page number"""
self.spaces = {}
"""Spacing information for each character, indexed by page and line number.
For character that has space behind it, it gives the index position of that
character in the line, the amount of space detected,
and whether this counts as a full white space.
"""
self.columns = {}
"""Column information, indexed by page and line number.
Spaces that are significantly larger than a normal white space
are interpreted as an emspace, and these are considered as column separators.
We remember the character positions where this happens plus the amount
of space in question.
Columns in the Lakhnawi PDF correspond to *hemistic* poems,
where lines are divided into two halves, each occupying a column.
See 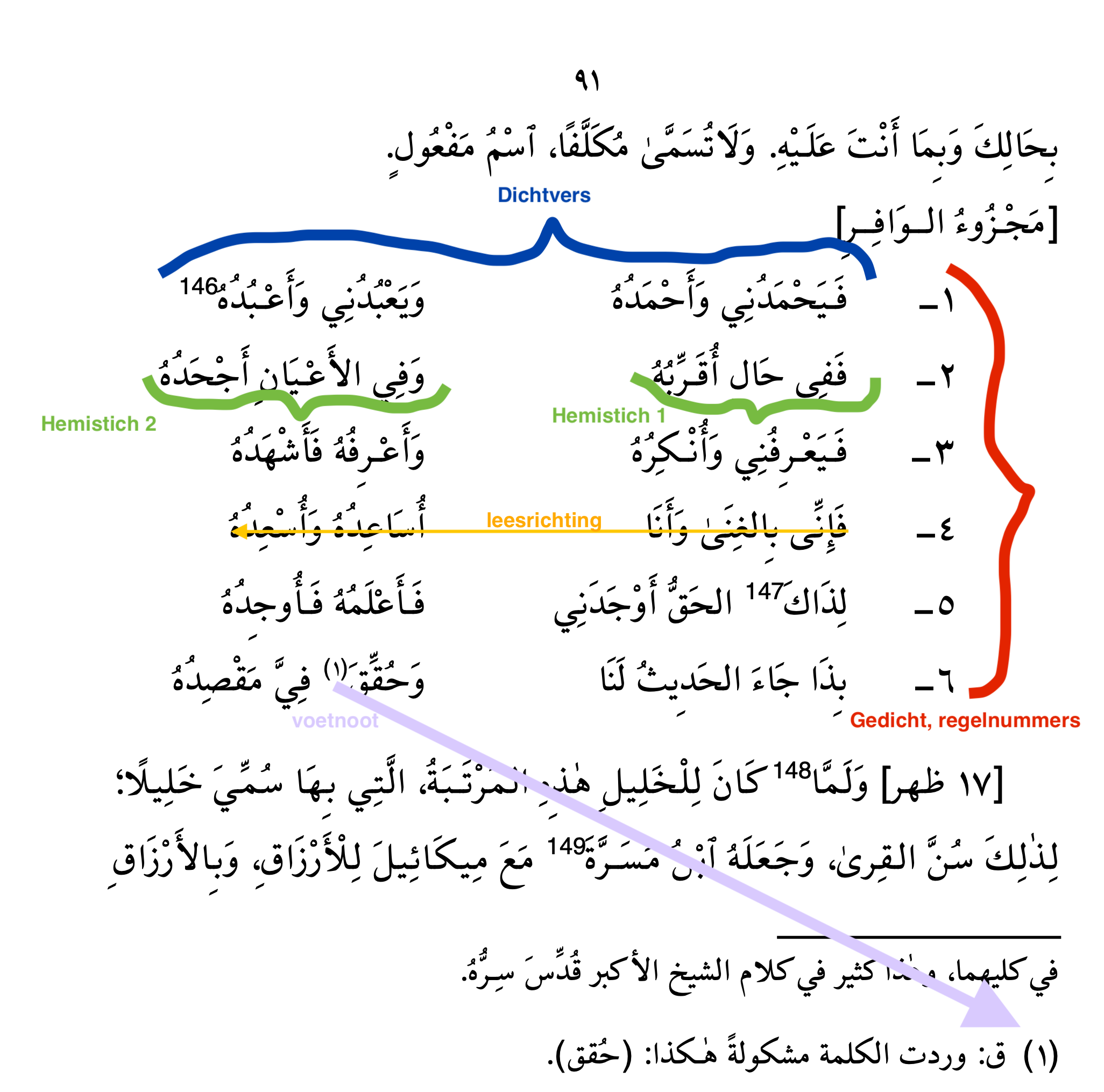
!!! caution "hemistic poems versus blocks"
This is very different from blocks (see `fusus.layout`) in OCRed texts,
where blocks have been detected because of vertical strokes
that separate columns.
The reading progress in a hemistic poem is not changed by the
column division, where as in the case of blocks, reading proceeds
by reading the complete blocks in order.
"""
self.doubles = {}
"""Glyphs with double unicode points.
Some private use characters have two unicode points assigned to them
by fonts in the PDF.
This is the cause that straightforward text extractions deliver
double occurrences of those letters. Even *fitz* does that.
We have collected these cases, and choose to use the lower unicode point,
which is usually an ordinary character, whereas the other is usually a
related presentational character.
This dictionary maps the lower character to the higher character.
"""
self.privateLetters = None
"""Private-use unicodes that correspond to full letters."""
self.privateDias = None
"""Private-use unicodes that correspond to diacritics."""
self.privateSpace = None
"""Private-use-unicode used to represent a space."""
self.good = True
"""Whether processing is still ok, i.e. no errors encountered."""
self.getCharConfig()
self.doc = fitz.open(SOURCE)
"""A handle to the PDF document, after it has been read by *fitz*."""
def close(self):
"""Close the PDF handle, offered by *fitz*."""
self.doc.close()
def setStyle(self):
"""Import the CSS styles into the notebook.
See `CSS`.
"""
display(HTML(CSS))
def getCharConfig(self):
"""Configure all character information.
Private-use characters, transformation rules, character categories.
"""
self.privateInfo()
self.setupRules()
self.getCharInfo()
def privateInfo(self):
"""Set up additional character categories wrt. private-use characters.
Several categories will receive additional members from the
private use characters.
"""
self.privateLetters = getSetFromDef(PRIVATE_LETTERS_DEF)
self.privateDias = getSetFromDef(PRIVATE_DIAS_DEF)
self.privateSpace = PRIVATE_SPACE
self.nospacings |= self.privateDias
# self.nospacings.add(PRIVATE_TATWEEL)
self.diacritics |= self.privateDias
self.diacriticLike |= self.privateDias
self.arabicLetters = self.arabic - self.privateDias
self.rls |= self.puas
def setupRules(self):
"""Set up character transformation rules.
Prepare for counting how much rules will be applied
when extracting text from pages of the Lakhnawi PDF.
"""
(self.replace, self.ruleIndex) = getDictFromDef(REPLACE_DEF)
if self.replace is None:
self.replace = {}
self.good = False
self.rulesApplied = collections.defaultdict(collections.Counter)
for rn in self.ruleIndex:
self.rulesApplied[rn] = collections.Counter()
def getCharInfo(self):
"""Obtain detailed character information by reading the font report file.
From this file we read:
* which are the private use characters?
* which of them have a double unicode?
The font file is
[here](https://github.com/among/fusus/blob/master/ur/Lakhnawi/FontReport-Lakhnawi.pdf).
"""
self.doubles = {}
self.privates = set()
doubles = self.doubles
privates = self.privates
finalSpace = self.finalSpace
puas = self.puas
doc = fitz.open(FONT)
for page in doc:
textPage = page.getTextPage()
data = textPage.extractText()
for (ln, line) in enumerate(data.split("\n")):
if line.startswith("U+"):
match = U_LINE_RE.match(line)
if not match:
continue
(main, rest) = match.group(1, 2)
main = main.lower()
nMain = int(main, base=16)
cMain = chr(nMain)
if cMain in puas:
privates.add(cMain)
continue
if cMain == chr(0):
continue
second = None
rest = rest.replace(" ", "")
if rest:
if HEX_RE.match(rest):
second = rest.lower()
if second:
nSecond = int(second, base=16)
cSecond = chr(nSecond)
if nSecond > nMain:
doubles[cMain] = cSecond
else:
doubles[cSecond] = cMain
doublesApplied = collections.defaultdict(collections.Counter)
for d in doubles:
doublesApplied[d] = collections.Counter()
self.doublesApplied = doublesApplied
finalsApplied = collections.defaultdict(collections.Counter)
for f in finalSpace:
finalsApplied[f] = collections.Counter()
self.finalsApplied = finalsApplied
def plainChar(self, c):
"""Show the character code of a character.
Parameters
----------
c: string
The character in question, may also be the empty string or
the integer 1 (diacritic place holder).
Returns
-------
string
The hexadecimal unicode point of `c`, between `⌊ ⌋` - brackets.
"""
if c == "":
return "⌊⌋"
if c in {1}:
return CODE_LETTER[c]
return f"⌊{ord(c):>04x}⌋"
def plainString(self, s):
"""Show the character codes of the characters in a string.
Parameters
----------
s: string
The string to show, may be empty, may contain place holders.
Returns
-------
string
The concatenation of the unicode points of the characters in the string,
each code point between brackets.
See also `Lakhnawi.plainChar()`.
"""
return " ".join(self.plainChar(c) for c in s)
def showChar(self, c):
"""Pretty display of a single unicode character.
We show the character itself and its name (if not a private-use one),
its hexadecimal code, and we indicate by coloring the kind of
white space that the character represents (ordinary space or emspace).
Parameters
----------
c: string
The character in question, may also be the empty string or
the integer 1 (diacritic place holder).
"""
if c in {1, 2}:
return f"""
<div class="ch p">
<div class="cn">{LETTER_KIND[c]}</div>
</div>
"""
if c == "":
extra = ""
ccode = ""
crep = "\u00a0"
cname = "EMPTY"
else:
puas = self.puas
rls = self.rls
ccode = (
f"""<span class="{"p" if c in puas else "c"}">{ord(c):>04x}</span>"""
)
crep = (
"??"
if c in puas
else f"""<span class="{"rc" if c in rls else "lc"}">{c}"""
)
cname = "" if c in puas else f"""<span class="c">{uName(c)}</span>"""
extra = (
"m" if c == EMSPACE else "s" if c == " " else ""
)
return f"""
<div class="ch{extra}">
<div class="cn">{ccode}</div>
<div class="cn"><span class="cni">{crep}</span></div>
<div class="cn">{cname}</div>
</div>
"""
def showString(self, s, asString=False):
"""Pretty display of a string as a series of unicode characters.
Parameters
----------
s: string
The string to display, may be empty, may contain place holders.
asString: boolean, optional `False`
If True, return the result as an HTML string.
Returns
-------
None | string
If `asString`, returns an HTML string, otherwise returns None,
but displays the HTML string.
See also `Lakhnawi.showChar()`.
"""
shtml = f"""<span class="r">{s}</span>"""
html = """<div class="sr">""" + (
"".join(self.showChar(c) for c in s) + "</div>"
)
if asString:
return f"""<span>{shtml}</span>{html}"""
display(HTML(f"""<p>{shtml}</p>{html}"""))
def showReplacements(self, rule=None, isApplied=False):
"""Show a character conversion rule and how it has been applied.
Parameters
----------
rule: string|int, optional `None`
A specification of zero or more rule numbers (see `fusus.lib.parseNums`).
If None, all rules will be taken.
isApplied: boolean, optional `False`
Only show rules that have been applied.
Returns
-------
None
Displays a table of rules with usage statistics.
"""
ruleIndex = self.ruleIndex
rulesApplied = self.rulesApplied
ruleNums = parseNums(rule)
ruleNums = (
set(ruleIndex)
if ruleNums is None
else sorted(r for r in ruleNums if r in ruleIndex)
)
html = []
totalRules = len(ruleIndex)
totalApplications = sum(sum(x.values()) for x in rulesApplied.values())
totalPages = len(set(chain.from_iterable(rulesApplied.values())))
ruleRep = "rule" + ("" if totalRules == 1 else "s")
appRep = "application" + ("" if totalApplications == 1 else "s")
pageRep = "page" + ("" if totalPages == 1 else "s")
html.append(
f"""
<p><b>{totalRules} {ruleRep} with
{totalApplications} {appRep} on {totalPages} {pageRep}</b></p>
<table>
"""
)
for (rn, applied) in sorted(
rulesApplied.items(), key=lambda x: (-sum(x[1].values()), x[0])
):
if rn not in ruleNums:
continue
(vals, d, repls, e) = ruleIndex[rn]
valRep = "".join(self.showChar(c) for c in vals)
replRep = "".join(self.showChar(c) for c in repls)
total = sum(applied.values())
if isApplied and not applied:
continue
if applied:
examplePageNum = sorted(applied, key=lambda p: -applied[p])[0]
nExamples = applied[examplePageNum]
appliedEx = f"e.g. page {examplePageNum} with {nExamples} applications"
else:
appliedEx = ""
appliedRep = f"<b>{total}</b> x applied on <i>{len(applied)}</i> pages"
html.append(
f"""
<tr>
<th>rule {rn}</th>
<td class="al">{appliedRep}</td>
<td class="al">{appliedEx}</td>
<td class="al">{valRep}</td>
<td class="al"><span class="lrg">⇒</span></td>
<td class="al">{replRep}</td>
</tr>
"""
)
html.append("<table>")
display(HTML("".join(html)))
def showDoubles(self, double=None):
"""Show a character with double entry and how often it occurs.
See `Lakhnawi.doubles`.
Parameters
----------
double: char, optional `None`
A character from the doubles list (`Lakhnawi.doubles`).
If None, all such characters will be taken.
isApplied: boolean, optional `False`
Only show rules that have been applied.
Returns
-------
None
Displays a table of double-entry characters with occurrence statistics.
"""
doubles = self.doubles
doublesApplied = self.doublesApplied
theseDoubles = (
set(doubles) if double is None else {double} if double in doubles else set()
)
html = []
totalDoubles = len(doubles)
totalApplications = sum(sum(x.values()) for x in doublesApplied.values())
totalPages = len(set(chain.from_iterable(doublesApplied.values())))
doubleRep = "double" + ("" if totalDoubles == 1 else "s")
appRep = "application" + ("" if totalApplications == 1 else "s")
pageRep = "page" + ("" if totalPages == 1 else "s")
html.append(
f"""
<p><b>{totalDoubles} {doubleRep} with
{totalApplications} {appRep} on {totalPages} {pageRep}</b></p>
<table>
"""
)
for (d, applied) in sorted(
doublesApplied.items(), key=lambda x: (-sum(x[1].values()), x[0])
):
if d not in theseDoubles:
continue
e = doubles[d]
doubleRep = f"{self.showChar(e)} ⇒ {self.showChar(d)}"
total = sum(applied.values())
if applied:
examplePageNum = sorted(applied, key=lambda p: -applied[p])[0]
nExamples = applied[examplePageNum]
appliedEx = f"e.g. page {examplePageNum} with {nExamples} applications"
else:
appliedEx = ""
appliedRep = f"<b>{total}</b> x applied on <i>{len(applied)}</i> pages"
html.append(
f"""
<tr>
<td class="al">{appliedRep}</td>
<td class="al">{appliedEx}</td>
<td class="al">{doubleRep}</td>
</tr>
"""
)
html.append("<table>")
display(HTML("".join(html)))
def showFinals(self, final=None):
"""Show a character with final form and how often it has been replaced.
Final forms will be normalized to ground forms
and sometimes a space will be added.
Parameters
----------
final: char, optional `None`
A character from the final space list (`fusus.char.UChar.finalSpace`).
If None, all such characters will be taken.
isApplied: boolean, optional `False`
Only show rules that have been applied.
Returns
-------
None
Displays a table of final space characters with occurrence statistics.
"""
finalSpace = self.finalSpace
finalsApplied = self.finalsApplied
theseFinals = (
finalSpace if final is None else {final} if final in finalSpace else set()
)
html = []
totalFinals = len(finalSpace)
totalApplications = sum(sum(x.values()) for x in finalsApplied.values())
totalPages = len(set(chain.from_iterable(finalsApplied.values())))
finalRep = "final" + ("" if totalFinals == 1 else "s")
appRep = "application" + ("" if totalApplications == 1 else "s")
pageRep = "page" + ("" if totalPages == 1 else "s")
html.append(
f"""
<p><b>{totalFinals} {finalRep} with
{totalApplications} {appRep} on {totalPages} {pageRep}</b></p>
<table>
"""
)
for (f, applied) in sorted(
finalsApplied.items(), key=lambda x: (-sum(x[1].values()), x[0])
):
if f not in theseFinals:
continue
finalRep = self.showChar(f)
total = sum(applied.values())
if applied:
examplePageNum = sorted(applied, key=lambda p: -applied[p])[0]
nExamples = applied[examplePageNum]
appliedEx = f"e.g. page {examplePageNum} with {nExamples} applications"
else:
appliedEx = ""
appliedRep = f"<b>{total}</b> x applied on <i>{len(applied)}</i> pages"
html.append(
f"""
<tr>
<td class="al">{appliedRep}</td>
<td class="al">{appliedEx}</td>
<td class="al">{finalRep}</td>
</tr>
"""
)
html.append("<table>")
display(HTML("".join(html)))
def showLineHeights(self, pageNumSpec):
"""Shows how line heights have been determined.
The pages can be selected by page numbers.
Parameters
----------
pageNumSpec: None | int | string | iterable
As in `Lakhnawi.parsePageNums()`.
"""
heights = self.heights
clusteredHeights = self.clusteredHeights
for pageNum in self.parsePageNums(pageNumSpec):
theseHeights = heights[pageNum]
theseClusteredHeights = clusteredHeights[pageNum]
print(f"Line heights page {pageNum:>3}")
print("\nraw heights")
for k in sorted(theseHeights):
print(f"{theseHeights[k]:>4} characters @ height {int(round(k)):>4}")
print("line heights")
for (ln, kc) in enumerate(sorted(theseClusteredHeights)):
peak = ", ".join(
f"{int(round(k)):>4}" for k in sorted(theseClusteredHeights[kc])
)
print(
f"line {ln + 1:>2}: "
f"{sum(theseHeights[k] for k in theseClusteredHeights[kc]):>4}"
f" characters @height {peak}"
)
def parsePageNums(self, pageNumSpec):
"""Parses a value as one or more page numbers.
Parameters
----------
pageNumSpec: None | int | string | iterable
If `None` results in all page numbers.
If an `int`, it stands for that int.
If a `string`, it is allowed to be a comma separated list of
numbers or ranges, where a range is a lower bound and an upper bound
separated by a `-`.
If none of these, it should be an iterable of `int` values.
Returns
-------
None | iterable of int
Depending on the value.
"""
doc = self.doc
pageNums = (
list(range(1, len(doc) + 1))
if not pageNumSpec
else [pageNumSpec]
if type(pageNumSpec) is int
else setFromSpec(pageNumSpec)
if type(pageNumSpec) is str
else list(pageNumSpec)
)
return [i for i in sorted(pageNums) if 0 < i <= len(doc)]
def drawPages(self, pageNumSpec, clip=None):
"""Draws a (part) of page from the PDF as a raster image.
Parameters
----------
pageNumSpec: None | int | string | iterable
As in `Lakhnawi.parsePageNums()`.
clip: (int, int), optional `None`
If None: produces the whole page.
Otherwise it is `(top, bottom)`, and a stripe
from top to bottom will be displayed.
"""
doc = self.doc
for pageNum in self.parsePageNums(pageNumSpec):
page = doc[pageNum - 1]
if clip is not None:
clip = (0, clip[0], page.rect.width, clip[1])
pix = page.getPixmap(matrix=fitz.Matrix(4, 4), clip=clip, alpha=False)
display(HTML(f"""<p><b>page {pageNum}</b></p>"""))
display(Image(data=pix.getPNGData(), format=DEFAULT_EXTENSION))
def getPages(
self,
pageNumSpec,
refreshConfig=False,
doRules=True,
doFilter=True,
onlyFnRules=False,
):
"""Reads pages of the PDF and extracts text.
This does all of the hard work of the text extraction.
It saves the textual data in attributes of the Lakhnawi object,
augmented with all kinds of diagnostic information.
From all this data, various output representations can be generated
rather easily by other methods.
Parameters
----------
pageNumSpec: None | int | string | iterable
As in `Lakhnawi.parsePageNums()`.
refreshConfig: boolean, optional `False`
If `True`, rereads all character configuration.
Ideal when you are iteratively developing the character configuration.
doRules: boolean, optional `True`
If `False`, suppresses the application of character transformation
rules. Mainly used when debugging other aspects of the text extraction.
doFilter: boolean, optional `True`
If `False`, suppresses the application of unicode normalization,
by which presentational characters are transformed into sequences
of ordinary, basic characters.
Used for debugging.
onlyFnRules: boolean, optional `False`
If `True`, skips most of the conversion.
Only determine where the footnote rules are.
Used for debugging.
Returns
-------
None
The effect is that attributes of the Lakhnawi object
are filled:
* `Lakhnawi.heights`
* `Lakhnawi.clusteredHeights`
* `Lakhnawi.fnRules`
For the other attributes, see `Lakhnawi.collectPage()`.
!!! hint "multiple runs"
If you do multiple runs of this function for different pages,
the results will not overwrite each other in general,
because the attributes hold the results in dictionaries
keyed by page number.
"""
if not self.good:
print("SKIPPING because of config errors")
return
fnRules = self.fnRules
spaces = self.spaces
columns = self.columns
self.doRules = doRules
self.doFilter = doFilter
ruleIndex = self.ruleIndex
rulesApplied = self.rulesApplied
if refreshConfig:
self.getCharConfig()
for rn in ruleIndex:
rulesApplied[rn] = collections.Counter()
for (i, pageNum) in enumerate(self.parsePageNums(pageNumSpec)):
self.pageNum = pageNum
rep = (
f"{i + 1:>4} (page {pageNum:>4})"
if pageNum != i + 1
else (f"{i + 1:>4}" + " " * 12)
)
sys.stdout.write(f"\r\t{rep}")
sys.stdout.flush()
doc = self.doc
page = doc[pageNum - 1]
theseFnRules = set()
for fnRule in page.getDrawings():
if RECT in fnRule and fnRule.get(COLOR, None):
rect = fnRule[RECT]
width = rect.x1 - rect.x0
if width > FNRULE_WIDTH:
theseFnRules.add(int(round(rect.y1)))
fnRules[pageNum] = tuple(sorted(theseFnRules))
spaces[pageNum] = {}
columns[pageNum] = {}
if onlyFnRules:
continue
textPage = page.getTextPage()
data = textPage.extractRAWDICT()
self.collectPage(data)
def getPageRaw(self, pageNum):
"""Do a rough/raw text extract of a specific page.
The *fitz* method
[extractRAWDICT()](https://pymupdf.readthedocs.io/en/latest/textpage.html#TextPage.extractRAWDICT)
is used to obtain very detailed information about each character on that page.
Used for debugging.
Parameters
----------
pageNum: int
A valid page number.
It is the sequence number of the page within the PDF, counting from 1.
Returns
-------
None
It pretty prints the output of the fitz method, which is a big
and deep dictionary.
"""
self.pageNum = pageNum
rep = f"page {pageNum:>4}"
sys.stdout.write(f"{rep}")
sys.stdout.flush()
doc = self.doc
page = doc[pageNum - 1]
textPage = page.getTextPage()
data = textPage.extractRAWDICT()
pprint(data)
def getPageObj(self, pageNum):
"""Get the *fitz* object for a specific page.
Used for debugging.
Parameters
----------
pageNum: int
A valid page number.
It is the sequence number of the page within the PDF, counting from 1.
Returns
-------
object
A *fitz*
[page object](https://pymupdf.readthedocs.io/en/latest/page.html)
"""
self.pageNum = pageNum
doc = self.doc
return doc[pageNum - 1]
def plainPages(self, pageNumSpec):
"""Outputs processed pages as plain text.
Uses `Lakhnawi.plainLine()`.
Parameters
----------
pageNumSpec: None | int | string | iterable
As in `Lakhnawi.parsePageNums()`.
Returns
-------
None
The plain text is printed to the output.
"""
text = self.text
for pageNum in self.parsePageNums(pageNumSpec):
lines = text.get(pageNum, [])
for (i, line) in enumerate(lines):
print(self.plainLine(line))
def tsvPages(self, pageNumSpec):
"""Outputs processed pages as tab-separated data.
See `fusus.convert` for the details of the output format.
Uses
`Lakhnawi.tsvLine()`.
and `Lakhnawi.tsvHeadLine()`.
Parameters
----------
pageNumSpec: None | int | string | iterable
As in `Lakhnawi.parsePageNums()`.
Returns
-------
None
The tab-separated data is written to a single tsv file.
There is a heading row.
The file is in `fusus.parameters.UR_DIR`, under `Lakhnawi`.
The name of the file includes a page specification.
"""
text = self.text
destDir = f"{UR_DIR}/{NAME}"
pageNums = self.parsePageNums(pageNumSpec)
if not os.path.exists(destDir):
os.makedirs(destDir, exist_ok=True)
pageNumRep = ALL_PAGES if pageNumSpec is None else str(pageNumSpec)
filePath = f"{destDir}/{pageNumRep}.tsv"
fh = open(filePath, "w")
fh.write(self.tsvHeadLine())
for pageNum in pageNums:
lines = text.get(pageNum, [])
for (ln, line) in enumerate(lines):
fh.write(self.tsvLine(line, pageNum, ln + 1))
fh.close()
print(f"TSV data written to {unexpanduser(filePath)}")
def htmlPages(
self,
pageNumSpec,
line=None,
showSpaces=False,
export=False,
singleFile=False,
toc=False,
):
"""Outputs processed pages as formatted HTML pages.
Uses
`Lakhnawi.htmlLine()`.
The HTML output is suitable to read the extracted text.
Its layout matches the original closely, which makes it easier
to see where the output deviates from the source page.
Parameters
----------
pageNumSpec: None | int | string | iterable
As in `Lakhnawi.parsePageNums()`.
line: None | int | string | iterable
A specification of zero or more line numbers (see `fusus.lib.parseNums`).
showSpaces: boolean, optional `False`
If `True`, shows the spaces with a conspicuous coloured background.
export: boolean, optional `False`
If `True`, writes the HTML results to disk.
In this case, the HTML will not be displayed in the notebook.
singleFile: boolean, optional `False`
Only meaningful is `export=True`.
If `True`, writes the output to a single HTML file,
otherwise to one file per page, in a directory called `html`.
toc: boolean, optional `False`
Only meaningful is `export=True` and `singleFile=True`.
If `True`, writes a table of contents to the file.
The TOC points to every page that is included in the output file.
Returns
-------
None
Depending on `export`, the page is displayed in the notebook
where this function is called, or exported to a file on disk.
The file is in `fusus.parameters.UR_DIR`, under `Lakhnawi`.
The name of the file includes a page specification.
"""
self.showSpaces = showSpaces
text = self.text
destDir = f"{UR_DIR}/{NAME}" if singleFile else f"{UR_DIR}/{NAME}/html"
pageNums = self.parsePageNums(pageNumSpec)
lineNums = parseNums(line)
lineNums = None if lineNums is None else set(lineNums)
filesWritten = 0
if export:
if not os.path.exists(destDir):
os.makedirs(destDir, exist_ok=True)
if singleFile:
pageNumRep = ALL_PAGES if pageNumSpec is None else str(pageNumSpec)
tocRep = "-with-toc" if toc else ""
filePath = f"{destDir}/{pageNumRep}{tocRep}.html"
fh = open(filePath, "w")
fh.write(preHtml(f"{pageNumRep}{tocRep}"))
if toc:
toc = getToc(pageNums)
fh.write(
f"""
<div class="window">
<div class="sidebar">
{toc}
</div>
<div class="pages bypage">
"""
)
else:
fh.write(
"""
<div class="pages">
"""
)
pageClass = "page" + ("" if export else "c")
for pageNum in pageNums:
lines = text.get(pageNum, [])
nLines = len(lines)
html = []
html.append(
f"""
<div class="{pageClass}">
<div class="phead"><a name="p{pageNum:>03}">{pageNum}</a></div>
"""
)
prevMulti = False
for (i, line) in enumerate(lines):
if lineNums is not None and i + 1 not in lineNums:
continue
html.append(self.htmlLine(line, prevMulti, i == nLines - 1))
prevMulti = len(line) > 1
html.append("""</div>""")
if export:
htmlRep = "".join(html)
if singleFile:
fh.write(htmlRep)
else:
html = preHtml(pageNum) + htmlRep + POST_HTML
filePath = f"{destDir}/p{pageNum:>03}.html"
with open(filePath, "w") as fh:
fh.write(html)
filesWritten += 1
else:
display(HTML("\n".join(html)))
if export and singleFile:
fh.write(
"""
</div>
"""
)
if toc:
fh.write(
"""
</div>
"""
)
fh.write(POST_HTML)
fh.close()
print(f"HTML written to {unexpanduser(filePath)}")
if export and not singleFile:
print(f"{filesWritten} HTML files written to {unexpanduser(destDir)}/")
def showLines(
self,
pageNumSpec,
line=None,
start=None,
end=None,
search=None,
orig=False,
every=False,
):
"""Outputs processed lines as a formatted HTML table.
The lines can be selected by page numbers and line numbers.
Within the selected lines, the characters can be selected by
start/end postions, or by characters of interest.
All of these indices start at 1.
Parameters
----------
pageNumSpec: None | int | string | iterable
As in `Lakhnawi.parsePageNums()`.
line: None | int | string | iterable
A specification of zero or more line numbers (see `fusus.lib.parseNums`).
start: integer, optional `None`
Starting word position in each line to be output.
If `None`, starts at the beginning of each line.
end: integer, optional `None`
End word position in each line to be output.
If `None`, ends at the end of each line.
search: string or iterable of char, optional `None`
If not none, all characters in `search` are deemed interesting.
All occurrences of these characters within the selected lines are
displayed, included a small context.
orig: boolean, optional `False`
Only meaningful if `search` is given.
If `True`: the check for interesting
characters is done in the original, untranslated characters.
Otherwise, interesting characters are looked up in the translated
characters.
every: boolean, optional `False`
Only meaningful if `search` is given.
If `True`, when looking for interesting characters, all occurrences will
be retrieved, otherwise only the first one.
Returns
-------
None
The output material will be displayed in the notebook.
"""
lines = self.lines
pageNums = self.parsePageNums(pageNumSpec)
lineNums = parseNums(line)
myLines = {pageNum: lines[pageNum] for pageNum in pageNums if pageNum in lines}
html = []
html.append("<table>")
html.append(
"""
<tr>
<th>seq</th>
<th>top</th>
<th>bottom</th>
<th>left</th>
<th>right</th>
<th>spacing</th>
<th>font</th>
<th>size</th>
<th>orig char</th>
<th>char</th>
</tr>
"""
)
shift = 5
for (pageNum, pageLines) in myLines.items():
myLineNums = (
range(1, len(pageLines) + 1)
if lineNums is None
else [ln for ln in lineNums if 0 < ln <= len(pageLines)]
)
for ln in myLineNums:
chars = pageLines[ln - 1]
nChars = len(chars)
html.append(
f"""
<tr>
<th colspan=3>page {pageNum}</th>
<th colspan=2>line {ln}</th>
<th colspan=3>{nChars} characters</th>
</tr>
"""
)
if search is None:
ranges = [(max((start or 0) - 1, 0), min(end or nChars, nChars))]
else:
ranges = []
for (i, char) in enumerate(chars):
if search in char[-2 if orig else -1]:
occStart = max((i - shift, 0))
occEnd = min((i + shift + 1, nChars))
if ranges and occStart <= ranges[-1][1]:
ranges[-1][1] = occEnd
else:
ranges.append([occStart, occEnd])
if not every:
break
for (occStart, occEnd) in ranges:
for i in range(occStart, occEnd):
char = chars[i]
(le, to, ri, bo, font, size, spacing, oc, c) = char
html.append(
f"""
<tr>
<td><b>{i + 1}</b></td>
<td>{ptRepD(to)}</td>
<td>{ptRepD(bo)}</td>
<td>{ptRepD(le)}</td>
<td>{ptRepD(ri)}</td>
<td>{spacing}</td>
<td>{font}</td>
<td>{size}pt</td>
<td>{"".join(self.showChar(x) for x in reversed(oc))}</td>
<td>{"".join(self.showChar(x) for x in reversed(c))}</td>
</tr>
"""
)
if search and ranges and not every:
break
html.append("</table>")
display(HTML("".join(html)))
def showWords(self, pageNumSpec, line=None):
"""Outputs processed words as a formatted HTML table.
The lines can be selected by page numbers and line numbers.
All words within the selected lines are put into a table with
the same properties as in the TSV data,
see `Lakhnawi.tsvPages`.
Parameters
----------
pageNumSpec: None | int | string | iterable
As in `Lakhnawi.parsePageNums()`.
line: None | int | string | iterable
A specification of zero or more line numbers (see `fusus.lib.parseNums`).
Returns
-------
None
The output material will be displayed in the notebook.
"""
text = self.text
pageNums = self.parsePageNums(pageNumSpec)
lineNums = parseNums(line)
myLines = {pageNum: text[pageNum] for pageNum in pageNums if pageNum in text}
html = []
html.append("<table>")
html.append(
"""
<tr>
<th>page</th>
<th>line</th>
<th>col</th>
<th>span</th>
<th>dir</th>
<th>left</th>
<th>top</th>
<th>right</th>
<th>bottom</th>
<th>letters</th>
<th>punc</th>
</tr>
"""
)
for (pageNum, pageLines) in myLines.items():
myLineNums = (
range(1, len(pageLines) + 1)
if lineNums is None
else [ln for ln in lineNums if 0 < ln <= len(pageLines)]
)
for ln in myLineNums:
cols = pageLines[ln - 1]
for (cn, spans) in enumerate(cols):
for (sn, (dr, words)) in enumerate(spans):
for (letters, punc, (le, to, ri, bo)) in words:
html.append(
f"""
<tr>
<td><b>{pageNum}</b></td>
<td><b>{ln}</b></td>
<td><i>{cn + 1}</i></td>
<td><i>{sn + 1}</i></td>
<td><i>{dr}</i></td>
<td>{ptRep(le)}</td>
<td>{ptRep(to)}</td>
<td>{ptRep(ri)}</td>
<td>{ptRep(bo)}</td>
<td>{self.showString(letters, asString=True)}</td>
<td>{self.showString(punc, asString=True)}</td>
</tr>
"""
)
html.append("</table>")
display(HTML("".join(html)))
def showUsedChars(
self,
pageNumSpec,
orig=False,
onlyPuas=False,
onlyPresentational=False,
long=False,
byOcc=False,
):
"""Show used characters.
Gives an overview of character usage, either in the input PDF, or in
the text output.
Parameters
----------
pageNumSpec: None | int | string | iterable
As in `Lakhnawi.parsePageNums()`.
orig: boolean, optional `False`
If `True`: shows characters of the original PDF.
Otherwise, shows characters of the translated output/
onlyPuas: boolean, optional `False`
If `True`, the result is restricted to private use characters.
onlyPresentational: boolean, optional `False`
If `True`, the result is restricted to presentational characters.
See `fusus.char.UChar.presentational`.
long: boolean, optional `False`
If `True`, for each character output the complete list of pages
where the character occurs. Otherwise, show only the most
prominent pages.
byOcc: boolean, optional `False`
If `True`, sort the results by first occurrence of the characters.
Otherwise, sort the results by unicode code point of the character.
Returns
-------
None
The output material will be displayed in the notebook.
"""
presentational = self.presentational
pageNums = self.parsePageNums(pageNumSpec)
text = self.text
lines = self.lines
puas = self.puas
charsOut = collections.defaultdict(collections.Counter)
def keyByOcc(c):
pageNums = charsOut[c]
return -sum(pageNums.values())
sortKey = keyByOcc if byOcc else lambda x: x
if orig:
lns = {pageNum: lines[pageNum] for pageNum in pageNums if pageNum in lines}
for (pageNum, pageLines) in lns.items():
for line in pageLines:
for char in line:
c = char[-2]
if c in puas or (
not onlyPuas
and (c in presentational or not onlyPresentational)
):
charsOut[c][pageNum] += 1
else:
texts = {pageNum: text[pageNum] for pageNum in pageNums if pageNum in text}
for (pageNum, pageText) in texts.items():
for line in pageText:
for col in line:
for span in col:
for word in span[1]:
letters = word[0]
punc = word[1]
thesePuas = PUA_RE.findall(letters)
for pua in thesePuas:
charsOut[chr(int(pua, base=16))][pageNum] += 1
if not onlyPuas:
rest = PUA_RE.sub("", f"{letters}{punc}")
for c in rest:
if not (
onlyPresentational
and c not in presentational
):
charsOut[c][pageNum] += 1
totalChars = len(charsOut)
totalPages = len(set(chain.from_iterable(charsOut.values())))
totalOccs = sum(sum(pns.values()) for pns in charsOut.values())
charRep = "character" + ("" if totalChars == 1 else "s")
occRep = "occurence" + ("" if totalOccs == 1 else "s")
pageRep = "page" + ("" if totalPages == 1 else "s")
label = "private use " if onlyPuas else ""
html = []
html.append(
f"""
<p><b>{totalChars} {label}{charRep} in {totalOccs} {occRep}
on {totalPages} {pageRep}</b></p>
<table>
"""
)
for c in sorted(charsOut, key=sortKey):
pageNums = charsOut[c]
nPageNums = len(pageNums)
pageRep = "page" + ("" if nPageNums == 1 else "s")
thistotal = sum(pageNums.values())
examplePageNum = sorted(pageNums, key=lambda p: -pageNums[p])[0]
nExamples = pageNums[examplePageNum]
html.append(
f"""
<tr>
<td class="al">{self.showChar(c)}</td>
<td class="al"><b>{thistotal}</b> on <i>{nPageNums}</i> {pageRep}</td>
<td class="al">e.g. page {examplePageNum} with <b>{nExamples}</b> occurrences</td>
</tr>
"""
)
if long:
for pn in sorted(pageNums):
occs = pageNums[pn]
html.append(
f"""
<tr>
<td></td>
<td class="al"><i>page {pn:>3}</i>: <b>{occs:>3}</b></td>
</tr>
"""
)
html.append("</table>")
display(HTML("".join(html)))
def showColumns(self, pageNumSpec):
"""Show used characters.
Gives an overview of the columns in each line.
The result is a readable, ascii overview of the columns
that exists in the lines of the selected pages.
It is useful to visually check column detection for many pages.
Parameters
----------
pageNumSpec: None | int | string | iterable
As in `Lakhnawi.parsePageNums()`.
Returns
-------
None
The output material will be displayed in the notebook.
"""
pageNums = self.parsePageNums(pageNumSpec)
columns = self.columns
for pageNum in pageNums:
if pageNum not in columns:
continue
lineInfo = columns[pageNum]
multiple = []
for lNum in sorted(lineInfo):
(threshold, emspaces) = lineInfo[lNum]
nEmspaces = len(emspaces)
if threshold is not None and nEmspaces > 0:
multiple.append((lNum, threshold, emspaces))
if not len(multiple):
print(f"page {pageNum:>3} -")
else:
print(f"page {pageNum:>3}:")
for (lNum, threshold, emspaces) in multiple:
nEmspaces = len(emspaces)
print(f"\t{lNum:>2}: {'- ' * (nEmspaces + 1)}")
def showSpacing(self, pageNumSpec, line=None):
"""Show where the spaces are.
Gives an overview of the white space positions in each line.
It is useful to debug the horizontal white space algorithm.
Parameters
----------
pageNumSpec: None | int | string | iterable
As in `Lakhnawi.parsePageNums()`.
line: None | int | string | iterable
A specification of zero or more line numbers (see `fusus.lib.parseNums`).
Returns
-------
None
The output material will be displayed in the notebook.
"""
pageNums = self.parsePageNums(pageNumSpec)
lineNums = parseNums(line)
lineNums = None if lineNums is None else set(lineNums)
spaces = self.spaces
for pageNum in pageNums:
if pageNum not in spaces:
continue
print(f"page {pageNum:>3}")
lineInfo = spaces[pageNum]
for (ln, spaces) in lineInfo.items():
if lineNums is not None and ln not in lineNums:
continue
print(f"\tline {ln:>2}")
for (i, after, isSpace) in spaces:
print(f"\t\t{i + 1:>3} {'] [' if isSpace else ']==['} {after}")
def collectPage(self, data):
"""Transforms raw text into proper textual data.
Called by `Lakhnawi.getPages()` and delivers its results
to attributes of the Lakhnawi object.
Here are they
* `Lakhnawi.lines`
* `Lakhnawi.doubles`
* `Lakhnawi.text`
They are all dictionaries, keyed by page number first and then by line.
Parameters
----------
data: dict
as obtained by the
[extractRAWDICT()](https://pymupdf.readthedocs.io/en/latest/textpage.html#TextPage.extractRAWDICT)
method of *fitz*.
Returns
-------
None
"""
doubles = self.doubles
doublesApplied = self.doublesApplied
pageNum = self.pageNum
nospacings = self.nospacings
fnRules = self.fnRules
bracketMap = self.bracketMap
text = self.text
fnRule = fnRules.get(pageNum, None)
fnRule = fnRule[0] if fnRule else None
chars = []
prevChar = None
prevFont = None
prevSize = None
def addChar():
box = prevChar["bbox"]
yBot = box[3]
# skip chars below the footnote rule, if any
if fnRule is not None and yBot > fnRule:
return
c = prevChar["c"]
cr = "" if isEuDigit(c) else c
cr = bracketMap.get(cr, cr)
chars.append(
(
*box,
prevFont,
prevSize,
"" if c in nospacings else True,
c,
cr,
)
)
def collectChars(data, font, size):
nonlocal prevChar
nonlocal prevFont
nonlocal prevSize
if type(data) is list:
for elem in data:
collectChars(elem, font, size)
elif type(data) is dict:
if "font" in data:
font = data["font"]
if "size" in data:
size = data["size"]
if "c" in data:
c = data["c"]
skip = False
if c == " ":
skip = True
if prevChar is not None:
pc = prevChar["c"]
if pc in doubles and doubles[pc] == c:
skip = True
doublesApplied[pc][pageNum] += 1
if c in doubles and doubles[c] == pc:
prevChar = data
skip = True
doublesApplied[c][pageNum] += 1
if not skip:
if prevChar is not None:
addChar()
prevChar = data
prevFont = font
prevSize = size
for (k, v) in data.items():
if type(v) in {list, dict}:
collectChars(v, font, size)
collectChars(data, None, None)
if prevChar is not None:
addChar()
clusterKeyCharV = self.clusterVert(chars)
lines = {}
for char in sorted(chars, key=lambda c: (clusterKeyCharV(c), keyCharH(c))):
k = clusterKeyCharV(char)
lines.setdefault(k, []).append(list(char))
theseLines = list(lines.values())
if theseLines and self.isPageNum(theseLines[0]):
theseLines = theseLines[1:]
# remove arabic numerals between brackets
for chars in theseLines:
nChars = len(chars)
if not nChars:
continue
i = 0
while i < nChars:
char = chars[i]
nextI = i + 1
if char[-1] == "(":
found = None
for j in range(i + 1, nChars):
theChar = chars[j][-1]
if theChar == ")":
found = j + 1
nextI = found
break
if isArDigit(theChar):
continue
nextI = j
break
if found is not None:
for j in range(i, found):
chars[j][-1] = ""
i = found
i = nextI
self.lines[pageNum] = tuple(
chars for chars in theseLines if not all(c[-1] == "" for c in chars)
)
text[pageNum] = []
for (ln, line) in enumerate(self.lines[pageNum]):
self.trimLine(pageNum, ln + 1, line)
def isPageNum(self, chars):
"""Checks whether a series of characters represents an arabic number.
Parameters
----------
chars: iterable of char reocrds
"""
return 1 <= len(chars) <= 3 and all(isArDigit(c[-1]) for c in chars)
def trimLine(self, pageNum, ln, chars):
"""Map character sequences to other sequences.
Two tasks:
1. Map private use characters to well-known unicode characters
2. Insert space characters where the next character is separated from the
previous one.
Complications:
Diacritical characters are mostly contained in a very wide box that overlaps
with the boxes of the other characters. So the diacritical boxes must not be
taken into account.
Private use characters often come in sequences, so a sequence of characters
must be transformed to another sequence.
We do the tramsformation before the space insertion, because otherwise we
might insert the space at the wrong point.
When we transform characters we need to retain the box information,
because we still have to insert the space.
That's why we have as input a list of character records, where each record
is itself a list with box information, orginal character, modified characters
and space information.
When we transform characters, we modify character records in place.
We do not add or remove character records.
The last member of a character record is the modified sequence.
This can be zero, one, or multiple characters.
The second last member is the original character.
Initially, the the last and second last member of each record are equal.
We call these members the original character and the result string.
Space will be appended at the last member of the appropriate character records.
The transformations are given as a set of rules.
See `REPLACE_DEFS`.
A rule consists of a sequence of characters to match and a sequence of
characters to replace the match with. We call them the match sequence and the
replacement sequence of the rule.
For each character in the input list we check which rules have a match sequence
that start with this character.
Of these rules, we start with the one with the longest match sequence.
We then check, by looking ahead, whether the whole match sequence matches the
input.
For the purposes of matching, we look into the result strings of the character,
not to the original characters. This will prevent some rules to be applied
after an earlier rule has been applied. This is intentional, and results
in a more simple rule set.
If there is a match, we walk through all the characters in the input for the
length of the match sequence of the rule.
For each input character record, we set its replacement string to the
corresponding member of the replacement sequence of the rule.
If the replacement sequence has run out, we replace with the empty string.
If after this process the replacement sequence has not been exhausted,
we join the remaining characters in the replacement string and append it
after the replacement string of the last input character that we have visited.
After succesful application of a rule, we do not apply other rules that would
have been applicable at this point. Instead, we move our starting point to the
next character record in the sequence and repeat the matching process.
It might be that a character is replaced multiple times, for example when
it is reached by a rule while looking ahead 3 places, and then later by a
different rule looking ahead two places.
However, once a character matches the first member of the match sequence of
a rule, and the rule matches and is applied, that character will not be
changed anymore by any other rule.
!!! caution "place holders for diacritics"
The following functionality exists in the code, but is not needed anymore
to process the Lakhnawi PDF.
The match sequence may contain the character `d`, which is a placeholder
for a diacritic sign. It will match any diacritic.
The replacement sequence of such a rule may or may not contain a `d`.
It is an error if the replacement seqience of a rule contains a `d` while
its match sequence does not.
It is also an error of there are multiple `d`s in a match sequence
of a replacement sequence.
If so, the working of this rule is effectively two rules:
Suppose the rule is
x d y => r d s
where x, y, r, s are sequences of arbitrary length.
If the rule matches the input, then first the rule
x => r
will be applied at the current position.
Then we shift temporarily to the position right after where the d has matched,
and apply the rule
y => s
Then we shift back to the orginal position plus one, and continue applying
rules.
"""
replace = self.replace
puas = self.puas
neutrals = self.neutrals
rls = self.rls
rulesApplied = self.rulesApplied
spaces = self.spaces
columns = self.columns
diacritics = self.diacritics
punct = self.punct
diacriticLike = self.diacriticLike
arabicLetters = self.arabicLetters
presentationalC = self.presentationalC
presentationalD = self.presentationalD
finalSpace = self.finalSpace
finalsApplied = self.finalsApplied
nonLetter = self.nonLetter
doRules = self.doRules
doFilter = self.doFilter
nChars = len(chars)
# rule application stage
if doRules:
for (i, char) in enumerate(chars):
c = char[-1]
if c in replace:
rules = replace[c]
for (rn, vals, d, repls, e) in rules:
nVals = len(vals)
if i + nVals > nChars:
# not enough characters left to match this rule
continue
if not all(
(
d is not None
and j == d
and chars[i + j][-1]
in (diacritics if vals[d] == 1 else arabicLetters)
)
or chars[i + j][-1] == vals[j]
for j in range(nVals)
):
# the rule does not match after all
continue
# the rule matches: we are going to fill in the replacements
# if there is a diacritic in the match sequence or the
# replacement sequence, we restrict ourselves to the parts
# before the diacritics.
rulesApplied[rn][pageNum] += 1
nRepls = len(repls)
dEnd = nVals if d is None else d
eEnd = nRepls if e is None else e
# so, we are going to replace from here to dEnd (not including)
for j in range(dEnd):
# put the appropriate replacement character in the
# replacement part of the character record
# After running out of replacement characters, put in ""
chars[i + j][-1] = repls[j] if j < eEnd else ""
if eEnd > dEnd:
# if there are replacement characters left, put them
# in after the last character that we have visited.
if dEnd == 0:
# In case we have not visited any yet,
# we put them in before the current character
cd = chars[i + dEnd][-1]
r = "".join(repls[dEnd + 1 :])
chars[i + dEnd][-1] = f"{r}{cd}"
else:
# this is the normal case
chars[i + dEnd - 1][-1] += "".join(repls[dEnd:eEnd])
# if there is a diacritic in the match sequence
# we are going to perform the rule for the part
# after the diacritic
# Note that the case where d is None and e is not None
# does not occur
if d is not None:
# we set the starting points: just after the diacritics
dStart = d + 1
# if the replacement part does not have a diacritic,
# we have already consumed it, and we start right after it
eStart = nRepls if e is None else e + 1
# we compute the number of characters that still need to be
# matched and to be replaced
dn = nVals - dStart
en = nRepls - eStart
# we perform the replacement analogously to what we did
# for the first part
for j in range(dn):
# put the appropriate replacement character in the
# replacement part of the character record
# After running out of replacement characters, put in ""
chars[i + dStart + j][-1] = (
repls[eStart + j] if eStart + j < nRepls else ""
)
if en > dn:
# if there are replacement characters left, put them
# in after the last character that we have visited.
chars[i + nVals - 1][-1] += "".join(
repls[eStart + dn :]
)
break
# sift out all presentational characters
if doFilter:
trailSpace = False
for (i, char) in enumerate(chars):
c = char[-1]
string = ""
for x in c:
if trailSpace:
if x not in diacriticLike:
if x not in nonLetter:
if string == "" and i > 0:
chars[i - 1][-1] += " "
else:
string += " "
trailSpace = False
hasFinalSpace = x in finalSpace
y = (
normalizeC(x)
if x in presentationalC
else normalizeD(x)
if x in presentationalD
else x
).strip()
space = " " if hasFinalSpace or x in punct else ""
if hasFinalSpace:
finalsApplied[x][pageNum] += 1
string += y
if space:
trailSpace = True
char[-1] = string
if trailSpace:
if chars:
chars[-1][-1] += " "
# add horizontal spacing
theseSpaces = []
spaces[pageNum][ln] = theseSpaces
threshold = None
theseColumns = [threshold, []]
columns[pageNum][ln] = theseColumns
prevLeft = None
prevLeftI = None
for (i, char) in enumerate(chars):
spacing = char[-3]
if spacing:
left = char[0]
right = char[2]
if prevLeft is not None:
prevChar = chars[prevLeftI]
after = prevLeft - right
theAfter = ptRepD(after)
isSpace = theAfter >= SPACE_THRESHOLD
if isSpace:
lastChar = chars[i - 1]
if not lastChar[-1].endswith(" "):
lastChar[-1] += " "
prevChar[-3] = f"⌊{theAfter}⌋" if isSpace else f"«{theAfter}»"
theseSpaces.append((i - 1, theAfter, isSpace))
prevLeft = left
prevLeftI = i
if chars:
chars[-1][-3] = "end"
# change big spaces to emspaces
nSpaces = sum(1 for x in theseSpaces if x[2])
if nSpaces == 1:
threshold = 90
elif nSpaces > 1:
spacesGrowing = sorted(x[1] for x in theseSpaces if x[2])
maxSpace = spacesGrowing[-1]
medialSpace = spacesGrowing[nSpaces // 2]
if maxSpace > 4 * medialSpace:
threshold = maxSpace - medialSpace
if threshold is not None:
theseColumns[0] = threshold
for (i, after, isSpace) in theseSpaces:
if isSpace and after > threshold:
theseColumns[1].append((i, after))
char = chars[i]
char[-1] = char[-1].rstrip(" ") + EMSPACE
# remove space between alef and initial follower,
# provided the alef is the single letter in its word.
# also for the words yeh+alef(final) and mem+alef(final) do:
# insert a space behind the alef(final)
curLen = 0
prevCons = None
pprevCons = None
for (i, char) in enumerate(chars):
c = char[-1]
co = char[-2]
r = ""
isAFinal = isAlefFinal(co)
for x in c:
skip = False
if x == " ":
if curLen == 1: # and prevC in PROCLITICS:
skip = True
curLen = 0
prevCons = None
pprevCons = None
elif x in arabicLetters:
curLen += 1
if 2 <= curLen <= 3 and isAFinal:
if isMeemOrYeh(prevCons) and (curLen == 2 or isWaw(pprevCons)):
x += " "
curLen = 0
prevCons = None
pprevCons = None
pprevCons = prevCons
prevCons = x
if not skip:
r += x
char[-1] = r
# divide lines into columns
emspaces = theseColumns[1]
emspacePositions = {t[0] for t in emspaces}
columnedChars = [[]]
dest = columnedChars[-1]
for (i, char) in enumerate(chars):
if i in emspacePositions:
if char[-1]:
dest.append(char)
columnedChars.append([])
dest = columnedChars[-1]
else:
dest.append(char)
# divide columns into ranges
# and chunk the ranges into words
# and save the word boundary boxes
text = self.text
# text is a dict keyed by pageNum and the values are tuples of line data
# a line datum is a list of columns
# a column is a list of spans
# a span is a pair of a direction char ("l" or "r") plus a list of word data
# a word datum is a string plus a word box
# a word box is a (left, top, right, bottom) tuple
result = []
text.setdefault(pageNum, []).append(result)
prevDir = "r"
# we transform letters into chunks, where each chunk is a pair of
# word material
# punctuation material
outChars = [[], []]
inWord = True
box = [None, None, None, None]
def addWord():
if outChars[0] or outChars[1]:
wordCharsRep = "".join(
outChars[0] if prevDir == "r" else reversed(outChars[0])
)
puncCharsRep = "".join(
outChars[1] if prevDir == "r" else reversed(outChars[1])
)
lastSpan = None if len(result[-1]) == 0 else result[-1][-1]
element = (wordCharsRep, puncCharsRep, tuple(box))
if lastSpan is None or lastSpan[0] != prevDir:
result[-1].append((prevDir, [element]))
else:
result[-1][-1][-1].append(element)
def setBox(char):
for (i, coor) in enumerate(char[0:4]):
if (
(b := box[i]) is None
or (i < 2 and coor < b)
or (i >= 2 and coor > b)
):
box[i] = coor
for chars in columnedChars:
result.append([])
outChars = [[], []]
box = [None, None, None, None]
for char in chars:
c = char[-1]
if c == "":
continue
for d in c:
spaceSeen = d in {" ", EMSPACE}
changeWord = not inWord and d not in nonLetter
if spaceSeen:
outChars[1].append(d)
if spaceSeen or changeWord:
addWord()
box = [None, None, None, None]
outChars = [[d] if changeWord else [], []]
inWord = True
continue
thisDir = prevDir if d in neutrals else "r" if d in rls else "l"
if prevDir != thisDir:
addWord()
box = [None, None, None, None]
outChars = [[], []]
inWord = True
prevDir = thisDir
if inWord:
if d in nonLetter:
inWord = False
dest = 0 if inWord else 1
rep = d
if d in puas:
rep = f"⌊{ord(d):>04x}⌋"
outChars[dest].append(rep)
setBox(char)
addWord()
def plainLine(self, columns):
"""Outputs a processed line as plain text.
Used by `Lakhnawi.plainPages()`.
Parameters
----------
columns: iterable
An iterable of columns that make up a line.
Each column is an iterable of spans.
Spans contain words plus an indication of the writing direction
for that span.
Returns
-------
string
The concatenation of all words in all spans separated by white space.
"""
return "\t".join(
" ".join(
" ".join(f"{word[0]}{word[1]}" for word in span[1]) for span in spans
)
for spans in columns
)
def tsvHeadLine(self):
"""Outputs the field names of a word in TSV data.
See `Lakhnawi.tsvPages()` for the structure of TSV data
as output format for the extracted text of the Lakhnawi PDF.
Returns
-------
string
A tab-separated line of field names.
"""
return "page\tline\tcolumn\tspan\tdirection\tleft\ttop\tright\tbottom\tletters\tpunc\n"
def tsvLine(self, columns, pageNum, ln):
"""Outputs a processed line as lines of tab-separated fields for each word.
Used by `Lakhnawi.tsvPages()`.
Parameters
----------
columns: iterable
An iterable of columns that make up a line.
Each column is an iterable of spans.
Spans contain words plus an indication of the writing direction
for that span.
pageNum: int
The page number of the page where this line occurs.
Returns
-------
string
The concatenation of the TSV lines for all words in all spans
in all columns.
"""
material = []
for (cn, spans) in enumerate(columns):
for (sn, (dr, words)) in enumerate(spans):
for (letters, punc, (le, to, ri, bo)) in words:
material.append(
(
"\t".join(
str(x)
for x in (
pageNum,
ln,
cn + 1,
sn + 1,
dr,
ptRep(le),
ptRep(to),
ptRep(ri),
ptRep(bo),
letters,
punc,
)
)
)
+ "\n"
)
return "".join(material)
def htmlLine(self, columns, prevMulti, isLast):
"""Outputs a processed line as HTML.
Used by `Lakhnawi.htmlPages()`.
Parameters
----------
columns: iterable
An iterable of columns that make up a line.
Each column is an iterable of spans.
Spans contain words plus an indication of the writing direction
for that span.
prevMulti: boolean
Whether the preceding line has multiple columns.
isLast: boolean
Whether this line is the last line on the page.
Returns
-------
string
The concatenation of the TSV lines for all words in all spans
in all columns.
"""
showSpaces = self.showSpaces
result = []
nCols = len(columns)
multi = nCols > 1
if prevMulti and not multi:
result.append("</table>\n")
elif not prevMulti and multi:
result.append("""<table class="linecols">\n""")
if multi:
result.append("<tr>\n")
for spans in columns:
result.append(
f"""\t<td class="cols col{nCols}">""" if multi else """<p class="r">"""
)
for (textDir, words) in spans:
result.append(f"""<span class="{textDir}">""")
for word in words:
letters = normalizeD(word[0])
letters = letters.replace("⌊", """<span class="p">""").replace(
"⌋", "</span>"
)
if showSpaces:
letters = f"""<span class="box">{letters}</span>"""
punc = word[1]
if showSpaces:
punc = punc.replace(" ", """<span class="sp"> </span>""")
result.append(f"{letters}{punc}")
result.append("""</span>""")
result.append("</td>\n" if multi else "</p>\n")
if multi:
result.append("</tr>\n")
if isLast:
result.append("</table>\n")
return "".join(result)
def clusterVert(self, data):
"""Cluster characters into lines based on their bounding boxes.
Most characters on a line have their middle line in approximately the same height.
But diacritics of characters in that line may occupy different heights.
Without intervention, these would be clustered on separate lines.
We take care to cluster them into the same lines as their main characters.
It involves getting an idea of the regular line height, and clustering boxes
that fall between the lines with the line above or below, whichever is closest.
The result of the clustering is delivered as a key function, which will
be used to sort characters.
Parameters
----------
data: iterable of record
The character records
Returns
-------
function
A key function that assigns to each character record a value
that corresponds to the vertical position of a real line,
which is a clustered set of characters.
The information on the vertical clustering of lines
is delivered in the attributes `Lakhnawi.heights` and
`Lakhnawi.clusteredHeights`, on a page by page basis.
"""
pageNum = self.pageNum
heights = collections.Counter()
for char in data:
k = keyCharV(char)
heights[k] += 1
peaks = sorted(heights)
if len(peaks) > 1:
nDistances = len(peaks) - 1
distances = sorted(peaks[i + 1] - peaks[i] for i in range(nDistances))
# remove the biggest distances if > 50,
# to prevent outliers pulling the average too high
for _ in range(2):
if len(distances) > 1:
if distances[-1] > 50:
distances = distances[0:-1]
# remove distances < 15, which are much smaller than a line
distances = [d for d in distances if d > 15]
nDistances = len(distances)
avPeakDist = sum(distances) / nDistances
peakThreshold = avPeakDist * LINE_CLUSTER_FACTOR
clusteredHeights = {}
for (k, n) in sorted(heights.items(), key=lambda x: (-x[1], x[0])):
added = False
for kc in clusteredHeights:
if abs(k - kc) <= peakThreshold:
clusteredHeights[kc].add(k)
added = True
break
if not added:
clusteredHeights[k] = {k}
toCluster = {}
for (kc, ks) in clusteredHeights.items():
for k in ks:
toCluster[k] = kc
self.heights[pageNum] = heights
self.clusteredHeights[pageNum] = clusteredHeights
def clusterKeyCharV(char):
k = keyCharV(char)
return toCluster[k]
return clusterKeyCharV
def keyCharV(char):
"""The vertical position of the middle of a character.
Used to sort the characters of a page in the vertical direction.
Parameters
----------
char: record
Returns
-------
float
The height of the middle of the character.
"""
return (char[3] + char[1]) / 2
def keyCharH(char):
"""Sort key to sort the characters of a line horizontally.
Basically, characters whose right edge are closer to the right edge of the page
come before characters whose right edges are further left.
So we could sort on minus the x coordinate of the right edge.
However, there are complications. Sometimes characters have the same right edge.
Diacritics usually start right
after the letter they are on together with the next letter.
So they should come before that next letter.
In those cases we take the width into account.
Private use diacritics usually have a big width, they are wider than letters.
So if we sort wider characters before narrower characters, we get that right.
However, normal unicode diacritics have a typical width of zero, and also
these should come before the next letter.
We can solve that by sorting by a key defined as 1 divided by the width
if the width is nonzero, and 0 if the the width is zero.
Then zero width characters come first, then wide characters, then narrow characters.
One extra complication: the widths are not integers but fractions.
Sometimes a the diacritic and the next letter have an almost equal right edge,
but not quite equal, and the wrong one comes first.
We can solve that by rounding.
Parameters
----------
char: record
Returns
-------
(int, float)
"""
width = abs(int(round(char[2] - char[0])))
widthKey = (1 / width) if width else 0
rightKey = int(round(char[2]))
return (-rightKey, widthKey)Global variables
var CSS-
Styles to render extracted text.
The styles are chosen such that the extracted text looks as similar as possible to the PDF display.
var FNRULE_WIDTH-
Width of the rule that separates body text from footnote text.
var LETTER_CODE_DEF-
Defines place holder
din rule definitions. var POST_HTML-
HTML code postfixed to the HTML representation of a page.
var REPLACE_DEF-
Character replace rules
There are two parts: (1) character replace rules (2) notes.
Each rule consists of a left hand side, then
=>, then a right hand side, then:and then a short description. The short description may contain references to notes in the notes section, which is a list of commented lines at the end of the whole string.The left and right hand sides consist of one or more hexadecimal character codes, joined by the
+sign.The meaning is that when the left hand side matches a portion of the input text, the output text, which is otherwise a copy of the input text, will have that portion replaced by the right hand side.
The exact application of rules has some subtleties which will be dealt with in
Laknawi.trimLine. var SPACE_THRESHOLD-
Amount of separation between words.
Character boxes this far apart imply that there is a white space between them. The unit is 0.1 pixel.
Functions
def getDictFromDef(defs)-
Interpret a string as a dictionary.
Parameters
defs:string- A string containing definitions of character replace rules.
Only for rules
We only use this functions for the rules in
REPLACE_DEF.Expand source code Browse git
def getDictFromDef(defs): """Interpret a string as a dictionary. Parameters ---------- defs: string A string containing definitions of character replace rules. !!! note "Only for rules" We only use this functions for the rules in `REPLACE_DEF`. """ rules = [] rn = 0 good = True for (i, line) in enumerate(defs.strip().split("\n")): parts = line.split("#", maxsplit=1) if len(parts) > 1: line = parts[0] line = line.strip() if not line: continue match = REPLACE_RE.match(line) if not match: print(f"MALFORMED REPLACE DEF @{i}: {line}") good = False continue rn += 1 (valStr, replStr, comment) = match.group(1, 2, 3) vals = [] d = None for (i, val) in enumerate(valStr.split("+")): if val in {"d"}: if d is not None: print(f"MULTIPLE d in RULE @{i}: rule {rn}: {line}") good = False d = i vals.append(LETTER_CODE[val]) else: vals.append(chr(int(val, base=16))) repls = [] e = None if replStr: for (i, repl) in enumerate(replStr.split("+")): if repl in {"d"}: if e is not None: print(f"MULTIPLE d in RULE @{i}: rule {rn}: {line}") good = False e = i repls.append(LETTER_CODE[repl]) else: repls.append(chr(int(repl, base=16))) if d is None and e is not None: print(f"d in REPLACEMENT but not in MATCH @[i]: rule {rn}: {line}") good = False rules.append((rn, tuple(vals), d, tuple(repls), e)) if not good: return None result = {} ruleIndex = {} for (rn, vals, d, repls, e) in sorted(rules, key=lambda x: (-len(x[1]), str(x[1]))): result.setdefault(vals[0], []).append((rn, vals, d, repls, e)) ruleIndex[rn] = (vals, d, repls, e) return (result, ruleIndex) def getToc(pageNums)-
Generate a Table Of Contents for multiple HTML pages.
Parameter
pageNums: iterable if int The page numbers of the pages in the HTML file.
Expand source code Browse git
def getToc(pageNums): """Generate a Table Of Contents for multiple HTML pages. Parameter --------- pageNums: iterable if int The page numbers of the pages in the HTML file. """ limit = 60 html = [] html.append("""<div class="toc">""") j = 0 for (i, pageNum) in enumerate(pageNums): if j == limit: j = 0 html.append("""</div>\n<div class="toc">""") html.append(f"""<a href="#p{pageNum:>03}">p {pageNum}</a><br>""") j += 1 html.append("""</div>""") return "\n".join(html) def keyCharH(char)-
Sort key to sort the characters of a line horizontally.
Basically, characters whose right edge are closer to the right edge of the page come before characters whose right edges are further left.
So we could sort on minus the x coordinate of the right edge.
However, there are complications. Sometimes characters have the same right edge.
Diacritics usually start right after the letter they are on together with the next letter.
So they should come before that next letter. In those cases we take the width into account.
Private use diacritics usually have a big width, they are wider than letters. So if we sort wider characters before narrower characters, we get that right.
However, normal unicode diacritics have a typical width of zero, and also these should come before the next letter.
We can solve that by sorting by a key defined as 1 divided by the width if the width is nonzero, and 0 if the the width is zero.
Then zero width characters come first, then wide characters, then narrow characters.
One extra complication: the widths are not integers but fractions.
Sometimes a the diacritic and the next letter have an almost equal right edge, but not quite equal, and the wrong one comes first.
We can solve that by rounding.
Parameters
char:record
Returns
(int, float)
Expand source code Browse git
def keyCharH(char): """Sort key to sort the characters of a line horizontally. Basically, characters whose right edge are closer to the right edge of the page come before characters whose right edges are further left. So we could sort on minus the x coordinate of the right edge. However, there are complications. Sometimes characters have the same right edge. Diacritics usually start right after the letter they are on together with the next letter. So they should come before that next letter. In those cases we take the width into account. Private use diacritics usually have a big width, they are wider than letters. So if we sort wider characters before narrower characters, we get that right. However, normal unicode diacritics have a typical width of zero, and also these should come before the next letter. We can solve that by sorting by a key defined as 1 divided by the width if the width is nonzero, and 0 if the the width is zero. Then zero width characters come first, then wide characters, then narrow characters. One extra complication: the widths are not integers but fractions. Sometimes a the diacritic and the next letter have an almost equal right edge, but not quite equal, and the wrong one comes first. We can solve that by rounding. Parameters ---------- char: record Returns ------- (int, float) """ width = abs(int(round(char[2] - char[0]))) widthKey = (1 / width) if width else 0 rightKey = int(round(char[2])) return (-rightKey, widthKey) def keyCharV(char)-
The vertical position of the middle of a character.
Used to sort the characters of a page in the vertical direction.
Parameters
char:record
Returns
float- The height of the middle of the character.
Expand source code Browse git
def keyCharV(char): """The vertical position of the middle of a character. Used to sort the characters of a page in the vertical direction. Parameters ---------- char: record Returns ------- float The height of the middle of the character. """ return (char[3] + char[1]) / 2 def preHtml(pageNum)-
Generate HTML code to be prefixed to the HTML representation of a page.
Parameters
pageNum:string- The page number of the page for which HTML is generated.
Expand source code Browse git
def preHtml(pageNum): """Generate HTML code to be prefixed to the HTML representation of a page. Parameters ---------- pageNum: string The page number of the page for which HTML is generated. """ return f"""\ <html> <head> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"/> <meta charset="utf-8"/> <title>Lakhnawi {pageNum}</title> {CSS} </head> <body> """ def ptRep(p)-
Represent a float as an integer.
Parameters
p:float- We round it to the nearest integer.
A none value is converted to
?.
Expand source code Browse git
def ptRep(p): """Represent a float as an integer. Parameters ---------- p: float We round it to the nearest integer. A none value is converted to `?`. """ return "?" if p is None else int(round(p)) def ptRepD(p)-
Represent a float as an integer with enhanced precision.
Parameters
p:float- We multiply it by 10, then round it to the nearest integer.
A none value is converted to
?.
Expand source code Browse git
def ptRepD(p): """Represent a float as an integer with enhanced precision. Parameters ---------- p: float We multiply it by 10, then round it to the nearest integer. A none value is converted to `?`. """ return "?" if p is None else int(round(p * 10))
Classes
class Lakhnawi-
Text extraction from the Lakhnawi PDF.
This class makes use of the
UCharclass which defines several categories of characters. By extending that class, the Lakhnawi class makes use of those categories. It also adds specific characters to some of those categories, especially the private use characters that occur in the Lakhnawi PDF.We use fitz (
pip3 install PyMuPDF) for PDF reading.Expand source code Browse git
class Lakhnawi(UChar): def __init__(self): """Text extraction from the Lakhnawi PDF. This class makes use of the `fusus.char.UChar` class which defines several categories of characters. By extending that class, the Lakhnawi class makes use of those categories. It also adds specific characters to some of those categories, especially the private use characters that occur in the Lakhnawi PDF. We use *fitz* (`pip3 install PyMuPDF`) for PDF reading. """ super().__init__() self.heights = {} """Heights of characters, indexed by page number.""" self.clusteredHeights = {} """Clustered heights of characters, indexed by page number. The clustered heights correspond to the lines on a page. """ self.lines = {} """Lines as tuples of original character objects, indexed by page number""" self.text = {} """Lines as tuples of converted character objects, indexed by page number""" self.fnRules = {} """Vertical positions of footnote lines, indexed by page number""" self.spaces = {} """Spacing information for each character, indexed by page and line number. For character that has space behind it, it gives the index position of that character in the line, the amount of space detected, and whether this counts as a full white space. """ self.columns = {} """Column information, indexed by page and line number. Spaces that are significantly larger than a normal white space are interpreted as an emspace, and these are considered as column separators. We remember the character positions where this happens plus the amount of space in question. Columns in the Lakhnawi PDF correspond to *hemistic* poems, where lines are divided into two halves, each occupying a column. See  !!! caution "hemistic poems versus blocks" This is very different from blocks (see `fusus.layout`) in OCRed texts, where blocks have been detected because of vertical strokes that separate columns. The reading progress in a hemistic poem is not changed by the column division, where as in the case of blocks, reading proceeds by reading the complete blocks in order. """ self.doubles = {} """Glyphs with double unicode points. Some private use characters have two unicode points assigned to them by fonts in the PDF. This is the cause that straightforward text extractions deliver double occurrences of those letters. Even *fitz* does that. We have collected these cases, and choose to use the lower unicode point, which is usually an ordinary character, whereas the other is usually a related presentational character. This dictionary maps the lower character to the higher character. """ self.privateLetters = None """Private-use unicodes that correspond to full letters.""" self.privateDias = None """Private-use unicodes that correspond to diacritics.""" self.privateSpace = None """Private-use-unicode used to represent a space.""" self.good = True """Whether processing is still ok, i.e. no errors encountered.""" self.getCharConfig() self.doc = fitz.open(SOURCE) """A handle to the PDF document, after it has been read by *fitz*.""" def close(self): """Close the PDF handle, offered by *fitz*.""" self.doc.close() def setStyle(self): """Import the CSS styles into the notebook. See `CSS`. """ display(HTML(CSS)) def getCharConfig(self): """Configure all character information. Private-use characters, transformation rules, character categories. """ self.privateInfo() self.setupRules() self.getCharInfo() def privateInfo(self): """Set up additional character categories wrt. private-use characters. Several categories will receive additional members from the private use characters. """ self.privateLetters = getSetFromDef(PRIVATE_LETTERS_DEF) self.privateDias = getSetFromDef(PRIVATE_DIAS_DEF) self.privateSpace = PRIVATE_SPACE self.nospacings |= self.privateDias # self.nospacings.add(PRIVATE_TATWEEL) self.diacritics |= self.privateDias self.diacriticLike |= self.privateDias self.arabicLetters = self.arabic - self.privateDias self.rls |= self.puas def setupRules(self): """Set up character transformation rules. Prepare for counting how much rules will be applied when extracting text from pages of the Lakhnawi PDF. """ (self.replace, self.ruleIndex) = getDictFromDef(REPLACE_DEF) if self.replace is None: self.replace = {} self.good = False self.rulesApplied = collections.defaultdict(collections.Counter) for rn in self.ruleIndex: self.rulesApplied[rn] = collections.Counter() def getCharInfo(self): """Obtain detailed character information by reading the font report file. From this file we read: * which are the private use characters? * which of them have a double unicode? The font file is [here](https://github.com/among/fusus/blob/master/ur/Lakhnawi/FontReport-Lakhnawi.pdf). """ self.doubles = {} self.privates = set() doubles = self.doubles privates = self.privates finalSpace = self.finalSpace puas = self.puas doc = fitz.open(FONT) for page in doc: textPage = page.getTextPage() data = textPage.extractText() for (ln, line) in enumerate(data.split("\n")): if line.startswith("U+"): match = U_LINE_RE.match(line) if not match: continue (main, rest) = match.group(1, 2) main = main.lower() nMain = int(main, base=16) cMain = chr(nMain) if cMain in puas: privates.add(cMain) continue if cMain == chr(0): continue second = None rest = rest.replace(" ", "") if rest: if HEX_RE.match(rest): second = rest.lower() if second: nSecond = int(second, base=16) cSecond = chr(nSecond) if nSecond > nMain: doubles[cMain] = cSecond else: doubles[cSecond] = cMain doublesApplied = collections.defaultdict(collections.Counter) for d in doubles: doublesApplied[d] = collections.Counter() self.doublesApplied = doublesApplied finalsApplied = collections.defaultdict(collections.Counter) for f in finalSpace: finalsApplied[f] = collections.Counter() self.finalsApplied = finalsApplied def plainChar(self, c): """Show the character code of a character. Parameters ---------- c: string The character in question, may also be the empty string or the integer 1 (diacritic place holder). Returns ------- string The hexadecimal unicode point of `c`, between `⌊ ⌋` - brackets. """ if c == "": return "⌊⌋" if c in {1}: return CODE_LETTER[c] return f"⌊{ord(c):>04x}⌋" def plainString(self, s): """Show the character codes of the characters in a string. Parameters ---------- s: string The string to show, may be empty, may contain place holders. Returns ------- string The concatenation of the unicode points of the characters in the string, each code point between brackets. See also `Lakhnawi.plainChar()`. """ return " ".join(self.plainChar(c) for c in s) def showChar(self, c): """Pretty display of a single unicode character. We show the character itself and its name (if not a private-use one), its hexadecimal code, and we indicate by coloring the kind of white space that the character represents (ordinary space or emspace). Parameters ---------- c: string The character in question, may also be the empty string or the integer 1 (diacritic place holder). """ if c in {1, 2}: return f""" <div class="ch p"> <div class="cn">{LETTER_KIND[c]}</div> </div> """ if c == "": extra = "" ccode = "" crep = "\u00a0" cname = "EMPTY" else: puas = self.puas rls = self.rls ccode = ( f"""<span class="{"p" if c in puas else "c"}">{ord(c):>04x}</span>""" ) crep = ( "??" if c in puas else f"""<span class="{"rc" if c in rls else "lc"}">{c}""" ) cname = "" if c in puas else f"""<span class="c">{uName(c)}</span>""" extra = ( "m" if c == EMSPACE else "s" if c == " " else "" ) return f""" <div class="ch{extra}"> <div class="cn">{ccode}</div> <div class="cn"><span class="cni">{crep}</span></div> <div class="cn">{cname}</div> </div> """ def showString(self, s, asString=False): """Pretty display of a string as a series of unicode characters. Parameters ---------- s: string The string to display, may be empty, may contain place holders. asString: boolean, optional `False` If True, return the result as an HTML string. Returns ------- None | string If `asString`, returns an HTML string, otherwise returns None, but displays the HTML string. See also `Lakhnawi.showChar()`. """ shtml = f"""<span class="r">{s}</span>""" html = """<div class="sr">""" + ( "".join(self.showChar(c) for c in s) + "</div>" ) if asString: return f"""<span>{shtml}</span>{html}""" display(HTML(f"""<p>{shtml}</p>{html}""")) def showReplacements(self, rule=None, isApplied=False): """Show a character conversion rule and how it has been applied. Parameters ---------- rule: string|int, optional `None` A specification of zero or more rule numbers (see `fusus.lib.parseNums`). If None, all rules will be taken. isApplied: boolean, optional `False` Only show rules that have been applied. Returns ------- None Displays a table of rules with usage statistics. """ ruleIndex = self.ruleIndex rulesApplied = self.rulesApplied ruleNums = parseNums(rule) ruleNums = ( set(ruleIndex) if ruleNums is None else sorted(r for r in ruleNums if r in ruleIndex) ) html = [] totalRules = len(ruleIndex) totalApplications = sum(sum(x.values()) for x in rulesApplied.values()) totalPages = len(set(chain.from_iterable(rulesApplied.values()))) ruleRep = "rule" + ("" if totalRules == 1 else "s") appRep = "application" + ("" if totalApplications == 1 else "s") pageRep = "page" + ("" if totalPages == 1 else "s") html.append( f""" <p><b>{totalRules} {ruleRep} with {totalApplications} {appRep} on {totalPages} {pageRep}</b></p> <table> """ ) for (rn, applied) in sorted( rulesApplied.items(), key=lambda x: (-sum(x[1].values()), x[0]) ): if rn not in ruleNums: continue (vals, d, repls, e) = ruleIndex[rn] valRep = "".join(self.showChar(c) for c in vals) replRep = "".join(self.showChar(c) for c in repls) total = sum(applied.values()) if isApplied and not applied: continue if applied: examplePageNum = sorted(applied, key=lambda p: -applied[p])[0] nExamples = applied[examplePageNum] appliedEx = f"e.g. page {examplePageNum} with {nExamples} applications" else: appliedEx = "" appliedRep = f"<b>{total}</b> x applied on <i>{len(applied)}</i> pages" html.append( f""" <tr> <th>rule {rn}</th> <td class="al">{appliedRep}</td> <td class="al">{appliedEx}</td> <td class="al">{valRep}</td> <td class="al"><span class="lrg">⇒</span></td> <td class="al">{replRep}</td> </tr> """ ) html.append("<table>") display(HTML("".join(html))) def showDoubles(self, double=None): """Show a character with double entry and how often it occurs. See `Lakhnawi.doubles`. Parameters ---------- double: char, optional `None` A character from the doubles list (`Lakhnawi.doubles`). If None, all such characters will be taken. isApplied: boolean, optional `False` Only show rules that have been applied. Returns ------- None Displays a table of double-entry characters with occurrence statistics. """ doubles = self.doubles doublesApplied = self.doublesApplied theseDoubles = ( set(doubles) if double is None else {double} if double in doubles else set() ) html = [] totalDoubles = len(doubles) totalApplications = sum(sum(x.values()) for x in doublesApplied.values()) totalPages = len(set(chain.from_iterable(doublesApplied.values()))) doubleRep = "double" + ("" if totalDoubles == 1 else "s") appRep = "application" + ("" if totalApplications == 1 else "s") pageRep = "page" + ("" if totalPages == 1 else "s") html.append( f""" <p><b>{totalDoubles} {doubleRep} with {totalApplications} {appRep} on {totalPages} {pageRep}</b></p> <table> """ ) for (d, applied) in sorted( doublesApplied.items(), key=lambda x: (-sum(x[1].values()), x[0]) ): if d not in theseDoubles: continue e = doubles[d] doubleRep = f"{self.showChar(e)} ⇒ {self.showChar(d)}" total = sum(applied.values()) if applied: examplePageNum = sorted(applied, key=lambda p: -applied[p])[0] nExamples = applied[examplePageNum] appliedEx = f"e.g. page {examplePageNum} with {nExamples} applications" else: appliedEx = "" appliedRep = f"<b>{total}</b> x applied on <i>{len(applied)}</i> pages" html.append( f""" <tr> <td class="al">{appliedRep}</td> <td class="al">{appliedEx}</td> <td class="al">{doubleRep}</td> </tr> """ ) html.append("<table>") display(HTML("".join(html))) def showFinals(self, final=None): """Show a character with final form and how often it has been replaced. Final forms will be normalized to ground forms and sometimes a space will be added. Parameters ---------- final: char, optional `None` A character from the final space list (`fusus.char.UChar.finalSpace`). If None, all such characters will be taken. isApplied: boolean, optional `False` Only show rules that have been applied. Returns ------- None Displays a table of final space characters with occurrence statistics. """ finalSpace = self.finalSpace finalsApplied = self.finalsApplied theseFinals = ( finalSpace if final is None else {final} if final in finalSpace else set() ) html = [] totalFinals = len(finalSpace) totalApplications = sum(sum(x.values()) for x in finalsApplied.values()) totalPages = len(set(chain.from_iterable(finalsApplied.values()))) finalRep = "final" + ("" if totalFinals == 1 else "s") appRep = "application" + ("" if totalApplications == 1 else "s") pageRep = "page" + ("" if totalPages == 1 else "s") html.append( f""" <p><b>{totalFinals} {finalRep} with {totalApplications} {appRep} on {totalPages} {pageRep}</b></p> <table> """ ) for (f, applied) in sorted( finalsApplied.items(), key=lambda x: (-sum(x[1].values()), x[0]) ): if f not in theseFinals: continue finalRep = self.showChar(f) total = sum(applied.values()) if applied: examplePageNum = sorted(applied, key=lambda p: -applied[p])[0] nExamples = applied[examplePageNum] appliedEx = f"e.g. page {examplePageNum} with {nExamples} applications" else: appliedEx = "" appliedRep = f"<b>{total}</b> x applied on <i>{len(applied)}</i> pages" html.append( f""" <tr> <td class="al">{appliedRep}</td> <td class="al">{appliedEx}</td> <td class="al">{finalRep}</td> </tr> """ ) html.append("<table>") display(HTML("".join(html))) def showLineHeights(self, pageNumSpec): """Shows how line heights have been determined. The pages can be selected by page numbers. Parameters ---------- pageNumSpec: None | int | string | iterable As in `Lakhnawi.parsePageNums()`. """ heights = self.heights clusteredHeights = self.clusteredHeights for pageNum in self.parsePageNums(pageNumSpec): theseHeights = heights[pageNum] theseClusteredHeights = clusteredHeights[pageNum] print(f"Line heights page {pageNum:>3}") print("\nraw heights") for k in sorted(theseHeights): print(f"{theseHeights[k]:>4} characters @ height {int(round(k)):>4}") print("line heights") for (ln, kc) in enumerate(sorted(theseClusteredHeights)): peak = ", ".join( f"{int(round(k)):>4}" for k in sorted(theseClusteredHeights[kc]) ) print( f"line {ln + 1:>2}: " f"{sum(theseHeights[k] for k in theseClusteredHeights[kc]):>4}" f" characters @height {peak}" ) def parsePageNums(self, pageNumSpec): """Parses a value as one or more page numbers. Parameters ---------- pageNumSpec: None | int | string | iterable If `None` results in all page numbers. If an `int`, it stands for that int. If a `string`, it is allowed to be a comma separated list of numbers or ranges, where a range is a lower bound and an upper bound separated by a `-`. If none of these, it should be an iterable of `int` values. Returns ------- None | iterable of int Depending on the value. """ doc = self.doc pageNums = ( list(range(1, len(doc) + 1)) if not pageNumSpec else [pageNumSpec] if type(pageNumSpec) is int else setFromSpec(pageNumSpec) if type(pageNumSpec) is str else list(pageNumSpec) ) return [i for i in sorted(pageNums) if 0 < i <= len(doc)] def drawPages(self, pageNumSpec, clip=None): """Draws a (part) of page from the PDF as a raster image. Parameters ---------- pageNumSpec: None | int | string | iterable As in `Lakhnawi.parsePageNums()`. clip: (int, int), optional `None` If None: produces the whole page. Otherwise it is `(top, bottom)`, and a stripe from top to bottom will be displayed. """ doc = self.doc for pageNum in self.parsePageNums(pageNumSpec): page = doc[pageNum - 1] if clip is not None: clip = (0, clip[0], page.rect.width, clip[1]) pix = page.getPixmap(matrix=fitz.Matrix(4, 4), clip=clip, alpha=False) display(HTML(f"""<p><b>page {pageNum}</b></p>""")) display(Image(data=pix.getPNGData(), format=DEFAULT_EXTENSION)) def getPages( self, pageNumSpec, refreshConfig=False, doRules=True, doFilter=True, onlyFnRules=False, ): """Reads pages of the PDF and extracts text. This does all of the hard work of the text extraction. It saves the textual data in attributes of the Lakhnawi object, augmented with all kinds of diagnostic information. From all this data, various output representations can be generated rather easily by other methods. Parameters ---------- pageNumSpec: None | int | string | iterable As in `Lakhnawi.parsePageNums()`. refreshConfig: boolean, optional `False` If `True`, rereads all character configuration. Ideal when you are iteratively developing the character configuration. doRules: boolean, optional `True` If `False`, suppresses the application of character transformation rules. Mainly used when debugging other aspects of the text extraction. doFilter: boolean, optional `True` If `False`, suppresses the application of unicode normalization, by which presentational characters are transformed into sequences of ordinary, basic characters. Used for debugging. onlyFnRules: boolean, optional `False` If `True`, skips most of the conversion. Only determine where the footnote rules are. Used for debugging. Returns ------- None The effect is that attributes of the Lakhnawi object are filled: * `Lakhnawi.heights` * `Lakhnawi.clusteredHeights` * `Lakhnawi.fnRules` For the other attributes, see `Lakhnawi.collectPage()`. !!! hint "multiple runs" If you do multiple runs of this function for different pages, the results will not overwrite each other in general, because the attributes hold the results in dictionaries keyed by page number. """ if not self.good: print("SKIPPING because of config errors") return fnRules = self.fnRules spaces = self.spaces columns = self.columns self.doRules = doRules self.doFilter = doFilter ruleIndex = self.ruleIndex rulesApplied = self.rulesApplied if refreshConfig: self.getCharConfig() for rn in ruleIndex: rulesApplied[rn] = collections.Counter() for (i, pageNum) in enumerate(self.parsePageNums(pageNumSpec)): self.pageNum = pageNum rep = ( f"{i + 1:>4} (page {pageNum:>4})" if pageNum != i + 1 else (f"{i + 1:>4}" + " " * 12) ) sys.stdout.write(f"\r\t{rep}") sys.stdout.flush() doc = self.doc page = doc[pageNum - 1] theseFnRules = set() for fnRule in page.getDrawings(): if RECT in fnRule and fnRule.get(COLOR, None): rect = fnRule[RECT] width = rect.x1 - rect.x0 if width > FNRULE_WIDTH: theseFnRules.add(int(round(rect.y1))) fnRules[pageNum] = tuple(sorted(theseFnRules)) spaces[pageNum] = {} columns[pageNum] = {} if onlyFnRules: continue textPage = page.getTextPage() data = textPage.extractRAWDICT() self.collectPage(data) def getPageRaw(self, pageNum): """Do a rough/raw text extract of a specific page. The *fitz* method [extractRAWDICT()](https://pymupdf.readthedocs.io/en/latest/textpage.html#TextPage.extractRAWDICT) is used to obtain very detailed information about each character on that page. Used for debugging. Parameters ---------- pageNum: int A valid page number. It is the sequence number of the page within the PDF, counting from 1. Returns ------- None It pretty prints the output of the fitz method, which is a big and deep dictionary. """ self.pageNum = pageNum rep = f"page {pageNum:>4}" sys.stdout.write(f"{rep}") sys.stdout.flush() doc = self.doc page = doc[pageNum - 1] textPage = page.getTextPage() data = textPage.extractRAWDICT() pprint(data) def getPageObj(self, pageNum): """Get the *fitz* object for a specific page. Used for debugging. Parameters ---------- pageNum: int A valid page number. It is the sequence number of the page within the PDF, counting from 1. Returns ------- object A *fitz* [page object](https://pymupdf.readthedocs.io/en/latest/page.html) """ self.pageNum = pageNum doc = self.doc return doc[pageNum - 1] def plainPages(self, pageNumSpec): """Outputs processed pages as plain text. Uses `Lakhnawi.plainLine()`. Parameters ---------- pageNumSpec: None | int | string | iterable As in `Lakhnawi.parsePageNums()`. Returns ------- None The plain text is printed to the output. """ text = self.text for pageNum in self.parsePageNums(pageNumSpec): lines = text.get(pageNum, []) for (i, line) in enumerate(lines): print(self.plainLine(line)) def tsvPages(self, pageNumSpec): """Outputs processed pages as tab-separated data. See `fusus.convert` for the details of the output format. Uses `Lakhnawi.tsvLine()`. and `Lakhnawi.tsvHeadLine()`. Parameters ---------- pageNumSpec: None | int | string | iterable As in `Lakhnawi.parsePageNums()`. Returns ------- None The tab-separated data is written to a single tsv file. There is a heading row. The file is in `fusus.parameters.UR_DIR`, under `Lakhnawi`. The name of the file includes a page specification. """ text = self.text destDir = f"{UR_DIR}/{NAME}" pageNums = self.parsePageNums(pageNumSpec) if not os.path.exists(destDir): os.makedirs(destDir, exist_ok=True) pageNumRep = ALL_PAGES if pageNumSpec is None else str(pageNumSpec) filePath = f"{destDir}/{pageNumRep}.tsv" fh = open(filePath, "w") fh.write(self.tsvHeadLine()) for pageNum in pageNums: lines = text.get(pageNum, []) for (ln, line) in enumerate(lines): fh.write(self.tsvLine(line, pageNum, ln + 1)) fh.close() print(f"TSV data written to {unexpanduser(filePath)}") def htmlPages( self, pageNumSpec, line=None, showSpaces=False, export=False, singleFile=False, toc=False, ): """Outputs processed pages as formatted HTML pages. Uses `Lakhnawi.htmlLine()`. The HTML output is suitable to read the extracted text. Its layout matches the original closely, which makes it easier to see where the output deviates from the source page. Parameters ---------- pageNumSpec: None | int | string | iterable As in `Lakhnawi.parsePageNums()`. line: None | int | string | iterable A specification of zero or more line numbers (see `fusus.lib.parseNums`). showSpaces: boolean, optional `False` If `True`, shows the spaces with a conspicuous coloured background. export: boolean, optional `False` If `True`, writes the HTML results to disk. In this case, the HTML will not be displayed in the notebook. singleFile: boolean, optional `False` Only meaningful is `export=True`. If `True`, writes the output to a single HTML file, otherwise to one file per page, in a directory called `html`. toc: boolean, optional `False` Only meaningful is `export=True` and `singleFile=True`. If `True`, writes a table of contents to the file. The TOC points to every page that is included in the output file. Returns ------- None Depending on `export`, the page is displayed in the notebook where this function is called, or exported to a file on disk. The file is in `fusus.parameters.UR_DIR`, under `Lakhnawi`. The name of the file includes a page specification. """ self.showSpaces = showSpaces text = self.text destDir = f"{UR_DIR}/{NAME}" if singleFile else f"{UR_DIR}/{NAME}/html" pageNums = self.parsePageNums(pageNumSpec) lineNums = parseNums(line) lineNums = None if lineNums is None else set(lineNums) filesWritten = 0 if export: if not os.path.exists(destDir): os.makedirs(destDir, exist_ok=True) if singleFile: pageNumRep = ALL_PAGES if pageNumSpec is None else str(pageNumSpec) tocRep = "-with-toc" if toc else "" filePath = f"{destDir}/{pageNumRep}{tocRep}.html" fh = open(filePath, "w") fh.write(preHtml(f"{pageNumRep}{tocRep}")) if toc: toc = getToc(pageNums) fh.write( f""" <div class="window"> <div class="sidebar"> {toc} </div> <div class="pages bypage"> """ ) else: fh.write( """ <div class="pages"> """ ) pageClass = "page" + ("" if export else "c") for pageNum in pageNums: lines = text.get(pageNum, []) nLines = len(lines) html = [] html.append( f""" <div class="{pageClass}"> <div class="phead"><a name="p{pageNum:>03}">{pageNum}</a></div> """ ) prevMulti = False for (i, line) in enumerate(lines): if lineNums is not None and i + 1 not in lineNums: continue html.append(self.htmlLine(line, prevMulti, i == nLines - 1)) prevMulti = len(line) > 1 html.append("""</div>""") if export: htmlRep = "".join(html) if singleFile: fh.write(htmlRep) else: html = preHtml(pageNum) + htmlRep + POST_HTML filePath = f"{destDir}/p{pageNum:>03}.html" with open(filePath, "w") as fh: fh.write(html) filesWritten += 1 else: display(HTML("\n".join(html))) if export and singleFile: fh.write( """ </div> """ ) if toc: fh.write( """ </div> """ ) fh.write(POST_HTML) fh.close() print(f"HTML written to {unexpanduser(filePath)}") if export and not singleFile: print(f"{filesWritten} HTML files written to {unexpanduser(destDir)}/") def showLines( self, pageNumSpec, line=None, start=None, end=None, search=None, orig=False, every=False, ): """Outputs processed lines as a formatted HTML table. The lines can be selected by page numbers and line numbers. Within the selected lines, the characters can be selected by start/end postions, or by characters of interest. All of these indices start at 1. Parameters ---------- pageNumSpec: None | int | string | iterable As in `Lakhnawi.parsePageNums()`. line: None | int | string | iterable A specification of zero or more line numbers (see `fusus.lib.parseNums`). start: integer, optional `None` Starting word position in each line to be output. If `None`, starts at the beginning of each line. end: integer, optional `None` End word position in each line to be output. If `None`, ends at the end of each line. search: string or iterable of char, optional `None` If not none, all characters in `search` are deemed interesting. All occurrences of these characters within the selected lines are displayed, included a small context. orig: boolean, optional `False` Only meaningful if `search` is given. If `True`: the check for interesting characters is done in the original, untranslated characters. Otherwise, interesting characters are looked up in the translated characters. every: boolean, optional `False` Only meaningful if `search` is given. If `True`, when looking for interesting characters, all occurrences will be retrieved, otherwise only the first one. Returns ------- None The output material will be displayed in the notebook. """ lines = self.lines pageNums = self.parsePageNums(pageNumSpec) lineNums = parseNums(line) myLines = {pageNum: lines[pageNum] for pageNum in pageNums if pageNum in lines} html = [] html.append("<table>") html.append( """ <tr> <th>seq</th> <th>top</th> <th>bottom</th> <th>left</th> <th>right</th> <th>spacing</th> <th>font</th> <th>size</th> <th>orig char</th> <th>char</th> </tr> """ ) shift = 5 for (pageNum, pageLines) in myLines.items(): myLineNums = ( range(1, len(pageLines) + 1) if lineNums is None else [ln for ln in lineNums if 0 < ln <= len(pageLines)] ) for ln in myLineNums: chars = pageLines[ln - 1] nChars = len(chars) html.append( f""" <tr> <th colspan=3>page {pageNum}</th> <th colspan=2>line {ln}</th> <th colspan=3>{nChars} characters</th> </tr> """ ) if search is None: ranges = [(max((start or 0) - 1, 0), min(end or nChars, nChars))] else: ranges = [] for (i, char) in enumerate(chars): if search in char[-2 if orig else -1]: occStart = max((i - shift, 0)) occEnd = min((i + shift + 1, nChars)) if ranges and occStart <= ranges[-1][1]: ranges[-1][1] = occEnd else: ranges.append([occStart, occEnd]) if not every: break for (occStart, occEnd) in ranges: for i in range(occStart, occEnd): char = chars[i] (le, to, ri, bo, font, size, spacing, oc, c) = char html.append( f""" <tr> <td><b>{i + 1}</b></td> <td>{ptRepD(to)}</td> <td>{ptRepD(bo)}</td> <td>{ptRepD(le)}</td> <td>{ptRepD(ri)}</td> <td>{spacing}</td> <td>{font}</td> <td>{size}pt</td> <td>{"".join(self.showChar(x) for x in reversed(oc))}</td> <td>{"".join(self.showChar(x) for x in reversed(c))}</td> </tr> """ ) if search and ranges and not every: break html.append("</table>") display(HTML("".join(html))) def showWords(self, pageNumSpec, line=None): """Outputs processed words as a formatted HTML table. The lines can be selected by page numbers and line numbers. All words within the selected lines are put into a table with the same properties as in the TSV data, see `Lakhnawi.tsvPages`. Parameters ---------- pageNumSpec: None | int | string | iterable As in `Lakhnawi.parsePageNums()`. line: None | int | string | iterable A specification of zero or more line numbers (see `fusus.lib.parseNums`). Returns ------- None The output material will be displayed in the notebook. """ text = self.text pageNums = self.parsePageNums(pageNumSpec) lineNums = parseNums(line) myLines = {pageNum: text[pageNum] for pageNum in pageNums if pageNum in text} html = [] html.append("<table>") html.append( """ <tr> <th>page</th> <th>line</th> <th>col</th> <th>span</th> <th>dir</th> <th>left</th> <th>top</th> <th>right</th> <th>bottom</th> <th>letters</th> <th>punc</th> </tr> """ ) for (pageNum, pageLines) in myLines.items(): myLineNums = ( range(1, len(pageLines) + 1) if lineNums is None else [ln for ln in lineNums if 0 < ln <= len(pageLines)] ) for ln in myLineNums: cols = pageLines[ln - 1] for (cn, spans) in enumerate(cols): for (sn, (dr, words)) in enumerate(spans): for (letters, punc, (le, to, ri, bo)) in words: html.append( f""" <tr> <td><b>{pageNum}</b></td> <td><b>{ln}</b></td> <td><i>{cn + 1}</i></td> <td><i>{sn + 1}</i></td> <td><i>{dr}</i></td> <td>{ptRep(le)}</td> <td>{ptRep(to)}</td> <td>{ptRep(ri)}</td> <td>{ptRep(bo)}</td> <td>{self.showString(letters, asString=True)}</td> <td>{self.showString(punc, asString=True)}</td> </tr> """ ) html.append("</table>") display(HTML("".join(html))) def showUsedChars( self, pageNumSpec, orig=False, onlyPuas=False, onlyPresentational=False, long=False, byOcc=False, ): """Show used characters. Gives an overview of character usage, either in the input PDF, or in the text output. Parameters ---------- pageNumSpec: None | int | string | iterable As in `Lakhnawi.parsePageNums()`. orig: boolean, optional `False` If `True`: shows characters of the original PDF. Otherwise, shows characters of the translated output/ onlyPuas: boolean, optional `False` If `True`, the result is restricted to private use characters. onlyPresentational: boolean, optional `False` If `True`, the result is restricted to presentational characters. See `fusus.char.UChar.presentational`. long: boolean, optional `False` If `True`, for each character output the complete list of pages where the character occurs. Otherwise, show only the most prominent pages. byOcc: boolean, optional `False` If `True`, sort the results by first occurrence of the characters. Otherwise, sort the results by unicode code point of the character. Returns ------- None The output material will be displayed in the notebook. """ presentational = self.presentational pageNums = self.parsePageNums(pageNumSpec) text = self.text lines = self.lines puas = self.puas charsOut = collections.defaultdict(collections.Counter) def keyByOcc(c): pageNums = charsOut[c] return -sum(pageNums.values()) sortKey = keyByOcc if byOcc else lambda x: x if orig: lns = {pageNum: lines[pageNum] for pageNum in pageNums if pageNum in lines} for (pageNum, pageLines) in lns.items(): for line in pageLines: for char in line: c = char[-2] if c in puas or ( not onlyPuas and (c in presentational or not onlyPresentational) ): charsOut[c][pageNum] += 1 else: texts = {pageNum: text[pageNum] for pageNum in pageNums if pageNum in text} for (pageNum, pageText) in texts.items(): for line in pageText: for col in line: for span in col: for word in span[1]: letters = word[0] punc = word[1] thesePuas = PUA_RE.findall(letters) for pua in thesePuas: charsOut[chr(int(pua, base=16))][pageNum] += 1 if not onlyPuas: rest = PUA_RE.sub("", f"{letters}{punc}") for c in rest: if not ( onlyPresentational and c not in presentational ): charsOut[c][pageNum] += 1 totalChars = len(charsOut) totalPages = len(set(chain.from_iterable(charsOut.values()))) totalOccs = sum(sum(pns.values()) for pns in charsOut.values()) charRep = "character" + ("" if totalChars == 1 else "s") occRep = "occurence" + ("" if totalOccs == 1 else "s") pageRep = "page" + ("" if totalPages == 1 else "s") label = "private use " if onlyPuas else "" html = [] html.append( f""" <p><b>{totalChars} {label}{charRep} in {totalOccs} {occRep} on {totalPages} {pageRep}</b></p> <table> """ ) for c in sorted(charsOut, key=sortKey): pageNums = charsOut[c] nPageNums = len(pageNums) pageRep = "page" + ("" if nPageNums == 1 else "s") thistotal = sum(pageNums.values()) examplePageNum = sorted(pageNums, key=lambda p: -pageNums[p])[0] nExamples = pageNums[examplePageNum] html.append( f""" <tr> <td class="al">{self.showChar(c)}</td> <td class="al"><b>{thistotal}</b> on <i>{nPageNums}</i> {pageRep}</td> <td class="al">e.g. page {examplePageNum} with <b>{nExamples}</b> occurrences</td> </tr> """ ) if long: for pn in sorted(pageNums): occs = pageNums[pn] html.append( f""" <tr> <td></td> <td class="al"><i>page {pn:>3}</i>: <b>{occs:>3}</b></td> </tr> """ ) html.append("</table>") display(HTML("".join(html))) def showColumns(self, pageNumSpec): """Show used characters. Gives an overview of the columns in each line. The result is a readable, ascii overview of the columns that exists in the lines of the selected pages. It is useful to visually check column detection for many pages. Parameters ---------- pageNumSpec: None | int | string | iterable As in `Lakhnawi.parsePageNums()`. Returns ------- None The output material will be displayed in the notebook. """ pageNums = self.parsePageNums(pageNumSpec) columns = self.columns for pageNum in pageNums: if pageNum not in columns: continue lineInfo = columns[pageNum] multiple = [] for lNum in sorted(lineInfo): (threshold, emspaces) = lineInfo[lNum] nEmspaces = len(emspaces) if threshold is not None and nEmspaces > 0: multiple.append((lNum, threshold, emspaces)) if not len(multiple): print(f"page {pageNum:>3} -") else: print(f"page {pageNum:>3}:") for (lNum, threshold, emspaces) in multiple: nEmspaces = len(emspaces) print(f"\t{lNum:>2}: {'- ' * (nEmspaces + 1)}") def showSpacing(self, pageNumSpec, line=None): """Show where the spaces are. Gives an overview of the white space positions in each line. It is useful to debug the horizontal white space algorithm. Parameters ---------- pageNumSpec: None | int | string | iterable As in `Lakhnawi.parsePageNums()`. line: None | int | string | iterable A specification of zero or more line numbers (see `fusus.lib.parseNums`). Returns ------- None The output material will be displayed in the notebook. """ pageNums = self.parsePageNums(pageNumSpec) lineNums = parseNums(line) lineNums = None if lineNums is None else set(lineNums) spaces = self.spaces for pageNum in pageNums: if pageNum not in spaces: continue print(f"page {pageNum:>3}") lineInfo = spaces[pageNum] for (ln, spaces) in lineInfo.items(): if lineNums is not None and ln not in lineNums: continue print(f"\tline {ln:>2}") for (i, after, isSpace) in spaces: print(f"\t\t{i + 1:>3} {'] [' if isSpace else ']==['} {after}") def collectPage(self, data): """Transforms raw text into proper textual data. Called by `Lakhnawi.getPages()` and delivers its results to attributes of the Lakhnawi object. Here are they * `Lakhnawi.lines` * `Lakhnawi.doubles` * `Lakhnawi.text` They are all dictionaries, keyed by page number first and then by line. Parameters ---------- data: dict as obtained by the [extractRAWDICT()](https://pymupdf.readthedocs.io/en/latest/textpage.html#TextPage.extractRAWDICT) method of *fitz*. Returns ------- None """ doubles = self.doubles doublesApplied = self.doublesApplied pageNum = self.pageNum nospacings = self.nospacings fnRules = self.fnRules bracketMap = self.bracketMap text = self.text fnRule = fnRules.get(pageNum, None) fnRule = fnRule[0] if fnRule else None chars = [] prevChar = None prevFont = None prevSize = None def addChar(): box = prevChar["bbox"] yBot = box[3] # skip chars below the footnote rule, if any if fnRule is not None and yBot > fnRule: return c = prevChar["c"] cr = "" if isEuDigit(c) else c cr = bracketMap.get(cr, cr) chars.append( ( *box, prevFont, prevSize, "" if c in nospacings else True, c, cr, ) ) def collectChars(data, font, size): nonlocal prevChar nonlocal prevFont nonlocal prevSize if type(data) is list: for elem in data: collectChars(elem, font, size) elif type(data) is dict: if "font" in data: font = data["font"] if "size" in data: size = data["size"] if "c" in data: c = data["c"] skip = False if c == " ": skip = True if prevChar is not None: pc = prevChar["c"] if pc in doubles and doubles[pc] == c: skip = True doublesApplied[pc][pageNum] += 1 if c in doubles and doubles[c] == pc: prevChar = data skip = True doublesApplied[c][pageNum] += 1 if not skip: if prevChar is not None: addChar() prevChar = data prevFont = font prevSize = size for (k, v) in data.items(): if type(v) in {list, dict}: collectChars(v, font, size) collectChars(data, None, None) if prevChar is not None: addChar() clusterKeyCharV = self.clusterVert(chars) lines = {} for char in sorted(chars, key=lambda c: (clusterKeyCharV(c), keyCharH(c))): k = clusterKeyCharV(char) lines.setdefault(k, []).append(list(char)) theseLines = list(lines.values()) if theseLines and self.isPageNum(theseLines[0]): theseLines = theseLines[1:] # remove arabic numerals between brackets for chars in theseLines: nChars = len(chars) if not nChars: continue i = 0 while i < nChars: char = chars[i] nextI = i + 1 if char[-1] == "(": found = None for j in range(i + 1, nChars): theChar = chars[j][-1] if theChar == ")": found = j + 1 nextI = found break if isArDigit(theChar): continue nextI = j break if found is not None: for j in range(i, found): chars[j][-1] = "" i = found i = nextI self.lines[pageNum] = tuple( chars for chars in theseLines if not all(c[-1] == "" for c in chars) ) text[pageNum] = [] for (ln, line) in enumerate(self.lines[pageNum]): self.trimLine(pageNum, ln + 1, line) def isPageNum(self, chars): """Checks whether a series of characters represents an arabic number. Parameters ---------- chars: iterable of char reocrds """ return 1 <= len(chars) <= 3 and all(isArDigit(c[-1]) for c in chars) def trimLine(self, pageNum, ln, chars): """Map character sequences to other sequences. Two tasks: 1. Map private use characters to well-known unicode characters 2. Insert space characters where the next character is separated from the previous one. Complications: Diacritical characters are mostly contained in a very wide box that overlaps with the boxes of the other characters. So the diacritical boxes must not be taken into account. Private use characters often come in sequences, so a sequence of characters must be transformed to another sequence. We do the tramsformation before the space insertion, because otherwise we might insert the space at the wrong point. When we transform characters we need to retain the box information, because we still have to insert the space. That's why we have as input a list of character records, where each record is itself a list with box information, orginal character, modified characters and space information. When we transform characters, we modify character records in place. We do not add or remove character records. The last member of a character record is the modified sequence. This can be zero, one, or multiple characters. The second last member is the original character. Initially, the the last and second last member of each record are equal. We call these members the original character and the result string. Space will be appended at the last member of the appropriate character records. The transformations are given as a set of rules. See `REPLACE_DEFS`. A rule consists of a sequence of characters to match and a sequence of characters to replace the match with. We call them the match sequence and the replacement sequence of the rule. For each character in the input list we check which rules have a match sequence that start with this character. Of these rules, we start with the one with the longest match sequence. We then check, by looking ahead, whether the whole match sequence matches the input. For the purposes of matching, we look into the result strings of the character, not to the original characters. This will prevent some rules to be applied after an earlier rule has been applied. This is intentional, and results in a more simple rule set. If there is a match, we walk through all the characters in the input for the length of the match sequence of the rule. For each input character record, we set its replacement string to the corresponding member of the replacement sequence of the rule. If the replacement sequence has run out, we replace with the empty string. If after this process the replacement sequence has not been exhausted, we join the remaining characters in the replacement string and append it after the replacement string of the last input character that we have visited. After succesful application of a rule, we do not apply other rules that would have been applicable at this point. Instead, we move our starting point to the next character record in the sequence and repeat the matching process. It might be that a character is replaced multiple times, for example when it is reached by a rule while looking ahead 3 places, and then later by a different rule looking ahead two places. However, once a character matches the first member of the match sequence of a rule, and the rule matches and is applied, that character will not be changed anymore by any other rule. !!! caution "place holders for diacritics" The following functionality exists in the code, but is not needed anymore to process the Lakhnawi PDF. The match sequence may contain the character `d`, which is a placeholder for a diacritic sign. It will match any diacritic. The replacement sequence of such a rule may or may not contain a `d`. It is an error if the replacement seqience of a rule contains a `d` while its match sequence does not. It is also an error of there are multiple `d`s in a match sequence of a replacement sequence. If so, the working of this rule is effectively two rules: Suppose the rule is x d y => r d s where x, y, r, s are sequences of arbitrary length. If the rule matches the input, then first the rule x => r will be applied at the current position. Then we shift temporarily to the position right after where the d has matched, and apply the rule y => s Then we shift back to the orginal position plus one, and continue applying rules. """ replace = self.replace puas = self.puas neutrals = self.neutrals rls = self.rls rulesApplied = self.rulesApplied spaces = self.spaces columns = self.columns diacritics = self.diacritics punct = self.punct diacriticLike = self.diacriticLike arabicLetters = self.arabicLetters presentationalC = self.presentationalC presentationalD = self.presentationalD finalSpace = self.finalSpace finalsApplied = self.finalsApplied nonLetter = self.nonLetter doRules = self.doRules doFilter = self.doFilter nChars = len(chars) # rule application stage if doRules: for (i, char) in enumerate(chars): c = char[-1] if c in replace: rules = replace[c] for (rn, vals, d, repls, e) in rules: nVals = len(vals) if i + nVals > nChars: # not enough characters left to match this rule continue if not all( ( d is not None and j == d and chars[i + j][-1] in (diacritics if vals[d] == 1 else arabicLetters) ) or chars[i + j][-1] == vals[j] for j in range(nVals) ): # the rule does not match after all continue # the rule matches: we are going to fill in the replacements # if there is a diacritic in the match sequence or the # replacement sequence, we restrict ourselves to the parts # before the diacritics. rulesApplied[rn][pageNum] += 1 nRepls = len(repls) dEnd = nVals if d is None else d eEnd = nRepls if e is None else e # so, we are going to replace from here to dEnd (not including) for j in range(dEnd): # put the appropriate replacement character in the # replacement part of the character record # After running out of replacement characters, put in "" chars[i + j][-1] = repls[j] if j < eEnd else "" if eEnd > dEnd: # if there are replacement characters left, put them # in after the last character that we have visited. if dEnd == 0: # In case we have not visited any yet, # we put them in before the current character cd = chars[i + dEnd][-1] r = "".join(repls[dEnd + 1 :]) chars[i + dEnd][-1] = f"{r}{cd}" else: # this is the normal case chars[i + dEnd - 1][-1] += "".join(repls[dEnd:eEnd]) # if there is a diacritic in the match sequence # we are going to perform the rule for the part # after the diacritic # Note that the case where d is None and e is not None # does not occur if d is not None: # we set the starting points: just after the diacritics dStart = d + 1 # if the replacement part does not have a diacritic, # we have already consumed it, and we start right after it eStart = nRepls if e is None else e + 1 # we compute the number of characters that still need to be # matched and to be replaced dn = nVals - dStart en = nRepls - eStart # we perform the replacement analogously to what we did # for the first part for j in range(dn): # put the appropriate replacement character in the # replacement part of the character record # After running out of replacement characters, put in "" chars[i + dStart + j][-1] = ( repls[eStart + j] if eStart + j < nRepls else "" ) if en > dn: # if there are replacement characters left, put them # in after the last character that we have visited. chars[i + nVals - 1][-1] += "".join( repls[eStart + dn :] ) break # sift out all presentational characters if doFilter: trailSpace = False for (i, char) in enumerate(chars): c = char[-1] string = "" for x in c: if trailSpace: if x not in diacriticLike: if x not in nonLetter: if string == "" and i > 0: chars[i - 1][-1] += " " else: string += " " trailSpace = False hasFinalSpace = x in finalSpace y = ( normalizeC(x) if x in presentationalC else normalizeD(x) if x in presentationalD else x ).strip() space = " " if hasFinalSpace or x in punct else "" if hasFinalSpace: finalsApplied[x][pageNum] += 1 string += y if space: trailSpace = True char[-1] = string if trailSpace: if chars: chars[-1][-1] += " " # add horizontal spacing theseSpaces = [] spaces[pageNum][ln] = theseSpaces threshold = None theseColumns = [threshold, []] columns[pageNum][ln] = theseColumns prevLeft = None prevLeftI = None for (i, char) in enumerate(chars): spacing = char[-3] if spacing: left = char[0] right = char[2] if prevLeft is not None: prevChar = chars[prevLeftI] after = prevLeft - right theAfter = ptRepD(after) isSpace = theAfter >= SPACE_THRESHOLD if isSpace: lastChar = chars[i - 1] if not lastChar[-1].endswith(" "): lastChar[-1] += " " prevChar[-3] = f"⌊{theAfter}⌋" if isSpace else f"«{theAfter}»" theseSpaces.append((i - 1, theAfter, isSpace)) prevLeft = left prevLeftI = i if chars: chars[-1][-3] = "end" # change big spaces to emspaces nSpaces = sum(1 for x in theseSpaces if x[2]) if nSpaces == 1: threshold = 90 elif nSpaces > 1: spacesGrowing = sorted(x[1] for x in theseSpaces if x[2]) maxSpace = spacesGrowing[-1] medialSpace = spacesGrowing[nSpaces // 2] if maxSpace > 4 * medialSpace: threshold = maxSpace - medialSpace if threshold is not None: theseColumns[0] = threshold for (i, after, isSpace) in theseSpaces: if isSpace and after > threshold: theseColumns[1].append((i, after)) char = chars[i] char[-1] = char[-1].rstrip(" ") + EMSPACE # remove space between alef and initial follower, # provided the alef is the single letter in its word. # also for the words yeh+alef(final) and mem+alef(final) do: # insert a space behind the alef(final) curLen = 0 prevCons = None pprevCons = None for (i, char) in enumerate(chars): c = char[-1] co = char[-2] r = "" isAFinal = isAlefFinal(co) for x in c: skip = False if x == " ": if curLen == 1: # and prevC in PROCLITICS: skip = True curLen = 0 prevCons = None pprevCons = None elif x in arabicLetters: curLen += 1 if 2 <= curLen <= 3 and isAFinal: if isMeemOrYeh(prevCons) and (curLen == 2 or isWaw(pprevCons)): x += " " curLen = 0 prevCons = None pprevCons = None pprevCons = prevCons prevCons = x if not skip: r += x char[-1] = r # divide lines into columns emspaces = theseColumns[1] emspacePositions = {t[0] for t in emspaces} columnedChars = [[]] dest = columnedChars[-1] for (i, char) in enumerate(chars): if i in emspacePositions: if char[-1]: dest.append(char) columnedChars.append([]) dest = columnedChars[-1] else: dest.append(char) # divide columns into ranges # and chunk the ranges into words # and save the word boundary boxes text = self.text # text is a dict keyed by pageNum and the values are tuples of line data # a line datum is a list of columns # a column is a list of spans # a span is a pair of a direction char ("l" or "r") plus a list of word data # a word datum is a string plus a word box # a word box is a (left, top, right, bottom) tuple result = [] text.setdefault(pageNum, []).append(result) prevDir = "r" # we transform letters into chunks, where each chunk is a pair of # word material # punctuation material outChars = [[], []] inWord = True box = [None, None, None, None] def addWord(): if outChars[0] or outChars[1]: wordCharsRep = "".join( outChars[0] if prevDir == "r" else reversed(outChars[0]) ) puncCharsRep = "".join( outChars[1] if prevDir == "r" else reversed(outChars[1]) ) lastSpan = None if len(result[-1]) == 0 else result[-1][-1] element = (wordCharsRep, puncCharsRep, tuple(box)) if lastSpan is None or lastSpan[0] != prevDir: result[-1].append((prevDir, [element])) else: result[-1][-1][-1].append(element) def setBox(char): for (i, coor) in enumerate(char[0:4]): if ( (b := box[i]) is None or (i < 2 and coor < b) or (i >= 2 and coor > b) ): box[i] = coor for chars in columnedChars: result.append([]) outChars = [[], []] box = [None, None, None, None] for char in chars: c = char[-1] if c == "": continue for d in c: spaceSeen = d in {" ", EMSPACE} changeWord = not inWord and d not in nonLetter if spaceSeen: outChars[1].append(d) if spaceSeen or changeWord: addWord() box = [None, None, None, None] outChars = [[d] if changeWord else [], []] inWord = True continue thisDir = prevDir if d in neutrals else "r" if d in rls else "l" if prevDir != thisDir: addWord() box = [None, None, None, None] outChars = [[], []] inWord = True prevDir = thisDir if inWord: if d in nonLetter: inWord = False dest = 0 if inWord else 1 rep = d if d in puas: rep = f"⌊{ord(d):>04x}⌋" outChars[dest].append(rep) setBox(char) addWord() def plainLine(self, columns): """Outputs a processed line as plain text. Used by `Lakhnawi.plainPages()`. Parameters ---------- columns: iterable An iterable of columns that make up a line. Each column is an iterable of spans. Spans contain words plus an indication of the writing direction for that span. Returns ------- string The concatenation of all words in all spans separated by white space. """ return "\t".join( " ".join( " ".join(f"{word[0]}{word[1]}" for word in span[1]) for span in spans ) for spans in columns ) def tsvHeadLine(self): """Outputs the field names of a word in TSV data. See `Lakhnawi.tsvPages()` for the structure of TSV data as output format for the extracted text of the Lakhnawi PDF. Returns ------- string A tab-separated line of field names. """ return "page\tline\tcolumn\tspan\tdirection\tleft\ttop\tright\tbottom\tletters\tpunc\n" def tsvLine(self, columns, pageNum, ln): """Outputs a processed line as lines of tab-separated fields for each word. Used by `Lakhnawi.tsvPages()`. Parameters ---------- columns: iterable An iterable of columns that make up a line. Each column is an iterable of spans. Spans contain words plus an indication of the writing direction for that span. pageNum: int The page number of the page where this line occurs. Returns ------- string The concatenation of the TSV lines for all words in all spans in all columns. """ material = [] for (cn, spans) in enumerate(columns): for (sn, (dr, words)) in enumerate(spans): for (letters, punc, (le, to, ri, bo)) in words: material.append( ( "\t".join( str(x) for x in ( pageNum, ln, cn + 1, sn + 1, dr, ptRep(le), ptRep(to), ptRep(ri), ptRep(bo), letters, punc, ) ) ) + "\n" ) return "".join(material) def htmlLine(self, columns, prevMulti, isLast): """Outputs a processed line as HTML. Used by `Lakhnawi.htmlPages()`. Parameters ---------- columns: iterable An iterable of columns that make up a line. Each column is an iterable of spans. Spans contain words plus an indication of the writing direction for that span. prevMulti: boolean Whether the preceding line has multiple columns. isLast: boolean Whether this line is the last line on the page. Returns ------- string The concatenation of the TSV lines for all words in all spans in all columns. """ showSpaces = self.showSpaces result = [] nCols = len(columns) multi = nCols > 1 if prevMulti and not multi: result.append("</table>\n") elif not prevMulti and multi: result.append("""<table class="linecols">\n""") if multi: result.append("<tr>\n") for spans in columns: result.append( f"""\t<td class="cols col{nCols}">""" if multi else """<p class="r">""" ) for (textDir, words) in spans: result.append(f"""<span class="{textDir}">""") for word in words: letters = normalizeD(word[0]) letters = letters.replace("⌊", """<span class="p">""").replace( "⌋", "</span>" ) if showSpaces: letters = f"""<span class="box">{letters}</span>""" punc = word[1] if showSpaces: punc = punc.replace(" ", """<span class="sp"> </span>""") result.append(f"{letters}{punc}") result.append("""</span>""") result.append("</td>\n" if multi else "</p>\n") if multi: result.append("</tr>\n") if isLast: result.append("</table>\n") return "".join(result) def clusterVert(self, data): """Cluster characters into lines based on their bounding boxes. Most characters on a line have their middle line in approximately the same height. But diacritics of characters in that line may occupy different heights. Without intervention, these would be clustered on separate lines. We take care to cluster them into the same lines as their main characters. It involves getting an idea of the regular line height, and clustering boxes that fall between the lines with the line above or below, whichever is closest. The result of the clustering is delivered as a key function, which will be used to sort characters. Parameters ---------- data: iterable of record The character records Returns ------- function A key function that assigns to each character record a value that corresponds to the vertical position of a real line, which is a clustered set of characters. The information on the vertical clustering of lines is delivered in the attributes `Lakhnawi.heights` and `Lakhnawi.clusteredHeights`, on a page by page basis. """ pageNum = self.pageNum heights = collections.Counter() for char in data: k = keyCharV(char) heights[k] += 1 peaks = sorted(heights) if len(peaks) > 1: nDistances = len(peaks) - 1 distances = sorted(peaks[i + 1] - peaks[i] for i in range(nDistances)) # remove the biggest distances if > 50, # to prevent outliers pulling the average too high for _ in range(2): if len(distances) > 1: if distances[-1] > 50: distances = distances[0:-1] # remove distances < 15, which are much smaller than a line distances = [d for d in distances if d > 15] nDistances = len(distances) avPeakDist = sum(distances) / nDistances peakThreshold = avPeakDist * LINE_CLUSTER_FACTOR clusteredHeights = {} for (k, n) in sorted(heights.items(), key=lambda x: (-x[1], x[0])): added = False for kc in clusteredHeights: if abs(k - kc) <= peakThreshold: clusteredHeights[kc].add(k) added = True break if not added: clusteredHeights[k] = {k} toCluster = {} for (kc, ks) in clusteredHeights.items(): for k in ks: toCluster[k] = kc self.heights[pageNum] = heights self.clusteredHeights[pageNum] = clusteredHeights def clusterKeyCharV(char): k = keyCharV(char) return toCluster[k] return clusterKeyCharVAncestors
Instance variables
var clusteredHeights-
Clustered heights of characters, indexed by page number.
The clustered heights correspond to the lines on a page.
var columns-
Column information, indexed by page and line number.
Spaces that are significantly larger than a normal white space are interpreted as an emspace, and these are considered as column separators. We remember the character positions where this happens plus the amount of space in question.
Columns in the Lakhnawi PDF correspond to hemistic poems, where lines are divided into two halves, each occupying a column.
See

hemistic poems versus blocks
This is very different from blocks (see
fusus.layout) in OCRed texts, where blocks have been detected because of vertical strokes that separate columns.The reading progress in a hemistic poem is not changed by the column division, where as in the case of blocks, reading proceeds by reading the complete blocks in order.
var doc-
A handle to the PDF document, after it has been read by fitz.
var doubles-
Glyphs with double unicode points.
Some private use characters have two unicode points assigned to them by fonts in the PDF. This is the cause that straightforward text extractions deliver double occurrences of those letters. Even fitz does that.
We have collected these cases, and choose to use the lower unicode point, which is usually an ordinary character, whereas the other is usually a related presentational character.
This dictionary maps the lower character to the higher character.
var fnRules-
Vertical positions of footnote lines, indexed by page number
var good-
Whether processing is still ok, i.e. no errors encountered.
var heights-
Heights of characters, indexed by page number.
var lines-
Lines as tuples of original character objects, indexed by page number
var privateDias-
Private-use unicodes that correspond to diacritics.
var privateLetters-
Private-use unicodes that correspond to full letters.
var privateSpace-
Private-use-unicode used to represent a space.
var spaces-
Spacing information for each character, indexed by page and line number.
For character that has space behind it, it gives the index position of that character in the line, the amount of space detected, and whether this counts as a full white space.
var text-
Lines as tuples of converted character objects, indexed by page number
Methods
def close(self)-
Close the PDF handle, offered by fitz.
Expand source code Browse git
def close(self): """Close the PDF handle, offered by *fitz*.""" self.doc.close() def clusterVert(self, data)-
Cluster characters into lines based on their bounding boxes.
Most characters on a line have their middle line in approximately the same height. But diacritics of characters in that line may occupy different heights.
Without intervention, these would be clustered on separate lines. We take care to cluster them into the same lines as their main characters.
It involves getting an idea of the regular line height, and clustering boxes that fall between the lines with the line above or below, whichever is closest.
The result of the clustering is delivered as a key function, which will be used to sort characters.
Parameters
data:iterableofrecord- The character records
Returns
function-
A key function that assigns to each character record a value that corresponds to the vertical position of a real line, which is a clustered set of characters.
The information on the vertical clustering of lines is delivered in the attributes
Lakhnawi.heightsandLakhnawi.clusteredHeights, on a page by page basis.
Expand source code Browse git
def clusterVert(self, data): """Cluster characters into lines based on their bounding boxes. Most characters on a line have their middle line in approximately the same height. But diacritics of characters in that line may occupy different heights. Without intervention, these would be clustered on separate lines. We take care to cluster them into the same lines as their main characters. It involves getting an idea of the regular line height, and clustering boxes that fall between the lines with the line above or below, whichever is closest. The result of the clustering is delivered as a key function, which will be used to sort characters. Parameters ---------- data: iterable of record The character records Returns ------- function A key function that assigns to each character record a value that corresponds to the vertical position of a real line, which is a clustered set of characters. The information on the vertical clustering of lines is delivered in the attributes `Lakhnawi.heights` and `Lakhnawi.clusteredHeights`, on a page by page basis. """ pageNum = self.pageNum heights = collections.Counter() for char in data: k = keyCharV(char) heights[k] += 1 peaks = sorted(heights) if len(peaks) > 1: nDistances = len(peaks) - 1 distances = sorted(peaks[i + 1] - peaks[i] for i in range(nDistances)) # remove the biggest distances if > 50, # to prevent outliers pulling the average too high for _ in range(2): if len(distances) > 1: if distances[-1] > 50: distances = distances[0:-1] # remove distances < 15, which are much smaller than a line distances = [d for d in distances if d > 15] nDistances = len(distances) avPeakDist = sum(distances) / nDistances peakThreshold = avPeakDist * LINE_CLUSTER_FACTOR clusteredHeights = {} for (k, n) in sorted(heights.items(), key=lambda x: (-x[1], x[0])): added = False for kc in clusteredHeights: if abs(k - kc) <= peakThreshold: clusteredHeights[kc].add(k) added = True break if not added: clusteredHeights[k] = {k} toCluster = {} for (kc, ks) in clusteredHeights.items(): for k in ks: toCluster[k] = kc self.heights[pageNum] = heights self.clusteredHeights[pageNum] = clusteredHeights def clusterKeyCharV(char): k = keyCharV(char) return toCluster[k] return clusterKeyCharV def collectPage(self, data)-
Transforms raw text into proper textual data.
Called by
Lakhnawi.getPages()and delivers its results to attributes of the Lakhnawi object.Here are they
They are all dictionaries, keyed by page number first and then by line.
Parameters
data:dict- as obtained by the extractRAWDICT() method of fitz.
Returns
None
Expand source code Browse git
def collectPage(self, data): """Transforms raw text into proper textual data. Called by `Lakhnawi.getPages()` and delivers its results to attributes of the Lakhnawi object. Here are they * `Lakhnawi.lines` * `Lakhnawi.doubles` * `Lakhnawi.text` They are all dictionaries, keyed by page number first and then by line. Parameters ---------- data: dict as obtained by the [extractRAWDICT()](https://pymupdf.readthedocs.io/en/latest/textpage.html#TextPage.extractRAWDICT) method of *fitz*. Returns ------- None """ doubles = self.doubles doublesApplied = self.doublesApplied pageNum = self.pageNum nospacings = self.nospacings fnRules = self.fnRules bracketMap = self.bracketMap text = self.text fnRule = fnRules.get(pageNum, None) fnRule = fnRule[0] if fnRule else None chars = [] prevChar = None prevFont = None prevSize = None def addChar(): box = prevChar["bbox"] yBot = box[3] # skip chars below the footnote rule, if any if fnRule is not None and yBot > fnRule: return c = prevChar["c"] cr = "" if isEuDigit(c) else c cr = bracketMap.get(cr, cr) chars.append( ( *box, prevFont, prevSize, "" if c in nospacings else True, c, cr, ) ) def collectChars(data, font, size): nonlocal prevChar nonlocal prevFont nonlocal prevSize if type(data) is list: for elem in data: collectChars(elem, font, size) elif type(data) is dict: if "font" in data: font = data["font"] if "size" in data: size = data["size"] if "c" in data: c = data["c"] skip = False if c == " ": skip = True if prevChar is not None: pc = prevChar["c"] if pc in doubles and doubles[pc] == c: skip = True doublesApplied[pc][pageNum] += 1 if c in doubles and doubles[c] == pc: prevChar = data skip = True doublesApplied[c][pageNum] += 1 if not skip: if prevChar is not None: addChar() prevChar = data prevFont = font prevSize = size for (k, v) in data.items(): if type(v) in {list, dict}: collectChars(v, font, size) collectChars(data, None, None) if prevChar is not None: addChar() clusterKeyCharV = self.clusterVert(chars) lines = {} for char in sorted(chars, key=lambda c: (clusterKeyCharV(c), keyCharH(c))): k = clusterKeyCharV(char) lines.setdefault(k, []).append(list(char)) theseLines = list(lines.values()) if theseLines and self.isPageNum(theseLines[0]): theseLines = theseLines[1:] # remove arabic numerals between brackets for chars in theseLines: nChars = len(chars) if not nChars: continue i = 0 while i < nChars: char = chars[i] nextI = i + 1 if char[-1] == "(": found = None for j in range(i + 1, nChars): theChar = chars[j][-1] if theChar == ")": found = j + 1 nextI = found break if isArDigit(theChar): continue nextI = j break if found is not None: for j in range(i, found): chars[j][-1] = "" i = found i = nextI self.lines[pageNum] = tuple( chars for chars in theseLines if not all(c[-1] == "" for c in chars) ) text[pageNum] = [] for (ln, line) in enumerate(self.lines[pageNum]): self.trimLine(pageNum, ln + 1, line) def drawPages(self, pageNumSpec, clip=None)-
Draws a (part) of page from the PDF as a raster image.
Parameters
pageNumSpec:None | int | string | iterable- As in
Lakhnawi.parsePageNums(). clip:(int, int), optionalNone- If None: produces the whole page.
Otherwise it is
(top, bottom), and a stripe from top to bottom will be displayed.
Expand source code Browse git
def drawPages(self, pageNumSpec, clip=None): """Draws a (part) of page from the PDF as a raster image. Parameters ---------- pageNumSpec: None | int | string | iterable As in `Lakhnawi.parsePageNums()`. clip: (int, int), optional `None` If None: produces the whole page. Otherwise it is `(top, bottom)`, and a stripe from top to bottom will be displayed. """ doc = self.doc for pageNum in self.parsePageNums(pageNumSpec): page = doc[pageNum - 1] if clip is not None: clip = (0, clip[0], page.rect.width, clip[1]) pix = page.getPixmap(matrix=fitz.Matrix(4, 4), clip=clip, alpha=False) display(HTML(f"""<p><b>page {pageNum}</b></p>""")) display(Image(data=pix.getPNGData(), format=DEFAULT_EXTENSION)) def getCharConfig(self)-
Configure all character information.
Private-use characters, transformation rules, character categories.
Expand source code Browse git
def getCharConfig(self): """Configure all character information. Private-use characters, transformation rules, character categories. """ self.privateInfo() self.setupRules() self.getCharInfo() def getCharInfo(self)-
Obtain detailed character information by reading the font report file.
From this file we read:
- which are the private use characters?
- which of them have a double unicode?
The font file is here.
Expand source code Browse git
def getCharInfo(self): """Obtain detailed character information by reading the font report file. From this file we read: * which are the private use characters? * which of them have a double unicode? The font file is [here](https://github.com/among/fusus/blob/master/ur/Lakhnawi/FontReport-Lakhnawi.pdf). """ self.doubles = {} self.privates = set() doubles = self.doubles privates = self.privates finalSpace = self.finalSpace puas = self.puas doc = fitz.open(FONT) for page in doc: textPage = page.getTextPage() data = textPage.extractText() for (ln, line) in enumerate(data.split("\n")): if line.startswith("U+"): match = U_LINE_RE.match(line) if not match: continue (main, rest) = match.group(1, 2) main = main.lower() nMain = int(main, base=16) cMain = chr(nMain) if cMain in puas: privates.add(cMain) continue if cMain == chr(0): continue second = None rest = rest.replace(" ", "") if rest: if HEX_RE.match(rest): second = rest.lower() if second: nSecond = int(second, base=16) cSecond = chr(nSecond) if nSecond > nMain: doubles[cMain] = cSecond else: doubles[cSecond] = cMain doublesApplied = collections.defaultdict(collections.Counter) for d in doubles: doublesApplied[d] = collections.Counter() self.doublesApplied = doublesApplied finalsApplied = collections.defaultdict(collections.Counter) for f in finalSpace: finalsApplied[f] = collections.Counter() self.finalsApplied = finalsApplied def getPageObj(self, pageNum)-
Get the fitz object for a specific page.
Used for debugging.
Parameters
pageNum:int- A valid page number. It is the sequence number of the page within the PDF, counting from 1.
Returns
object- A fitz page object
Expand source code Browse git
def getPageObj(self, pageNum): """Get the *fitz* object for a specific page. Used for debugging. Parameters ---------- pageNum: int A valid page number. It is the sequence number of the page within the PDF, counting from 1. Returns ------- object A *fitz* [page object](https://pymupdf.readthedocs.io/en/latest/page.html) """ self.pageNum = pageNum doc = self.doc return doc[pageNum - 1] def getPageRaw(self, pageNum)-
Do a rough/raw text extract of a specific page.
The fitz method extractRAWDICT() is used to obtain very detailed information about each character on that page. Used for debugging.
Parameters
pageNum:int- A valid page number. It is the sequence number of the page within the PDF, counting from 1.
Returns
None- It pretty prints the output of the fitz method, which is a big and deep dictionary.
Expand source code Browse git
def getPageRaw(self, pageNum): """Do a rough/raw text extract of a specific page. The *fitz* method [extractRAWDICT()](https://pymupdf.readthedocs.io/en/latest/textpage.html#TextPage.extractRAWDICT) is used to obtain very detailed information about each character on that page. Used for debugging. Parameters ---------- pageNum: int A valid page number. It is the sequence number of the page within the PDF, counting from 1. Returns ------- None It pretty prints the output of the fitz method, which is a big and deep dictionary. """ self.pageNum = pageNum rep = f"page {pageNum:>4}" sys.stdout.write(f"{rep}") sys.stdout.flush() doc = self.doc page = doc[pageNum - 1] textPage = page.getTextPage() data = textPage.extractRAWDICT() pprint(data) def getPages(self, pageNumSpec, refreshConfig=False, doRules=True, doFilter=True, onlyFnRules=False)-
Reads pages of the PDF and extracts text.
This does all of the hard work of the text extraction. It saves the textual data in attributes of the Lakhnawi object, augmented with all kinds of diagnostic information.
From all this data, various output representations can be generated rather easily by other methods.
Parameters
pageNumSpec:None | int | string | iterable- As in
Lakhnawi.parsePageNums(). refreshConfig:boolean, optionalFalse- If
True, rereads all character configuration. Ideal when you are iteratively developing the character configuration. doRules:boolean, optionalTrue- If
False, suppresses the application of character transformation rules. Mainly used when debugging other aspects of the text extraction. doFilter:boolean, optionalTrue- If
False, suppresses the application of unicode normalization, by which presentational characters are transformed into sequences of ordinary, basic characters. Used for debugging. onlyFnRules:boolean, optionalFalse- If
True, skips most of the conversion. Only determine where the footnote rules are. Used for debugging.
Returns
None
The effect is that attributes of the Lakhnawi object are filled:
For the other attributes, see
Lakhnawi.collectPage().multiple runs
If you do multiple runs of this function for different pages, the results will not overwrite each other in general, because the attributes hold the results in dictionaries keyed by page number.
Expand source code Browse git
def getPages( self, pageNumSpec, refreshConfig=False, doRules=True, doFilter=True, onlyFnRules=False, ): """Reads pages of the PDF and extracts text. This does all of the hard work of the text extraction. It saves the textual data in attributes of the Lakhnawi object, augmented with all kinds of diagnostic information. From all this data, various output representations can be generated rather easily by other methods. Parameters ---------- pageNumSpec: None | int | string | iterable As in `Lakhnawi.parsePageNums()`. refreshConfig: boolean, optional `False` If `True`, rereads all character configuration. Ideal when you are iteratively developing the character configuration. doRules: boolean, optional `True` If `False`, suppresses the application of character transformation rules. Mainly used when debugging other aspects of the text extraction. doFilter: boolean, optional `True` If `False`, suppresses the application of unicode normalization, by which presentational characters are transformed into sequences of ordinary, basic characters. Used for debugging. onlyFnRules: boolean, optional `False` If `True`, skips most of the conversion. Only determine where the footnote rules are. Used for debugging. Returns ------- None The effect is that attributes of the Lakhnawi object are filled: * `Lakhnawi.heights` * `Lakhnawi.clusteredHeights` * `Lakhnawi.fnRules` For the other attributes, see `Lakhnawi.collectPage()`. !!! hint "multiple runs" If you do multiple runs of this function for different pages, the results will not overwrite each other in general, because the attributes hold the results in dictionaries keyed by page number. """ if not self.good: print("SKIPPING because of config errors") return fnRules = self.fnRules spaces = self.spaces columns = self.columns self.doRules = doRules self.doFilter = doFilter ruleIndex = self.ruleIndex rulesApplied = self.rulesApplied if refreshConfig: self.getCharConfig() for rn in ruleIndex: rulesApplied[rn] = collections.Counter() for (i, pageNum) in enumerate(self.parsePageNums(pageNumSpec)): self.pageNum = pageNum rep = ( f"{i + 1:>4} (page {pageNum:>4})" if pageNum != i + 1 else (f"{i + 1:>4}" + " " * 12) ) sys.stdout.write(f"\r\t{rep}") sys.stdout.flush() doc = self.doc page = doc[pageNum - 1] theseFnRules = set() for fnRule in page.getDrawings(): if RECT in fnRule and fnRule.get(COLOR, None): rect = fnRule[RECT] width = rect.x1 - rect.x0 if width > FNRULE_WIDTH: theseFnRules.add(int(round(rect.y1))) fnRules[pageNum] = tuple(sorted(theseFnRules)) spaces[pageNum] = {} columns[pageNum] = {} if onlyFnRules: continue textPage = page.getTextPage() data = textPage.extractRAWDICT() self.collectPage(data) def htmlLine(self, columns, prevMulti, isLast)-
Outputs a processed line as HTML.
Used by
Lakhnawi.htmlPages().Parameters
columns:iterable- An iterable of columns that make up a line. Each column is an iterable of spans. Spans contain words plus an indication of the writing direction for that span.
prevMulti:boolean- Whether the preceding line has multiple columns.
isLast:boolean- Whether this line is the last line on the page.
Returns
string- The concatenation of the TSV lines for all words in all spans in all columns.
Expand source code Browse git
def htmlLine(self, columns, prevMulti, isLast): """Outputs a processed line as HTML. Used by `Lakhnawi.htmlPages()`. Parameters ---------- columns: iterable An iterable of columns that make up a line. Each column is an iterable of spans. Spans contain words plus an indication of the writing direction for that span. prevMulti: boolean Whether the preceding line has multiple columns. isLast: boolean Whether this line is the last line on the page. Returns ------- string The concatenation of the TSV lines for all words in all spans in all columns. """ showSpaces = self.showSpaces result = [] nCols = len(columns) multi = nCols > 1 if prevMulti and not multi: result.append("</table>\n") elif not prevMulti and multi: result.append("""<table class="linecols">\n""") if multi: result.append("<tr>\n") for spans in columns: result.append( f"""\t<td class="cols col{nCols}">""" if multi else """<p class="r">""" ) for (textDir, words) in spans: result.append(f"""<span class="{textDir}">""") for word in words: letters = normalizeD(word[0]) letters = letters.replace("⌊", """<span class="p">""").replace( "⌋", "</span>" ) if showSpaces: letters = f"""<span class="box">{letters}</span>""" punc = word[1] if showSpaces: punc = punc.replace(" ", """<span class="sp"> </span>""") result.append(f"{letters}{punc}") result.append("""</span>""") result.append("</td>\n" if multi else "</p>\n") if multi: result.append("</tr>\n") if isLast: result.append("</table>\n") return "".join(result) def htmlPages(self, pageNumSpec, line=None, showSpaces=False, export=False, singleFile=False, toc=False)-
Outputs processed pages as formatted HTML pages.
Uses
Lakhnawi.htmlLine().The HTML output is suitable to read the extracted text. Its layout matches the original closely, which makes it easier to see where the output deviates from the source page.
Parameters
pageNumSpec:None | int | string | iterable- As in
Lakhnawi.parsePageNums(). line:None | int | string | iterable- A specification of zero or more line numbers (see
parseNums()). showSpaces:boolean, optionalFalse- If
True, shows the spaces with a conspicuous coloured background. export:boolean, optionalFalse- If
True, writes the HTML results to disk. In this case, the HTML will not be displayed in the notebook. singleFile:boolean, optionalFalse- Only meaningful is
export=True. IfTrue, writes the output to a single HTML file, otherwise to one file per page, in a directory calledhtml. toc:boolean, optionalFalse- Only meaningful is
export=TrueandsingleFile=True. IfTrue, writes a table of contents to the file. The TOC points to every page that is included in the output file.
Returns
Expand source code Browse git
def htmlPages( self, pageNumSpec, line=None, showSpaces=False, export=False, singleFile=False, toc=False, ): """Outputs processed pages as formatted HTML pages. Uses `Lakhnawi.htmlLine()`. The HTML output is suitable to read the extracted text. Its layout matches the original closely, which makes it easier to see where the output deviates from the source page. Parameters ---------- pageNumSpec: None | int | string | iterable As in `Lakhnawi.parsePageNums()`. line: None | int | string | iterable A specification of zero or more line numbers (see `fusus.lib.parseNums`). showSpaces: boolean, optional `False` If `True`, shows the spaces with a conspicuous coloured background. export: boolean, optional `False` If `True`, writes the HTML results to disk. In this case, the HTML will not be displayed in the notebook. singleFile: boolean, optional `False` Only meaningful is `export=True`. If `True`, writes the output to a single HTML file, otherwise to one file per page, in a directory called `html`. toc: boolean, optional `False` Only meaningful is `export=True` and `singleFile=True`. If `True`, writes a table of contents to the file. The TOC points to every page that is included in the output file. Returns ------- None Depending on `export`, the page is displayed in the notebook where this function is called, or exported to a file on disk. The file is in `fusus.parameters.UR_DIR`, under `Lakhnawi`. The name of the file includes a page specification. """ self.showSpaces = showSpaces text = self.text destDir = f"{UR_DIR}/{NAME}" if singleFile else f"{UR_DIR}/{NAME}/html" pageNums = self.parsePageNums(pageNumSpec) lineNums = parseNums(line) lineNums = None if lineNums is None else set(lineNums) filesWritten = 0 if export: if not os.path.exists(destDir): os.makedirs(destDir, exist_ok=True) if singleFile: pageNumRep = ALL_PAGES if pageNumSpec is None else str(pageNumSpec) tocRep = "-with-toc" if toc else "" filePath = f"{destDir}/{pageNumRep}{tocRep}.html" fh = open(filePath, "w") fh.write(preHtml(f"{pageNumRep}{tocRep}")) if toc: toc = getToc(pageNums) fh.write( f""" <div class="window"> <div class="sidebar"> {toc} </div> <div class="pages bypage"> """ ) else: fh.write( """ <div class="pages"> """ ) pageClass = "page" + ("" if export else "c") for pageNum in pageNums: lines = text.get(pageNum, []) nLines = len(lines) html = [] html.append( f""" <div class="{pageClass}"> <div class="phead"><a name="p{pageNum:>03}">{pageNum}</a></div> """ ) prevMulti = False for (i, line) in enumerate(lines): if lineNums is not None and i + 1 not in lineNums: continue html.append(self.htmlLine(line, prevMulti, i == nLines - 1)) prevMulti = len(line) > 1 html.append("""</div>""") if export: htmlRep = "".join(html) if singleFile: fh.write(htmlRep) else: html = preHtml(pageNum) + htmlRep + POST_HTML filePath = f"{destDir}/p{pageNum:>03}.html" with open(filePath, "w") as fh: fh.write(html) filesWritten += 1 else: display(HTML("\n".join(html))) if export and singleFile: fh.write( """ </div> """ ) if toc: fh.write( """ </div> """ ) fh.write(POST_HTML) fh.close() print(f"HTML written to {unexpanduser(filePath)}") if export and not singleFile: print(f"{filesWritten} HTML files written to {unexpanduser(destDir)}/") def isPageNum(self, chars)-
Checks whether a series of characters represents an arabic number.
Parameters
chars:iterableofchar reocrds
Expand source code Browse git
def isPageNum(self, chars): """Checks whether a series of characters represents an arabic number. Parameters ---------- chars: iterable of char reocrds """ return 1 <= len(chars) <= 3 and all(isArDigit(c[-1]) for c in chars) def parsePageNums(self, pageNumSpec)-
Parses a value as one or more page numbers.
Parameters
pageNumSpec:None | int | string | iterable- If
Noneresults in all page numbers. If anint, it stands for that int. If astring, it is allowed to be a comma separated list of numbers or ranges, where a range is a lower bound and an upper bound separated by a-. If none of these, it should be an iterable ofintvalues.
Returns
None | iterableofint- Depending on the value.
Expand source code Browse git
def parsePageNums(self, pageNumSpec): """Parses a value as one or more page numbers. Parameters ---------- pageNumSpec: None | int | string | iterable If `None` results in all page numbers. If an `int`, it stands for that int. If a `string`, it is allowed to be a comma separated list of numbers or ranges, where a range is a lower bound and an upper bound separated by a `-`. If none of these, it should be an iterable of `int` values. Returns ------- None | iterable of int Depending on the value. """ doc = self.doc pageNums = ( list(range(1, len(doc) + 1)) if not pageNumSpec else [pageNumSpec] if type(pageNumSpec) is int else setFromSpec(pageNumSpec) if type(pageNumSpec) is str else list(pageNumSpec) ) return [i for i in sorted(pageNums) if 0 < i <= len(doc)] def plainChar(self, c)-
Show the character code of a character.
Parameters
c:string- The character in question, may also be the empty string or the integer 1 (diacritic place holder).
Returns
string- The hexadecimal unicode point of
c, between⌊ ⌋- brackets.
Expand source code Browse git
def plainChar(self, c): """Show the character code of a character. Parameters ---------- c: string The character in question, may also be the empty string or the integer 1 (diacritic place holder). Returns ------- string The hexadecimal unicode point of `c`, between `⌊ ⌋` - brackets. """ if c == "": return "⌊⌋" if c in {1}: return CODE_LETTER[c] return f"⌊{ord(c):>04x}⌋" def plainLine(self, columns)-
Outputs a processed line as plain text.
Used by
Lakhnawi.plainPages().Parameters
columns:iterable- An iterable of columns that make up a line. Each column is an iterable of spans. Spans contain words plus an indication of the writing direction for that span.
Returns
string- The concatenation of all words in all spans separated by white space.
Expand source code Browse git
def plainLine(self, columns): """Outputs a processed line as plain text. Used by `Lakhnawi.plainPages()`. Parameters ---------- columns: iterable An iterable of columns that make up a line. Each column is an iterable of spans. Spans contain words plus an indication of the writing direction for that span. Returns ------- string The concatenation of all words in all spans separated by white space. """ return "\t".join( " ".join( " ".join(f"{word[0]}{word[1]}" for word in span[1]) for span in spans ) for spans in columns ) def plainPages(self, pageNumSpec)-
Outputs processed pages as plain text.
Uses
Lakhnawi.plainLine().Parameters
pageNumSpec:None | int | string | iterable- As in
Lakhnawi.parsePageNums().
Returns
None- The plain text is printed to the output.
Expand source code Browse git
def plainPages(self, pageNumSpec): """Outputs processed pages as plain text. Uses `Lakhnawi.plainLine()`. Parameters ---------- pageNumSpec: None | int | string | iterable As in `Lakhnawi.parsePageNums()`. Returns ------- None The plain text is printed to the output. """ text = self.text for pageNum in self.parsePageNums(pageNumSpec): lines = text.get(pageNum, []) for (i, line) in enumerate(lines): print(self.plainLine(line)) def plainString(self, s)-
Show the character codes of the characters in a string.
Parameters
s:string- The string to show, may be empty, may contain place holders.
Returns
string- The concatenation of the unicode points of the characters in the string, each code point between brackets.
See also
Lakhnawi.plainChar().Expand source code Browse git
def plainString(self, s): """Show the character codes of the characters in a string. Parameters ---------- s: string The string to show, may be empty, may contain place holders. Returns ------- string The concatenation of the unicode points of the characters in the string, each code point between brackets. See also `Lakhnawi.plainChar()`. """ return " ".join(self.plainChar(c) for c in s) def privateInfo(self)-
Set up additional character categories wrt. private-use characters.
Several categories will receive additional members from the private use characters.
Expand source code Browse git
def privateInfo(self): """Set up additional character categories wrt. private-use characters. Several categories will receive additional members from the private use characters. """ self.privateLetters = getSetFromDef(PRIVATE_LETTERS_DEF) self.privateDias = getSetFromDef(PRIVATE_DIAS_DEF) self.privateSpace = PRIVATE_SPACE self.nospacings |= self.privateDias # self.nospacings.add(PRIVATE_TATWEEL) self.diacritics |= self.privateDias self.diacriticLike |= self.privateDias self.arabicLetters = self.arabic - self.privateDias self.rls |= self.puas def setStyle(self)-
Import the CSS styles into the notebook.
See
CSS.Expand source code Browse git
def setStyle(self): """Import the CSS styles into the notebook. See `CSS`. """ display(HTML(CSS)) def setupRules(self)-
Set up character transformation rules.
Prepare for counting how much rules will be applied when extracting text from pages of the Lakhnawi PDF.
Expand source code Browse git
def setupRules(self): """Set up character transformation rules. Prepare for counting how much rules will be applied when extracting text from pages of the Lakhnawi PDF. """ (self.replace, self.ruleIndex) = getDictFromDef(REPLACE_DEF) if self.replace is None: self.replace = {} self.good = False self.rulesApplied = collections.defaultdict(collections.Counter) for rn in self.ruleIndex: self.rulesApplied[rn] = collections.Counter() def showChar(self, c)-
Pretty display of a single unicode character.
We show the character itself and its name (if not a private-use one), its hexadecimal code, and we indicate by coloring the kind of white space that the character represents (ordinary space or emspace).
Parameters
c:string- The character in question, may also be the empty string or the integer 1 (diacritic place holder).
Expand source code Browse git
def showChar(self, c): """Pretty display of a single unicode character. We show the character itself and its name (if not a private-use one), its hexadecimal code, and we indicate by coloring the kind of white space that the character represents (ordinary space or emspace). Parameters ---------- c: string The character in question, may also be the empty string or the integer 1 (diacritic place holder). """ if c in {1, 2}: return f""" <div class="ch p"> <div class="cn">{LETTER_KIND[c]}</div> </div> """ if c == "": extra = "" ccode = "" crep = "\u00a0" cname = "EMPTY" else: puas = self.puas rls = self.rls ccode = ( f"""<span class="{"p" if c in puas else "c"}">{ord(c):>04x}</span>""" ) crep = ( "??" if c in puas else f"""<span class="{"rc" if c in rls else "lc"}">{c}""" ) cname = "" if c in puas else f"""<span class="c">{uName(c)}</span>""" extra = ( "m" if c == EMSPACE else "s" if c == " " else "" ) return f""" <div class="ch{extra}"> <div class="cn">{ccode}</div> <div class="cn"><span class="cni">{crep}</span></div> <div class="cn">{cname}</div> </div> """ def showColumns(self, pageNumSpec)-
Show used characters.
Gives an overview of the columns in each line. The result is a readable, ascii overview of the columns that exists in the lines of the selected pages.
It is useful to visually check column detection for many pages.
Parameters
pageNumSpec:None | int | string | iterable- As in
Lakhnawi.parsePageNums().
Returns
None- The output material will be displayed in the notebook.
Expand source code Browse git
def showColumns(self, pageNumSpec): """Show used characters. Gives an overview of the columns in each line. The result is a readable, ascii overview of the columns that exists in the lines of the selected pages. It is useful to visually check column detection for many pages. Parameters ---------- pageNumSpec: None | int | string | iterable As in `Lakhnawi.parsePageNums()`. Returns ------- None The output material will be displayed in the notebook. """ pageNums = self.parsePageNums(pageNumSpec) columns = self.columns for pageNum in pageNums: if pageNum not in columns: continue lineInfo = columns[pageNum] multiple = [] for lNum in sorted(lineInfo): (threshold, emspaces) = lineInfo[lNum] nEmspaces = len(emspaces) if threshold is not None and nEmspaces > 0: multiple.append((lNum, threshold, emspaces)) if not len(multiple): print(f"page {pageNum:>3} -") else: print(f"page {pageNum:>3}:") for (lNum, threshold, emspaces) in multiple: nEmspaces = len(emspaces) print(f"\t{lNum:>2}: {'- ' * (nEmspaces + 1)}") def showDoubles(self, double=None)-
Show a character with double entry and how often it occurs.
See
Lakhnawi.doubles.Parameters
double:char, optionalNone- A character from the doubles list (
Lakhnawi.doubles). If None, all such characters will be taken. isApplied:boolean, optionalFalse- Only show rules that have been applied.
Returns
None- Displays a table of double-entry characters with occurrence statistics.
Expand source code Browse git
def showDoubles(self, double=None): """Show a character with double entry and how often it occurs. See `Lakhnawi.doubles`. Parameters ---------- double: char, optional `None` A character from the doubles list (`Lakhnawi.doubles`). If None, all such characters will be taken. isApplied: boolean, optional `False` Only show rules that have been applied. Returns ------- None Displays a table of double-entry characters with occurrence statistics. """ doubles = self.doubles doublesApplied = self.doublesApplied theseDoubles = ( set(doubles) if double is None else {double} if double in doubles else set() ) html = [] totalDoubles = len(doubles) totalApplications = sum(sum(x.values()) for x in doublesApplied.values()) totalPages = len(set(chain.from_iterable(doublesApplied.values()))) doubleRep = "double" + ("" if totalDoubles == 1 else "s") appRep = "application" + ("" if totalApplications == 1 else "s") pageRep = "page" + ("" if totalPages == 1 else "s") html.append( f""" <p><b>{totalDoubles} {doubleRep} with {totalApplications} {appRep} on {totalPages} {pageRep}</b></p> <table> """ ) for (d, applied) in sorted( doublesApplied.items(), key=lambda x: (-sum(x[1].values()), x[0]) ): if d not in theseDoubles: continue e = doubles[d] doubleRep = f"{self.showChar(e)} ⇒ {self.showChar(d)}" total = sum(applied.values()) if applied: examplePageNum = sorted(applied, key=lambda p: -applied[p])[0] nExamples = applied[examplePageNum] appliedEx = f"e.g. page {examplePageNum} with {nExamples} applications" else: appliedEx = "" appliedRep = f"<b>{total}</b> x applied on <i>{len(applied)}</i> pages" html.append( f""" <tr> <td class="al">{appliedRep}</td> <td class="al">{appliedEx}</td> <td class="al">{doubleRep}</td> </tr> """ ) html.append("<table>") display(HTML("".join(html))) def showFinals(self, final=None)-
Show a character with final form and how often it has been replaced.
Final forms will be normalized to ground forms and sometimes a space will be added.
Parameters
final:char, optionalNone- A character from the final space list (
UChar.finalSpace). If None, all such characters will be taken. isApplied:boolean, optionalFalse- Only show rules that have been applied.
Returns
None- Displays a table of final space characters with occurrence statistics.
Expand source code Browse git
def showFinals(self, final=None): """Show a character with final form and how often it has been replaced. Final forms will be normalized to ground forms and sometimes a space will be added. Parameters ---------- final: char, optional `None` A character from the final space list (`fusus.char.UChar.finalSpace`). If None, all such characters will be taken. isApplied: boolean, optional `False` Only show rules that have been applied. Returns ------- None Displays a table of final space characters with occurrence statistics. """ finalSpace = self.finalSpace finalsApplied = self.finalsApplied theseFinals = ( finalSpace if final is None else {final} if final in finalSpace else set() ) html = [] totalFinals = len(finalSpace) totalApplications = sum(sum(x.values()) for x in finalsApplied.values()) totalPages = len(set(chain.from_iterable(finalsApplied.values()))) finalRep = "final" + ("" if totalFinals == 1 else "s") appRep = "application" + ("" if totalApplications == 1 else "s") pageRep = "page" + ("" if totalPages == 1 else "s") html.append( f""" <p><b>{totalFinals} {finalRep} with {totalApplications} {appRep} on {totalPages} {pageRep}</b></p> <table> """ ) for (f, applied) in sorted( finalsApplied.items(), key=lambda x: (-sum(x[1].values()), x[0]) ): if f not in theseFinals: continue finalRep = self.showChar(f) total = sum(applied.values()) if applied: examplePageNum = sorted(applied, key=lambda p: -applied[p])[0] nExamples = applied[examplePageNum] appliedEx = f"e.g. page {examplePageNum} with {nExamples} applications" else: appliedEx = "" appliedRep = f"<b>{total}</b> x applied on <i>{len(applied)}</i> pages" html.append( f""" <tr> <td class="al">{appliedRep}</td> <td class="al">{appliedEx}</td> <td class="al">{finalRep}</td> </tr> """ ) html.append("<table>") display(HTML("".join(html))) def showLineHeights(self, pageNumSpec)-
Shows how line heights have been determined.
The pages can be selected by page numbers.
Parameters
pageNumSpec:None | int | string | iterable- As in
Lakhnawi.parsePageNums().
Expand source code Browse git
def showLineHeights(self, pageNumSpec): """Shows how line heights have been determined. The pages can be selected by page numbers. Parameters ---------- pageNumSpec: None | int | string | iterable As in `Lakhnawi.parsePageNums()`. """ heights = self.heights clusteredHeights = self.clusteredHeights for pageNum in self.parsePageNums(pageNumSpec): theseHeights = heights[pageNum] theseClusteredHeights = clusteredHeights[pageNum] print(f"Line heights page {pageNum:>3}") print("\nraw heights") for k in sorted(theseHeights): print(f"{theseHeights[k]:>4} characters @ height {int(round(k)):>4}") print("line heights") for (ln, kc) in enumerate(sorted(theseClusteredHeights)): peak = ", ".join( f"{int(round(k)):>4}" for k in sorted(theseClusteredHeights[kc]) ) print( f"line {ln + 1:>2}: " f"{sum(theseHeights[k] for k in theseClusteredHeights[kc]):>4}" f" characters @height {peak}" ) def showLines(self, pageNumSpec, line=None, start=None, end=None, search=None, orig=False, every=False)-
Outputs processed lines as a formatted HTML table.
The lines can be selected by page numbers and line numbers.
Within the selected lines, the characters can be selected by start/end postions, or by characters of interest.
All of these indices start at 1.
Parameters
pageNumSpec:None | int | string | iterable- As in
Lakhnawi.parsePageNums(). line:None | int | string | iterable- A specification of zero or more line numbers (see
parseNums()). start:integer, optionalNone- Starting word position in each line to be output.
If
None, starts at the beginning of each line. end:integer, optionalNone- End word position in each line to be output.
If
None, ends at the end of each line. search:stringoriterableofchar, optionalNone- If not none, all characters in
searchare deemed interesting. All occurrences of these characters within the selected lines are displayed, included a small context. orig:boolean, optionalFalse- Only meaningful if
searchis given. IfTrue: the check for interesting characters is done in the original, untranslated characters. Otherwise, interesting characters are looked up in the translated characters. every:boolean, optionalFalse- Only meaningful if
searchis given. IfTrue, when looking for interesting characters, all occurrences will be retrieved, otherwise only the first one.
Returns
None- The output material will be displayed in the notebook.
Expand source code Browse git
def showLines( self, pageNumSpec, line=None, start=None, end=None, search=None, orig=False, every=False, ): """Outputs processed lines as a formatted HTML table. The lines can be selected by page numbers and line numbers. Within the selected lines, the characters can be selected by start/end postions, or by characters of interest. All of these indices start at 1. Parameters ---------- pageNumSpec: None | int | string | iterable As in `Lakhnawi.parsePageNums()`. line: None | int | string | iterable A specification of zero or more line numbers (see `fusus.lib.parseNums`). start: integer, optional `None` Starting word position in each line to be output. If `None`, starts at the beginning of each line. end: integer, optional `None` End word position in each line to be output. If `None`, ends at the end of each line. search: string or iterable of char, optional `None` If not none, all characters in `search` are deemed interesting. All occurrences of these characters within the selected lines are displayed, included a small context. orig: boolean, optional `False` Only meaningful if `search` is given. If `True`: the check for interesting characters is done in the original, untranslated characters. Otherwise, interesting characters are looked up in the translated characters. every: boolean, optional `False` Only meaningful if `search` is given. If `True`, when looking for interesting characters, all occurrences will be retrieved, otherwise only the first one. Returns ------- None The output material will be displayed in the notebook. """ lines = self.lines pageNums = self.parsePageNums(pageNumSpec) lineNums = parseNums(line) myLines = {pageNum: lines[pageNum] for pageNum in pageNums if pageNum in lines} html = [] html.append("<table>") html.append( """ <tr> <th>seq</th> <th>top</th> <th>bottom</th> <th>left</th> <th>right</th> <th>spacing</th> <th>font</th> <th>size</th> <th>orig char</th> <th>char</th> </tr> """ ) shift = 5 for (pageNum, pageLines) in myLines.items(): myLineNums = ( range(1, len(pageLines) + 1) if lineNums is None else [ln for ln in lineNums if 0 < ln <= len(pageLines)] ) for ln in myLineNums: chars = pageLines[ln - 1] nChars = len(chars) html.append( f""" <tr> <th colspan=3>page {pageNum}</th> <th colspan=2>line {ln}</th> <th colspan=3>{nChars} characters</th> </tr> """ ) if search is None: ranges = [(max((start or 0) - 1, 0), min(end or nChars, nChars))] else: ranges = [] for (i, char) in enumerate(chars): if search in char[-2 if orig else -1]: occStart = max((i - shift, 0)) occEnd = min((i + shift + 1, nChars)) if ranges and occStart <= ranges[-1][1]: ranges[-1][1] = occEnd else: ranges.append([occStart, occEnd]) if not every: break for (occStart, occEnd) in ranges: for i in range(occStart, occEnd): char = chars[i] (le, to, ri, bo, font, size, spacing, oc, c) = char html.append( f""" <tr> <td><b>{i + 1}</b></td> <td>{ptRepD(to)}</td> <td>{ptRepD(bo)}</td> <td>{ptRepD(le)}</td> <td>{ptRepD(ri)}</td> <td>{spacing}</td> <td>{font}</td> <td>{size}pt</td> <td>{"".join(self.showChar(x) for x in reversed(oc))}</td> <td>{"".join(self.showChar(x) for x in reversed(c))}</td> </tr> """ ) if search and ranges and not every: break html.append("</table>") display(HTML("".join(html))) def showReplacements(self, rule=None, isApplied=False)-
Show a character conversion rule and how it has been applied.
Parameters
rule:string|int, optionalNone- A specification of zero or more rule numbers (see
parseNums()). If None, all rules will be taken. isApplied:boolean, optionalFalse- Only show rules that have been applied.
Returns
None- Displays a table of rules with usage statistics.
Expand source code Browse git
def showReplacements(self, rule=None, isApplied=False): """Show a character conversion rule and how it has been applied. Parameters ---------- rule: string|int, optional `None` A specification of zero or more rule numbers (see `fusus.lib.parseNums`). If None, all rules will be taken. isApplied: boolean, optional `False` Only show rules that have been applied. Returns ------- None Displays a table of rules with usage statistics. """ ruleIndex = self.ruleIndex rulesApplied = self.rulesApplied ruleNums = parseNums(rule) ruleNums = ( set(ruleIndex) if ruleNums is None else sorted(r for r in ruleNums if r in ruleIndex) ) html = [] totalRules = len(ruleIndex) totalApplications = sum(sum(x.values()) for x in rulesApplied.values()) totalPages = len(set(chain.from_iterable(rulesApplied.values()))) ruleRep = "rule" + ("" if totalRules == 1 else "s") appRep = "application" + ("" if totalApplications == 1 else "s") pageRep = "page" + ("" if totalPages == 1 else "s") html.append( f""" <p><b>{totalRules} {ruleRep} with {totalApplications} {appRep} on {totalPages} {pageRep}</b></p> <table> """ ) for (rn, applied) in sorted( rulesApplied.items(), key=lambda x: (-sum(x[1].values()), x[0]) ): if rn not in ruleNums: continue (vals, d, repls, e) = ruleIndex[rn] valRep = "".join(self.showChar(c) for c in vals) replRep = "".join(self.showChar(c) for c in repls) total = sum(applied.values()) if isApplied and not applied: continue if applied: examplePageNum = sorted(applied, key=lambda p: -applied[p])[0] nExamples = applied[examplePageNum] appliedEx = f"e.g. page {examplePageNum} with {nExamples} applications" else: appliedEx = "" appliedRep = f"<b>{total}</b> x applied on <i>{len(applied)}</i> pages" html.append( f""" <tr> <th>rule {rn}</th> <td class="al">{appliedRep}</td> <td class="al">{appliedEx}</td> <td class="al">{valRep}</td> <td class="al"><span class="lrg">⇒</span></td> <td class="al">{replRep}</td> </tr> """ ) html.append("<table>") display(HTML("".join(html))) def showSpacing(self, pageNumSpec, line=None)-
Show where the spaces are.
Gives an overview of the white space positions in each line.
It is useful to debug the horizontal white space algorithm.
Parameters
pageNumSpec:None | int | string | iterable- As in
Lakhnawi.parsePageNums(). line:None | int | string | iterable- A specification of zero or more line numbers (see
parseNums()).
Returns
None- The output material will be displayed in the notebook.
Expand source code Browse git
def showSpacing(self, pageNumSpec, line=None): """Show where the spaces are. Gives an overview of the white space positions in each line. It is useful to debug the horizontal white space algorithm. Parameters ---------- pageNumSpec: None | int | string | iterable As in `Lakhnawi.parsePageNums()`. line: None | int | string | iterable A specification of zero or more line numbers (see `fusus.lib.parseNums`). Returns ------- None The output material will be displayed in the notebook. """ pageNums = self.parsePageNums(pageNumSpec) lineNums = parseNums(line) lineNums = None if lineNums is None else set(lineNums) spaces = self.spaces for pageNum in pageNums: if pageNum not in spaces: continue print(f"page {pageNum:>3}") lineInfo = spaces[pageNum] for (ln, spaces) in lineInfo.items(): if lineNums is not None and ln not in lineNums: continue print(f"\tline {ln:>2}") for (i, after, isSpace) in spaces: print(f"\t\t{i + 1:>3} {'] [' if isSpace else ']==['} {after}") def showString(self, s, asString=False)-
Pretty display of a string as a series of unicode characters.
Parameters
s:string- The string to display, may be empty, may contain place holders.
asString:boolean, optionalFalse- If True, return the result as an HTML string.
Returns
None | string- If
asString, returns an HTML string, otherwise returns None, but displays the HTML string.
See also
Lakhnawi.showChar().Expand source code Browse git
def showString(self, s, asString=False): """Pretty display of a string as a series of unicode characters. Parameters ---------- s: string The string to display, may be empty, may contain place holders. asString: boolean, optional `False` If True, return the result as an HTML string. Returns ------- None | string If `asString`, returns an HTML string, otherwise returns None, but displays the HTML string. See also `Lakhnawi.showChar()`. """ shtml = f"""<span class="r">{s}</span>""" html = """<div class="sr">""" + ( "".join(self.showChar(c) for c in s) + "</div>" ) if asString: return f"""<span>{shtml}</span>{html}""" display(HTML(f"""<p>{shtml}</p>{html}""")) def showUsedChars(self, pageNumSpec, orig=False, onlyPuas=False, onlyPresentational=False, long=False, byOcc=False)-
Show used characters.
Gives an overview of character usage, either in the input PDF, or in the text output.
Parameters
pageNumSpec:None | int | string | iterable- As in
Lakhnawi.parsePageNums(). orig:boolean, optionalFalse- If
True: shows characters of the original PDF. Otherwise, shows characters of the translated output/ onlyPuas:boolean, optionalFalse- If
True, the result is restricted to private use characters. onlyPresentational:boolean, optionalFalse- If
True, the result is restricted to presentational characters. SeeUChar.presentational. long:boolean, optionalFalse- If
True, for each character output the complete list of pages where the character occurs. Otherwise, show only the most prominent pages. byOcc:boolean, optionalFalse- If
True, sort the results by first occurrence of the characters. Otherwise, sort the results by unicode code point of the character.
Returns
None- The output material will be displayed in the notebook.
Expand source code Browse git
def showUsedChars( self, pageNumSpec, orig=False, onlyPuas=False, onlyPresentational=False, long=False, byOcc=False, ): """Show used characters. Gives an overview of character usage, either in the input PDF, or in the text output. Parameters ---------- pageNumSpec: None | int | string | iterable As in `Lakhnawi.parsePageNums()`. orig: boolean, optional `False` If `True`: shows characters of the original PDF. Otherwise, shows characters of the translated output/ onlyPuas: boolean, optional `False` If `True`, the result is restricted to private use characters. onlyPresentational: boolean, optional `False` If `True`, the result is restricted to presentational characters. See `fusus.char.UChar.presentational`. long: boolean, optional `False` If `True`, for each character output the complete list of pages where the character occurs. Otherwise, show only the most prominent pages. byOcc: boolean, optional `False` If `True`, sort the results by first occurrence of the characters. Otherwise, sort the results by unicode code point of the character. Returns ------- None The output material will be displayed in the notebook. """ presentational = self.presentational pageNums = self.parsePageNums(pageNumSpec) text = self.text lines = self.lines puas = self.puas charsOut = collections.defaultdict(collections.Counter) def keyByOcc(c): pageNums = charsOut[c] return -sum(pageNums.values()) sortKey = keyByOcc if byOcc else lambda x: x if orig: lns = {pageNum: lines[pageNum] for pageNum in pageNums if pageNum in lines} for (pageNum, pageLines) in lns.items(): for line in pageLines: for char in line: c = char[-2] if c in puas or ( not onlyPuas and (c in presentational or not onlyPresentational) ): charsOut[c][pageNum] += 1 else: texts = {pageNum: text[pageNum] for pageNum in pageNums if pageNum in text} for (pageNum, pageText) in texts.items(): for line in pageText: for col in line: for span in col: for word in span[1]: letters = word[0] punc = word[1] thesePuas = PUA_RE.findall(letters) for pua in thesePuas: charsOut[chr(int(pua, base=16))][pageNum] += 1 if not onlyPuas: rest = PUA_RE.sub("", f"{letters}{punc}") for c in rest: if not ( onlyPresentational and c not in presentational ): charsOut[c][pageNum] += 1 totalChars = len(charsOut) totalPages = len(set(chain.from_iterable(charsOut.values()))) totalOccs = sum(sum(pns.values()) for pns in charsOut.values()) charRep = "character" + ("" if totalChars == 1 else "s") occRep = "occurence" + ("" if totalOccs == 1 else "s") pageRep = "page" + ("" if totalPages == 1 else "s") label = "private use " if onlyPuas else "" html = [] html.append( f""" <p><b>{totalChars} {label}{charRep} in {totalOccs} {occRep} on {totalPages} {pageRep}</b></p> <table> """ ) for c in sorted(charsOut, key=sortKey): pageNums = charsOut[c] nPageNums = len(pageNums) pageRep = "page" + ("" if nPageNums == 1 else "s") thistotal = sum(pageNums.values()) examplePageNum = sorted(pageNums, key=lambda p: -pageNums[p])[0] nExamples = pageNums[examplePageNum] html.append( f""" <tr> <td class="al">{self.showChar(c)}</td> <td class="al"><b>{thistotal}</b> on <i>{nPageNums}</i> {pageRep}</td> <td class="al">e.g. page {examplePageNum} with <b>{nExamples}</b> occurrences</td> </tr> """ ) if long: for pn in sorted(pageNums): occs = pageNums[pn] html.append( f""" <tr> <td></td> <td class="al"><i>page {pn:>3}</i>: <b>{occs:>3}</b></td> </tr> """ ) html.append("</table>") display(HTML("".join(html))) def showWords(self, pageNumSpec, line=None)-
Outputs processed words as a formatted HTML table.
The lines can be selected by page numbers and line numbers.
All words within the selected lines are put into a table with the same properties as in the TSV data, see
Lakhnawi.tsvPages().Parameters
pageNumSpec:None | int | string | iterable- As in
Lakhnawi.parsePageNums(). line:None | int | string | iterable- A specification of zero or more line numbers (see
parseNums()).
Returns
None- The output material will be displayed in the notebook.
Expand source code Browse git
def showWords(self, pageNumSpec, line=None): """Outputs processed words as a formatted HTML table. The lines can be selected by page numbers and line numbers. All words within the selected lines are put into a table with the same properties as in the TSV data, see `Lakhnawi.tsvPages`. Parameters ---------- pageNumSpec: None | int | string | iterable As in `Lakhnawi.parsePageNums()`. line: None | int | string | iterable A specification of zero or more line numbers (see `fusus.lib.parseNums`). Returns ------- None The output material will be displayed in the notebook. """ text = self.text pageNums = self.parsePageNums(pageNumSpec) lineNums = parseNums(line) myLines = {pageNum: text[pageNum] for pageNum in pageNums if pageNum in text} html = [] html.append("<table>") html.append( """ <tr> <th>page</th> <th>line</th> <th>col</th> <th>span</th> <th>dir</th> <th>left</th> <th>top</th> <th>right</th> <th>bottom</th> <th>letters</th> <th>punc</th> </tr> """ ) for (pageNum, pageLines) in myLines.items(): myLineNums = ( range(1, len(pageLines) + 1) if lineNums is None else [ln for ln in lineNums if 0 < ln <= len(pageLines)] ) for ln in myLineNums: cols = pageLines[ln - 1] for (cn, spans) in enumerate(cols): for (sn, (dr, words)) in enumerate(spans): for (letters, punc, (le, to, ri, bo)) in words: html.append( f""" <tr> <td><b>{pageNum}</b></td> <td><b>{ln}</b></td> <td><i>{cn + 1}</i></td> <td><i>{sn + 1}</i></td> <td><i>{dr}</i></td> <td>{ptRep(le)}</td> <td>{ptRep(to)}</td> <td>{ptRep(ri)}</td> <td>{ptRep(bo)}</td> <td>{self.showString(letters, asString=True)}</td> <td>{self.showString(punc, asString=True)}</td> </tr> """ ) html.append("</table>") display(HTML("".join(html))) def trimLine(self, pageNum, ln, chars)-
Map character sequences to other sequences.
Two tasks:
- Map private use characters to well-known unicode characters
- Insert space characters where the next character is separated from the previous one.
Complications:
Diacritical characters are mostly contained in a very wide box that overlaps with the boxes of the other characters. So the diacritical boxes must not be taken into account.
Private use characters often come in sequences, so a sequence of characters must be transformed to another sequence.
We do the tramsformation before the space insertion, because otherwise we might insert the space at the wrong point.
When we transform characters we need to retain the box information, because we still have to insert the space.
That's why we have as input a list of character records, where each record is itself a list with box information, orginal character, modified characters and space information.
When we transform characters, we modify character records in place. We do not add or remove character records.
The last member of a character record is the modified sequence. This can be zero, one, or multiple characters. The second last member is the original character. Initially, the the last and second last member of each record are equal. We call these members the original character and the result string.
Space will be appended at the last member of the appropriate character records.
The transformations are given as a set of rules.
See
REPLACE_DEFS.A rule consists of a sequence of characters to match and a sequence of characters to replace the match with. We call them the match sequence and the replacement sequence of the rule.
For each character in the input list we check which rules have a match sequence that start with this character. Of these rules, we start with the one with the longest match sequence. We then check, by looking ahead, whether the whole match sequence matches the input. For the purposes of matching, we look into the result strings of the character, not to the original characters. This will prevent some rules to be applied after an earlier rule has been applied. This is intentional, and results in a more simple rule set.
If there is a match, we walk through all the characters in the input for the length of the match sequence of the rule. For each input character record, we set its replacement string to the corresponding member of the replacement sequence of the rule. If the replacement sequence has run out, we replace with the empty string. If after this process the replacement sequence has not been exhausted, we join the remaining characters in the replacement string and append it after the replacement string of the last input character that we have visited.
After succesful application of a rule, we do not apply other rules that would have been applicable at this point. Instead, we move our starting point to the next character record in the sequence and repeat the matching process.
It might be that a character is replaced multiple times, for example when it is reached by a rule while looking ahead 3 places, and then later by a different rule looking ahead two places.
However, once a character matches the first member of the match sequence of a rule, and the rule matches and is applied, that character will not be changed anymore by any other rule.
place holders for diacritics
The following functionality exists in the code, but is not needed anymore to process the Lakhnawi PDF.
The match sequence may contain the character
d, which is a placeholder for a diacritic sign. It will match any diacritic. The replacement sequence of such a rule may or may not contain ad. It is an error if the replacement seqience of a rule contains adwhile its match sequence does not. It is also an error of there are multipleds in a match sequence of a replacement sequence. If so, the working of this rule is effectively two rules:Suppose the rule is
x d y => r d s
where x, y, r, s are sequences of arbitrary length. If the rule matches the input, then first the rule
x => r
will be applied at the current position.
Then we shift temporarily to the position right after where the d has matched, and apply the rule
y => s
Then we shift back to the orginal position plus one, and continue applying rules.
Expand source code Browse git
def trimLine(self, pageNum, ln, chars): """Map character sequences to other sequences. Two tasks: 1. Map private use characters to well-known unicode characters 2. Insert space characters where the next character is separated from the previous one. Complications: Diacritical characters are mostly contained in a very wide box that overlaps with the boxes of the other characters. So the diacritical boxes must not be taken into account. Private use characters often come in sequences, so a sequence of characters must be transformed to another sequence. We do the tramsformation before the space insertion, because otherwise we might insert the space at the wrong point. When we transform characters we need to retain the box information, because we still have to insert the space. That's why we have as input a list of character records, where each record is itself a list with box information, orginal character, modified characters and space information. When we transform characters, we modify character records in place. We do not add or remove character records. The last member of a character record is the modified sequence. This can be zero, one, or multiple characters. The second last member is the original character. Initially, the the last and second last member of each record are equal. We call these members the original character and the result string. Space will be appended at the last member of the appropriate character records. The transformations are given as a set of rules. See `REPLACE_DEFS`. A rule consists of a sequence of characters to match and a sequence of characters to replace the match with. We call them the match sequence and the replacement sequence of the rule. For each character in the input list we check which rules have a match sequence that start with this character. Of these rules, we start with the one with the longest match sequence. We then check, by looking ahead, whether the whole match sequence matches the input. For the purposes of matching, we look into the result strings of the character, not to the original characters. This will prevent some rules to be applied after an earlier rule has been applied. This is intentional, and results in a more simple rule set. If there is a match, we walk through all the characters in the input for the length of the match sequence of the rule. For each input character record, we set its replacement string to the corresponding member of the replacement sequence of the rule. If the replacement sequence has run out, we replace with the empty string. If after this process the replacement sequence has not been exhausted, we join the remaining characters in the replacement string and append it after the replacement string of the last input character that we have visited. After succesful application of a rule, we do not apply other rules that would have been applicable at this point. Instead, we move our starting point to the next character record in the sequence and repeat the matching process. It might be that a character is replaced multiple times, for example when it is reached by a rule while looking ahead 3 places, and then later by a different rule looking ahead two places. However, once a character matches the first member of the match sequence of a rule, and the rule matches and is applied, that character will not be changed anymore by any other rule. !!! caution "place holders for diacritics" The following functionality exists in the code, but is not needed anymore to process the Lakhnawi PDF. The match sequence may contain the character `d`, which is a placeholder for a diacritic sign. It will match any diacritic. The replacement sequence of such a rule may or may not contain a `d`. It is an error if the replacement seqience of a rule contains a `d` while its match sequence does not. It is also an error of there are multiple `d`s in a match sequence of a replacement sequence. If so, the working of this rule is effectively two rules: Suppose the rule is x d y => r d s where x, y, r, s are sequences of arbitrary length. If the rule matches the input, then first the rule x => r will be applied at the current position. Then we shift temporarily to the position right after where the d has matched, and apply the rule y => s Then we shift back to the orginal position plus one, and continue applying rules. """ replace = self.replace puas = self.puas neutrals = self.neutrals rls = self.rls rulesApplied = self.rulesApplied spaces = self.spaces columns = self.columns diacritics = self.diacritics punct = self.punct diacriticLike = self.diacriticLike arabicLetters = self.arabicLetters presentationalC = self.presentationalC presentationalD = self.presentationalD finalSpace = self.finalSpace finalsApplied = self.finalsApplied nonLetter = self.nonLetter doRules = self.doRules doFilter = self.doFilter nChars = len(chars) # rule application stage if doRules: for (i, char) in enumerate(chars): c = char[-1] if c in replace: rules = replace[c] for (rn, vals, d, repls, e) in rules: nVals = len(vals) if i + nVals > nChars: # not enough characters left to match this rule continue if not all( ( d is not None and j == d and chars[i + j][-1] in (diacritics if vals[d] == 1 else arabicLetters) ) or chars[i + j][-1] == vals[j] for j in range(nVals) ): # the rule does not match after all continue # the rule matches: we are going to fill in the replacements # if there is a diacritic in the match sequence or the # replacement sequence, we restrict ourselves to the parts # before the diacritics. rulesApplied[rn][pageNum] += 1 nRepls = len(repls) dEnd = nVals if d is None else d eEnd = nRepls if e is None else e # so, we are going to replace from here to dEnd (not including) for j in range(dEnd): # put the appropriate replacement character in the # replacement part of the character record # After running out of replacement characters, put in "" chars[i + j][-1] = repls[j] if j < eEnd else "" if eEnd > dEnd: # if there are replacement characters left, put them # in after the last character that we have visited. if dEnd == 0: # In case we have not visited any yet, # we put them in before the current character cd = chars[i + dEnd][-1] r = "".join(repls[dEnd + 1 :]) chars[i + dEnd][-1] = f"{r}{cd}" else: # this is the normal case chars[i + dEnd - 1][-1] += "".join(repls[dEnd:eEnd]) # if there is a diacritic in the match sequence # we are going to perform the rule for the part # after the diacritic # Note that the case where d is None and e is not None # does not occur if d is not None: # we set the starting points: just after the diacritics dStart = d + 1 # if the replacement part does not have a diacritic, # we have already consumed it, and we start right after it eStart = nRepls if e is None else e + 1 # we compute the number of characters that still need to be # matched and to be replaced dn = nVals - dStart en = nRepls - eStart # we perform the replacement analogously to what we did # for the first part for j in range(dn): # put the appropriate replacement character in the # replacement part of the character record # After running out of replacement characters, put in "" chars[i + dStart + j][-1] = ( repls[eStart + j] if eStart + j < nRepls else "" ) if en > dn: # if there are replacement characters left, put them # in after the last character that we have visited. chars[i + nVals - 1][-1] += "".join( repls[eStart + dn :] ) break # sift out all presentational characters if doFilter: trailSpace = False for (i, char) in enumerate(chars): c = char[-1] string = "" for x in c: if trailSpace: if x not in diacriticLike: if x not in nonLetter: if string == "" and i > 0: chars[i - 1][-1] += " " else: string += " " trailSpace = False hasFinalSpace = x in finalSpace y = ( normalizeC(x) if x in presentationalC else normalizeD(x) if x in presentationalD else x ).strip() space = " " if hasFinalSpace or x in punct else "" if hasFinalSpace: finalsApplied[x][pageNum] += 1 string += y if space: trailSpace = True char[-1] = string if trailSpace: if chars: chars[-1][-1] += " " # add horizontal spacing theseSpaces = [] spaces[pageNum][ln] = theseSpaces threshold = None theseColumns = [threshold, []] columns[pageNum][ln] = theseColumns prevLeft = None prevLeftI = None for (i, char) in enumerate(chars): spacing = char[-3] if spacing: left = char[0] right = char[2] if prevLeft is not None: prevChar = chars[prevLeftI] after = prevLeft - right theAfter = ptRepD(after) isSpace = theAfter >= SPACE_THRESHOLD if isSpace: lastChar = chars[i - 1] if not lastChar[-1].endswith(" "): lastChar[-1] += " " prevChar[-3] = f"⌊{theAfter}⌋" if isSpace else f"«{theAfter}»" theseSpaces.append((i - 1, theAfter, isSpace)) prevLeft = left prevLeftI = i if chars: chars[-1][-3] = "end" # change big spaces to emspaces nSpaces = sum(1 for x in theseSpaces if x[2]) if nSpaces == 1: threshold = 90 elif nSpaces > 1: spacesGrowing = sorted(x[1] for x in theseSpaces if x[2]) maxSpace = spacesGrowing[-1] medialSpace = spacesGrowing[nSpaces // 2] if maxSpace > 4 * medialSpace: threshold = maxSpace - medialSpace if threshold is not None: theseColumns[0] = threshold for (i, after, isSpace) in theseSpaces: if isSpace and after > threshold: theseColumns[1].append((i, after)) char = chars[i] char[-1] = char[-1].rstrip(" ") + EMSPACE # remove space between alef and initial follower, # provided the alef is the single letter in its word. # also for the words yeh+alef(final) and mem+alef(final) do: # insert a space behind the alef(final) curLen = 0 prevCons = None pprevCons = None for (i, char) in enumerate(chars): c = char[-1] co = char[-2] r = "" isAFinal = isAlefFinal(co) for x in c: skip = False if x == " ": if curLen == 1: # and prevC in PROCLITICS: skip = True curLen = 0 prevCons = None pprevCons = None elif x in arabicLetters: curLen += 1 if 2 <= curLen <= 3 and isAFinal: if isMeemOrYeh(prevCons) and (curLen == 2 or isWaw(pprevCons)): x += " " curLen = 0 prevCons = None pprevCons = None pprevCons = prevCons prevCons = x if not skip: r += x char[-1] = r # divide lines into columns emspaces = theseColumns[1] emspacePositions = {t[0] for t in emspaces} columnedChars = [[]] dest = columnedChars[-1] for (i, char) in enumerate(chars): if i in emspacePositions: if char[-1]: dest.append(char) columnedChars.append([]) dest = columnedChars[-1] else: dest.append(char) # divide columns into ranges # and chunk the ranges into words # and save the word boundary boxes text = self.text # text is a dict keyed by pageNum and the values are tuples of line data # a line datum is a list of columns # a column is a list of spans # a span is a pair of a direction char ("l" or "r") plus a list of word data # a word datum is a string plus a word box # a word box is a (left, top, right, bottom) tuple result = [] text.setdefault(pageNum, []).append(result) prevDir = "r" # we transform letters into chunks, where each chunk is a pair of # word material # punctuation material outChars = [[], []] inWord = True box = [None, None, None, None] def addWord(): if outChars[0] or outChars[1]: wordCharsRep = "".join( outChars[0] if prevDir == "r" else reversed(outChars[0]) ) puncCharsRep = "".join( outChars[1] if prevDir == "r" else reversed(outChars[1]) ) lastSpan = None if len(result[-1]) == 0 else result[-1][-1] element = (wordCharsRep, puncCharsRep, tuple(box)) if lastSpan is None or lastSpan[0] != prevDir: result[-1].append((prevDir, [element])) else: result[-1][-1][-1].append(element) def setBox(char): for (i, coor) in enumerate(char[0:4]): if ( (b := box[i]) is None or (i < 2 and coor < b) or (i >= 2 and coor > b) ): box[i] = coor for chars in columnedChars: result.append([]) outChars = [[], []] box = [None, None, None, None] for char in chars: c = char[-1] if c == "": continue for d in c: spaceSeen = d in {" ", EMSPACE} changeWord = not inWord and d not in nonLetter if spaceSeen: outChars[1].append(d) if spaceSeen or changeWord: addWord() box = [None, None, None, None] outChars = [[d] if changeWord else [], []] inWord = True continue thisDir = prevDir if d in neutrals else "r" if d in rls else "l" if prevDir != thisDir: addWord() box = [None, None, None, None] outChars = [[], []] inWord = True prevDir = thisDir if inWord: if d in nonLetter: inWord = False dest = 0 if inWord else 1 rep = d if d in puas: rep = f"⌊{ord(d):>04x}⌋" outChars[dest].append(rep) setBox(char) addWord() def tsvHeadLine(self)-
Outputs the field names of a word in TSV data.
See
Lakhnawi.tsvPages()for the structure of TSV data as output format for the extracted text of the Lakhnawi PDF.Returns
string- A tab-separated line of field names.
Expand source code Browse git
def tsvHeadLine(self): """Outputs the field names of a word in TSV data. See `Lakhnawi.tsvPages()` for the structure of TSV data as output format for the extracted text of the Lakhnawi PDF. Returns ------- string A tab-separated line of field names. """ return "page\tline\tcolumn\tspan\tdirection\tleft\ttop\tright\tbottom\tletters\tpunc\n" def tsvLine(self, columns, pageNum, ln)-
Outputs a processed line as lines of tab-separated fields for each word.
Used by
Lakhnawi.tsvPages().Parameters
columns:iterable- An iterable of columns that make up a line. Each column is an iterable of spans. Spans contain words plus an indication of the writing direction for that span.
pageNum:int- The page number of the page where this line occurs.
Returns
string- The concatenation of the TSV lines for all words in all spans in all columns.
Expand source code Browse git
def tsvLine(self, columns, pageNum, ln): """Outputs a processed line as lines of tab-separated fields for each word. Used by `Lakhnawi.tsvPages()`. Parameters ---------- columns: iterable An iterable of columns that make up a line. Each column is an iterable of spans. Spans contain words plus an indication of the writing direction for that span. pageNum: int The page number of the page where this line occurs. Returns ------- string The concatenation of the TSV lines for all words in all spans in all columns. """ material = [] for (cn, spans) in enumerate(columns): for (sn, (dr, words)) in enumerate(spans): for (letters, punc, (le, to, ri, bo)) in words: material.append( ( "\t".join( str(x) for x in ( pageNum, ln, cn + 1, sn + 1, dr, ptRep(le), ptRep(to), ptRep(ri), ptRep(bo), letters, punc, ) ) ) + "\n" ) return "".join(material) def tsvPages(self, pageNumSpec)-
Outputs processed pages as tab-separated data.
See
fusus.convertfor the details of the output format.Uses
Lakhnawi.tsvLine(). andLakhnawi.tsvHeadLine().Parameters
pageNumSpec:None | int | string | iterable- As in
Lakhnawi.parsePageNums().
Returns
Expand source code Browse git
def tsvPages(self, pageNumSpec): """Outputs processed pages as tab-separated data. See `fusus.convert` for the details of the output format. Uses `Lakhnawi.tsvLine()`. and `Lakhnawi.tsvHeadLine()`. Parameters ---------- pageNumSpec: None | int | string | iterable As in `Lakhnawi.parsePageNums()`. Returns ------- None The tab-separated data is written to a single tsv file. There is a heading row. The file is in `fusus.parameters.UR_DIR`, under `Lakhnawi`. The name of the file includes a page specification. """ text = self.text destDir = f"{UR_DIR}/{NAME}" pageNums = self.parsePageNums(pageNumSpec) if not os.path.exists(destDir): os.makedirs(destDir, exist_ok=True) pageNumRep = ALL_PAGES if pageNumSpec is None else str(pageNumSpec) filePath = f"{destDir}/{pageNumRep}.tsv" fh = open(filePath, "w") fh.write(self.tsvHeadLine()) for pageNum in pageNums: lines = text.get(pageNum, []) for (ln, line) in enumerate(lines): fh.write(self.tsvLine(line, pageNum, ln + 1)) fh.close() print(f"TSV data written to {unexpanduser(filePath)}")
Inherited members